bones n joints Flashcards
(176 cards)
altered bone consistency
2 dz
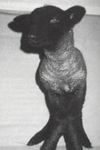
rickets
osteomylasia
thyroidectomy result in
hypothyroidism causing
- dry skin
- alopecia
- cataracts
- tetany
what causes primary hyperpyrathoidism
mostly adenomas→ increased pth→ osteoclastic bone resoption
• 1° hyperparathyroidism lesions
hypercalcemia
» renal stones
» renal destruction and hypertension
» fibrous osteodystrophy
2° hyperparathyroidism
- how is the level of ca
- what causes those levels of ca
- low
- chronic renal dz, nutritional imbalances eg. rickets, inadecuate vit d3, all bran diets, poor quality rouphages
lesions of 2° hyperparathyroidism
hypocalcemia –> increased mobilization
from bone –> fibrous osteodystrophy
fxns of calcitonin
think about ca abandance
decrease plasma calcium and phosphate levels
decrease the permeability of osteoblasts
decrease the activity of osteoclasts (think about ca abandanc
increases water and electrolyte secretion in the urine
in state of high ca,which hormones helps secrete Ca
gastrin
» glucagon
» dopamine
» ß adrenergic agonists
_absence of calcitonin, or chronic excess produced
by tumours, do not disturb calcium levels_
– Growth hormone effect on ca
increases urinary calcium excretion and intestinal
absorption, with a net gain
• increased rate of turnover assists in bone growth
Glucocorticoids effect on ca
• ecreases plasma calcium and phosphate levels by
reducing absorption by an anti-vitamin D action
and increasing urinary excretion
• long term effect ⇒osteoporosis
hyperthyroidism effect on ca
– hypercalcemia,
hypercalciuria (excess Ca excretion) and
osteoporosis
estrogen effect on ca
• inhibit the action of PTH on bone
decreased estrogen levels –> senile osteoporosis
osteopenia
loss of skeletal mass (too “little bone”)
Intramembranous (appositional) ossification
flat bones
periosteal surfaces of long bone
Endochondral ossification
bones with growth plates (long bones, etc.)
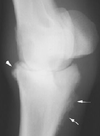
what kind of lesion do u find in hypertrophic osteodystrophy
metaphyseal lesion

Thickened and irregular epiphyseal cartilage is found in
rickets

, hyperparathyroidism lesion on bones
• fibrous osteodystrophy
chronic renal disease result in which endocrine abnormality
2° hyperparathyroidism and osseous lesions
displacement of bone marrow tissue can be due to
- fibrous tissue
- malignant neoplasm
- myelophthisic anemia
Disorders of bone resorption
ostreopetrosis
Disorders of bone formation
• Osteogenesis imperfecta
Disorders of bone modeling
Congenital cortical hyperostosis
• Craniomandibular osteopathy
Disorders of endochondral ossification
Chondrodystrophies
- Osteochondrosis
- Osteochondrosis dissecans (OCD)
- Epiphysiolysis
Cervical vertebral myelopathies