eyes and ears Flashcards
absence of the eye
Anophthalmos
incomplete separation, or early fusion, of paired globes
Synopthalmia

– abnormally small eye
micropthalmia
– inherited defect in Collie dogs
inversion of the eyelids → trichiasis
Entropion

– eversion of the eyelids
ectropion
– rubbing of the eyelashes against the eye surface
Trichiasis

failure of complete fusion of the lips of the embryonic
choroid fissure
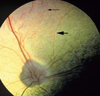
Coloboma
which part of the eye is most affected in coloboma
- the posterior portions of the eye (optic disc, iris, ciliary body) most often affected
- – inherited in Charolais cattle
what are the lesions of coloboma
- cavitation of the choroid and sclera
– cavity lined by a thinned retinal layer
- visual defects
– only in very severe cases

– etiopathogenesis Collie eye anomaly
- improper development of the optic cup
- abnormal formation of choroid and retina
- chorioretinal dysplasia or choroidal hypoplasia
Collie eye anomaly lesions/defects:
- abnormal retinal vessels
- areas of chorioretinal dysplasia or hypoplasia
- ectasia
– optic disc – sclera - posterior staphyloma
- ± severe visual impairment
sequela of collie eye anomali
- retinal degeneration and detachment
- intraocular hemorrhage
delayed or incomplete atrophy of the anterior
perilenticular vascular network results in
Persistent pupillary membrane
atrophy is frequently incomplete at birth
Persistent pupillary membrane lesions
- bloodless strands
– short, threadlike protrusions from the area of
the minor arterial circle (iris collarette)

Persistent pupillary membrane clinical significance
- obstructed vision
- corneal or lens opacity
– due to dysplasia of corneal endothelium or lens
because of contact with the strands

Partial or complete absence of an eyelid
Eyelid agenesis and coloboma
partial defect (coloboma) involving the upper
eyelid is the most common
» localized corneal dessication followed by
cutaneous metaplasia
abnormal or prolonged fusion or adhesion of
the eyelids
Ankyloblepharon
what is the function of physiological Ankyloblepharon
essential to protect the immature cornea from
infectious keratitis, dessication, and corneal
rupture
Congenital ankyloblepharon in dogs and cats persists into the 2nd week of life
inward rolling of the eyelid margin (inversion or
infolding) because of inadequate overall length
Entropion
what is the sequela of entropion
irritation of the cornea by the eyelid skin,
cilia, and/or hair
very common anomaly in purebred dogs
undue laxity of an excessively long
eyelid resulting in an outward gaping of the
eyelid margin
ectropion
what is the sequela of ectropion
chronic conjunctivitis and keratitis from
exposure to debris
presence of an ectopic row of cilia originating
from the ducts of the Meibomian glands
Distichiasis
what is sequela of Distichiasis
corneal ulceration