Brain Anatomy and Vasculature Flashcards
(39 cards)
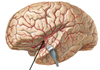
label this brain


how many arteries supply the cortex? cerebellum? brainstem?
- cortex - 3
- cerebellum - 3
- brainstem - many
which 3 arteries supply the brain/cortex?
- anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries
- the bulk of the supply is coming from the middle cerebral artery
which 3 arteries supply the cerebellum?
- superior cerebellar artery
- anterior and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries
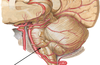
which branches of the internal carotid a. supply the brainstem?
- opthalmic a.
- anterior cerebral a.
- posterior cerebral a.
which branches of the vertebral a. supply the brainstem?
- posterior inferior cerebellar a. (PICA)
- basilar a.: anterior inferior cerebellar a. (AICA), superior cerebellar a. (SCA), and posterior cerebral artery
the cerebral arterial circle of willis (COW) supplies the brainstem. which branches make up the COW?
- anterior communicating a.
- anterior cerebral a.
- internal carotid a.
- posterior communicating a.
- posterior cerebral a.
what are the brainstem locations for all of the cranial nerves?

there are 3 tests to localize lesions (or lack of) in unconscious patients. what are they?
- midbrain - pupillary light reflex (input CN II, output CN III)
- pons - corneal reflex (input CN V, output CN VII)
- medulla - gag reflex (input CN IX, output CN X)
which 2 arteries supply the midbrain/mesencephalon?
- basilar a.
- posterior cerebral a. (choroidal branches)
which 3 arteries supply the pons/metencephalon?
- basilar a. almost entirely
- anterior inferior cerebellar a.
- some superior cerebellar a. in rostral dorsal pons
which 3 arteries supply the medulla oblongata?
- anterior spinal a. (in between vertebral aa.)
- vertebral a.
- posterior inferior cerebellar a.
what functions will be compromised if the middle cerebral a. is blocked?
- Sensory and Motor on the contralateral side (head, neck, upper limbs)
- speech, but ONLY if blockage is on dominant side
what functions will be compromised if the anterior cerebral a. is blocked?
Sensory and Motor on the contralateral side (lower limbs)
what functions will be compromised if the posterior cerebral a. is blocked?
vision
what are the 2 watershed areas of the cerebrum?
- anterior cerebral a. and middle cerebral a. watershed
- middle cerebral a. and posterior cerebral a. watershed
name the 2 dura mater cranial meninges. what do they separate?
- falx cerebri separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres
- tentorium cerebelli separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum
name the 6 dural venous sinuses in the order of drainage
- superior sagittal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- transverse sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- down to internal jugular vein
- cavernous sinus is anterior and a little superior to the sigmoid sinus - sits in sella turcica
- cavernous sinus and sigmoid sinus are connected via superior and inferior petrosal sinuses
which 5 structures run through the cavernous sinus?
- internal carotid a.
- CN III
- CN IV
- CN V
- CN VI
what are 2 alternate drainage routes of the brain and face?
- cavernous sinus
- pterygoid plexus
- blood can pool in these areas
what is the route of infection for the cavernous sinus? what will infection in this area combined with slow blood flow cause?
- face to brain via angular a. and v. (nasal area)
- clot = cavernous sinus thrombosis
- CN II, III, IV, V, VI, and pituitary will show signs
what is the confluent of sinuses?
it connects the superior sagittal sinus, the inferior sagittal sinus, and transfer sinuses
what is an epidural hematoma?
- potential space between dura mater and inner table of the skull fills with blood
- usually torn middle meningeal a.
- usually skull fracture
- lenticular (biconvex) shape
what is a subdural hematoma?
- potential space between dura mater and arachnoid mater (subdural)
- usually injury to bridging veins
- crescent shape, does not enter sulci