Carbohydrates, Lipids, Membranes Flashcards
(87 cards)
individual sugar unit with formula (CH2O)n.
Monosaccharide
2-10 sugar units
Disaccharide, tri-, tetra-, etc
greater than 10 sugar units
Oligosaccharide
larger polymer 10’s to 1000’s, may be linear or branched
Polysaccharide
What is the term for a sugar with a carbonyl group on the endmost carbon atom?
Aldose
What is the term for a sugar with a ketone group on one carbon atom?
Ketose
What makes a molecule alpha or beta?
Alpha- OH is up on the next carbon from the attached oxygen when moving clockwise
Beta - that same OH is down
How do you name sugars by carbon atoms?
triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose, etc.
Rich in hydroxyl (OH- ) groups
Carbohydrates
Tend to have the general formula of (CH2O)n where n ≥ 3
Carbohydrates
Single most abundant form of biomolecule found in nature
Carbohydrates
What are the cellular functions of carbohydrates?
energy storage and metabolism
cellular structure
linkers with other biomolecules (glycolipids, RNA/DNA, glycoproteins)
recognition molecules between cell types and cell structures
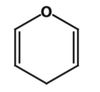
What is this?

Ketose
What is this?

Aldose
What is this?

Aldohexose
What is this?
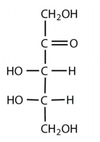
Ketopentose
What is this?
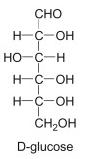
D-Glucose
What is this?

L-glucose
What is this?
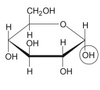
alpha D-glucose
What is this?

Beta D-glucose
What is this?

Beta L-glucose
What is this?

D-Fructose
What is this?

L-fructose
What is this?

alpha D-fructose