Cardiac Pathophysiology Flashcards
Dr. Mike Wacker (UMKC) (43 cards)
What are causes of valvular abnormalites?


What is mitral stenosis, and what would happen to the pressures in the LA and LV?


What is mitral regurgitation? What would happen to the LA and LV pressures compared to normal?

Blood flows back into the LA during systole, causing the LA to expand

What is aortic stenosis? What happens to LA and LV pressure, and pressure in the aorta compared to normal?

- Narrowing of the aortic valve, slow to open
- Increased afterload
- Cardiac hypertropy
- SV decreased
- LV pressure increases due to increased afterload

What are the three ways to do a transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)?

What does aortic regurgitation (insufficiency) do to LA, aortic, and LV pressure compared to normal?

- Blood flows back into LV from the aorta
- Increasing preload and stroke volume
- Chamber dilation

What are symptoms that a patient could have indicating valvular abnormalities?

When would you hear heart murmors for the different vavular abnormalites?

What are some causes of dialated cardiomyopathy and problems that it can lead to?

What are some causes of pathological hypertrophy and problems that it can lead to?

How is physiological hypertrophy different than pathological?


Possible causes of an MI? What problems does it lead to?
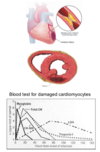

What are cardiomyocyte marker for an acute MI? At what levels is it indicitave of one?

What happens immediately after someone experiences an MI, and the following weeks after?

How does aspirin work and what does it do?

What do fibrate (Gemfibrozil) medications do and how do they work?

What do Statins (atorvastatin - Lipitor) do and how do they work?

What do PCSK9 inhibitors do and how do they work?

What is the difference between diastolic HF and systolic HF?

HFrEF is also called ______________
Systolic heart failure or volume overload
HFpEF is also called __________________
Diastolic HF or pressure overload
What changes happen in cardiomyocytes after heart failure?
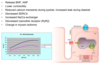
What causes arrythmias during heart failure?


How is there compensation during mild HF?



















