Cardiac Review Flashcards
(30 cards)
Diagnosis?

Cor triatriuatum
Sign and indication?

Double density sign - superimposed countor on the right heart from enlargement of the right side of left atrium
- Can also see splaing of the carina (angle of 90 degrees suggests enlargement)
- Can also see walking man sign

Sign and cause?

Walking man sign - posterior displacement of the left main stem brhoncus on the lateral radiograph creating and upside down “V” shape with the intersection of the right bronchus

Finding and association?

Echogenic focus in left ventricle
- calcified papillary muscle that usually goes away, can be normal
- associated with increased incidence of Downs (13%)
RCA perfuses SA node what % of the time?
What about the AV node?
RCA perfused SA node 60% of the time and AV node 90%
Diagnosis?

ALCAPA Anaomalous Left Coronary fromt he Pulmonary Artery
- aka Bland-White-Gardland Syndrome
- Infantile type where patients die early and adult type who are at risk of sudden cardiac death
- Steal syndrome is where there is reversal of flow in the LCA

Diagnosis?

Coronary Fistula
- abnormal connection between CA and cardiac chamber or great vessels - usually RCA to right cardiac chamber
- Think of this if you seen crazy big dilation of the coronaries
I say supra-valvular aortic stenosis
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS) is characterized by some or all or the following features:
- craniofacial dysmorphism (e.g. elfin facies)
- oral abnormalities
- short stature (50% of cases)
- mild to moderate mental retardation
- supravalvular aortic stenosis
- pulmonary artery stenosis
- renal insufficiency
- hypercalcemia
I say Biscupid Aortic Valve and Coarctation
Turners Syndrome
Pulmonary Stenosis levels and associations
- Supra-valvular - Williams Syndrome (same as AS)
- Valvular - Noonan’s Syndrome (Male version of Turner’s)
- TOF
Trivia - peripheral pulmonary stenosis is seen with Alagille’s Syndrome
Diagnosis?

Ebstein anomaly
- Massive “box-shaped” heart on CXR
- Seen in kids whose moms used Lithium
- Enlarged RA, decreased (atrialized) RV
Associated with tricuspid atresia
Findings
- Normal heart size with hypoplasia of RV (normal heart size differentiates from Ebsteins), almost always with ASD or PFO
- Associated with asplenia
Which is right arch configuration is associated with more congential heart disease?
Right arch with mirror image branching (more than aberrant left subclavian)
- Most commonly associated with TOF (90% will have TOF only 6% will have Truncus)
- Most clostely associated with Truncus (If a person has truncus then 33% will have right arch, if person has TOF then 25% will have right arch)
Congential Heart Anomalies
- Egg on String
- Snow man
- Boot shaped
- 3
- Box shaped
- Scimitar Sword
- Egg on String - Transposition
- Snow man - TAPVR (Supracardiac)
- Boot shaped - TOF
- 3 - Coarctation
- Box shaped - Ebstein
- non-cardiac causes of highoutput failure (Infantile hemangioendothelioma and vein of Galen malformation)
- Scimitar Sword - PAPVR with hypoplasia

Congenital Heart Flow Chart
If Cyanotic
- Side of Arch
- If Right then TOF or Truncus
- Truncus pulmonary vasculature is increased
- Heart size (massive Ebstein, pulmonary atresia w/o VSD or non-cardiac causes)
- Pulmonary blood flow
- Increased then TAPVR, D-transposition, Truncus, Tingle Ventricle
- Decreased or normal then TOF, Ebsteins, Tricuspid atresia

Cyanotic and Non Cyanotic Heart disorders
Cyanotic
- TOF
- TAPVR
- Transposition
- Truncus
- Tricuspid atresia
Non Cyanotic
- ASD, VSD, PDA, PAPVR, Coarctation
I say PDA you say these 3 things
- Prematurity
- Maternal Rubella
- Cyanotic Heart Disease
ASD subtypes, associations and factoids
- Secundum is most common and may spontaneously close
- Primum is larger and more likely to be symptomatic, located next to AV valve tissue
- Hand/thumb defects + ASD = Holt Oram
- Ostium primum (endocardial cushion defect) - think Downs Syndrome
- Sinus venosus ASD - PAPVR (usually Suprior Right PV)

Name 4 findings in TOF
- RVOT obstruction (often valvular)
- VSD
- Over-riding aorta
- RVH
Severity relates to how bad the RVOT obstruction
Famous shunt is Blalock-Taussig procedure
Truncus arteriosus associations
- VSD
- Right arch
- CATCH-22 DiGeorge Syndrome
Name Valves
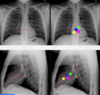
Green - pulmonary (highest)
Blue - aortic
Pink - mitral (most posterior)
Yellow - tricuspid (most apical)
Biventricular thombus
Eosinophilic Cardiomyopathy (Loeffler)
Diagnosis?

Myocarditis
- LGE non-vascular distribution, typically lateral free wall, pattern will be epicardial or mid wall (not endocardial)
- Often viral - coxackie virus
Diagnosis?

Cardiac Sarcoid
- High T2 as well as early and late GE
- Pattern of enchancement - focal wll thickening from edema which can mimic HCOM, often involves the septum






