Causal loops Chapter 1 Flashcards
(8 cards)
An arrow in a causal diagram represents a __________ physiological mechanism.
single, unique
The variable at the arrowhead is the _______________ .
effect
The variable at the tail of the arrow is the ______________.
cause
A blue arrow (or – sign at the arrowhead) shows that the mechanism is ________________.

inhibitory to the effect
A red arrow (or + at the arrowhead) shows that the mechanism is _________________.

excitatory to the effect
The number of arrows connecting a given cause to one other effect will equal ______________.
the number of separate physiological mechanisms that apply
If a continous, one way path exists from a variable back to itself, this path is called a____________.
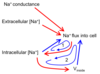
feedback loop
Consider that two blue arrows in series indicates inhibition of inhibition and this implies excitation.
Then a “blue loop” is a loop with an odd number of blue arrows in series and this sort of loop signifies ___________________.
Negative feedback (compensation for disturbances)


