Cavity Flashcards
(14 cards)
What is a cavity?
Cavity is described as a hole in the lung. It is an air containing space surrounded by a wall.
What are criteria for analysis when looking at cavities?
- Number
- Location
- Wall thickness
- Lining of wall
- Contents
- Other associated findings
When are multiple cavities seen?
Multiple cavities are seen in hematogenous etiology (metastatic, septic emboli, vasculitis) or bronchogenous etiology (aspiration abscess, tuberculosis, coccidiomycosis), bronchiectasis.
When are single cavities seen?
Single cavities: Primary lung cancer, post traumatic lung cyst and a large number of diseases also can present as a single cavity.
Where are aspiration abscesses primarily seen?
85% of aspiration lung abscess are located in superior segment of lower lobes, axillary sub segment of anterior and posterior segments of RUL You can rule out aspiration lung abscess when the cavity is located in the apical segment of upper lobes.
Where is TB usually seen in the lung?
TB classically occurs in apical segments of lower and upper lobes. TB is uncommon in anterior segments of lungs. Diabetics can develop basal segment TB, but otherwise it is rare.
What are some diseases that will present with thinning of the lung wall?
Thin walled cavities (less than 1 mm) can be seen in M. Kansasii, coccidiomycosis, open negative TB, blebs, congenital cysts and metastatic Cavitating squamous cell carcinoma from larynx or cervix.
What are some diseases that will present with thickening of the lung wall?
Thick walled cavities (greater than 5 mm) are due to aspiration lung abscess, necrotizing pneumonia, squamous cell cancer, Blastomycosis and Wegener’s granulomatosis.
What is shown in the image?

Aspiration Lung Abscess
Why does aspiration lung abscess occur in the superior segment of lower lobes?
These areas are gravity dependent when lying down
What is shown in the image?

Cavitating Squamous Cell Cancer
What is shown in the image?

Multiple Cavities
What is shown in the image?
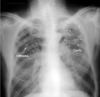
Tuberculosis
What is shown in the image?

Bullae - presents with multiple thin walled cavities


