Cell adhesion Meolcuels and Junctional Complexes Flashcards
(46 cards)
Simple non ciliated columnar epithelium is most likely to be found associated with which of hte following?
- urniary tract
- respiratory tract
- integument
- digestive tract
digetive tract
Junctional complexes are associated with which cellular domains
- Apical
- Basolateral
- Basal only
- Lateral only
Basolateral
Transtional epithelium is associated with which of the following system?
- Respiratory
- Lymphatic
- Cardiovascular
- Urniary
Urniary
Although not common,stratified cuboidal epithelium may be found in which of the following areas?
- Vaginal epithelium
- Part of the male urethra
- urniary bladder
- kidney tubuels
Male urethra
Lightly keratinizied stratified squamos epithelium is chareceristic of which of the following locations?
- Vaginal Epithelium
- Part of hte male urethra
- Urniary bladder
- kidney tubuels
Vaginal epithelium
Charecteristics of the basement membrane
- Basement membrane separates an epithelial layer from its connective tissue support
- Basement membrane is approxmimately 50-80nm thick
- Basement membrne consists of two components
–basal lamin-produced by the epithelium
–Reticular lamina produced by the connective tissue
-not a cellular membrane PAS+ can really see basement mebrane
Components of Basal Lamina
- Laminin -Fibronectin-
- Type IV collagen
– type IV collaen coes not form fibirls like type I collagen
– Type IV collagen is produced by epithelial cells ,unlike type I collagen which is secreted by fibroblasts
- Entactin(nidogen)
- Proteoglycans
Laminin:charecteristics
- This is the major component of the basal lamina; it consists of three chains:a,b,y
- Laminin has binding sites for integrins, type Iv collagen, entactin and proteoglycans(IE , heptran sulfate)
Fibronectin
-a protein made up of two polypeptide chains cross-linked by disulfide bonds
Forms of fibronectin
- Cellular-produced by fibroblasts;part of extracellular matrix
- Plasma-secreted into bloodstream by hepatocytes
Fibronecting binding sites for what molecules
- heparin
- integrins
- collagen
- Fibrin

- Laminin is hte major component of hte basal lamina
- consists of three disulfide linked polypeptide chains designated a, b,y chains
- Varients for each chain give rise to several laminin isoforms with different strucutre and fuction
- Have binding sites for cell surface receptors(integrins),type IV collagen, and other adhesioin proteins(ex. nidogen aka entactin)
- Laminin monomers self-associate to form a network that is part of the basal lamina

Fibronectin
- A glycoprotein formed by two identical chains joined by disulfide linkages close to the C-terminal
- two forms
- Plasma fibronectin-produced by hepatocytes and secreted into the bloodstream
- Cellular fibronectin-produced by fibroblasts ,forms part of the extracellular matrix
- Has binding sites for integrins, collagens , heparan sulfate and fibrin
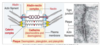
Cell Adhesion Molecules(CAMs)
- Depending on the need for calcium in their interactions with other molecules , cell adhesion molecules are divided into two groups
- Calcium dependent
- Cadherins
- Selectins
- Calcium indepndent
- Integrins
- Immunoglobulin superfamily molecules
- Calcium dependent

Classical Cadherins
- Major components in calcium mediated adherens junctions
- TYpically form cis and trans homophilic dimers
- include:
- E-cadherins:found in epithelial tissues
- N-Cadherins:found in nerve cells
- P-cadherins: found in the placenta

Nonclassical cadherins
- Include desmocollins and desmogleins
- Found in desmosomes(macula adherens)
E-Cadherins
- The most common type of cadherins
- Form dimers via a HVA binding face(Histidine-valine-alanine sequence)
- Found at tip of extracellular end of cadherin molecule
- calcium ion binds to four extracellular domains and facilitate cis-homophilic dimers
- Loss of e-cadherins is associated with invasive behaviors of tumor cells
- Cadherin molecules pass through the cell membrane and will have an intracellular and extracellular component
- Need to link cell to basement membrane and see other integrins linking together the cytoskeleton with other proteins
Catenins
- Small proteins that link the cytoplasmi end of a cadherin with cytoplasmi action
- three forms:
- B and y/plakogolobin catenins:
- Attached to cytoplasmic end of a cadherin
- Beta may also serve as a transcription cofactor
- Beta is also attached to alpha catenin
- insdie the cell
- a catenin
- Binds directly to cytoplasmic actin
- B and y/plakogolobin catenins:
- Serve as a major interface between the cadherins that hold adjacent cells together and the actin cytoskeletons of those cells
Selectins
- Selectins bind to carbohydrates;therefore , they belong to the lectin group
- The binding site for carbohydrates is located at the carbohydrate-recognition domain(CRD) at the extracellular end of the selectin
- Calcium binding sites are also found near the CRD and calcium is required for the binding activity
- Selectins are invovled in the movement of leukocytes from blood to tissues(extravasation)
- Extravasation-moving out of the blood cells
Selectins and types

- Selectins have three extracellular domains
- A carbohydrate recognition domain(CRD) specific for particular sugar(galactose, mannose,N-acetylgucosamine, and others)
- A domain homologous to a repeat found in epidermal growth factor(EGF-like)
- Many consensus repeats found in complement regulatory proteins
- 3 major types of selectins:
- L-selectin- carried by lymphocytes and with binding affinity to sulfated carbohydrates
- E-selectin-expressed by activated endothelial cells
- P-selectin-expressed by platelets and activated endothelial cells
- Selectins, together with integrins and intercellular cell adhesion molecules(ICAMs) play a siginifcant role in inflammation and in the periodic migration of lymphocytes from the circulation into lymphoid organs(homing)
Integrins
- Glycoproteins that are mainly involved in cell extracellular matrix interactions
- bind to both the extracellular matrix and to the cytoskeleton
- Consist of two subunits:
- Each integrin consists of one alpha subunit(17 kinds) and one beta subunit(8 kinds)
- Extracellular domains of integrins bind to molecules in the extracellular matrix such as fibronectin and laminin
- In hemidesmosomes , integrins link the basal domains of cells to the extracellular matrix via the intracellular tonofilaments(intermediate filaments such as keratin)
- intermediate filaments are slightly larger in diamter then actin

What sequence in fibronectin and laminin do integrins interact with?
- Interact with RGD(Arg-Gly-Asp)
Laminin and fibronectin in the basement membrane interact with what?
- collagen
- heparan sulfate proteoglycans
- entactin(nidogen)
How do integrins differ from other cell adhesion proteins

- Consist of two subunits
- Have a dual function
- Bind to the extracellular matrix
- Bind to the internal cytoskeleton
- a subunit of an integrin has two chains linked by a disulfide linkage and a globular head with binding sites for divalent cations
- B subunit has two significant charecteristics
- Extracellular chain contains repeating cysteine-rich regions
- Intracellular portion interacts with actin filaments through three connecting proteins:
- Talin
- Vinculin
- a-actinin