Cell Division Flashcards
(32 cards)
How many successive nuclear divisions?
Two

How many rounds of DNA Replication?
Only One
- A pair of chromosomes from each parent.
- Similar in length, gene position, and centromere location
Homologous Pairs

One length of DNA which contains genes.
Chromosome
A condensed chromosome joined at the centromere
Chromatid

Two identical chromatids formed by DNA replication
Joined at the Centromere
Sister Chromatids
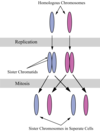
Region on chromosomes that contains kinetochores
Centromeres

Cylindrical organelles that develop the spindle fibres.
Centrioles

Contains two centrioles
Breaks down to allow centrioles to form spindle fibres
Centrosomes

Slender microtubules to which centromeres attach and are pulled apart.
Spindle Fibers
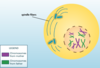
Cytoplasmic division of a cell
Cytokinesis
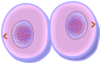
Pairing of two homologous chromosomes
Synapsis

A pair of two homologous chromosomes
Tetrad

Structure on the centromere at which sister chromatids join
Kinetochores

What happens in Interphase?

Interesting things happen!
Cell increases in mass
Genetic material doubles
Two centrosomes are produced from a single centrosome
What happens in Prophase I?

Homologous chromosomes PAIR UP
Chromosomes thicken and shorten (become visible)
Crossing over happens
Centrosomes move to the opposite sides of the cell.
Spindle Fibres form
Nuclear membrane disintegrates
Nucleolus breaks down
What happens in Metaphase I?

Chromosomes MEET IN THE MIDDLE!
Chromosomes attach to Spindle Fibres at the centromere
Spindle fibres align the chromosomes along the equatorial plate on each side.
What happens in Anaphase I?

Chromosomes get PULLED APART
Spindle fibres contract and pull choromatids to the opposite sides of the cell
Sister chromatids remain attached
What happens in Telophase I?

Now there are TWO!
Chromosomes uncoil
Spindle fibres disintegrate
Centrioles replicate
Nuclear membrane forms
Cell undergoes cytokinesis, forming two haploid cells containing duplicated chromosomes
What happens in Prophase ll?

Nuclear Membrane breaks down
Centrosomes and Centrioles move to the opposite sides of the cell.
Spindle Fibres form
Genetic material DOES NOT duplicate
What happens in Metaphase II?

Spindle fibres align the chromosomes along the cell equator
Equatorial metaphase plate is rotated by 90 degrees
What happens in Anaphase II?

Sister chromatids are pulled apart
Chromosomes move to the opposite sides of the cell
What happens in Telophase II?

Nuclear membrane forms again
Chromatids lengthen and break apart
Spindle fibres disintegrate
Cell undergoes cytokinesis, resulting in 4 haploid gametes
Period of rest that some species enter between Meiosis I and Meiosis II
Interkinesis









