DNA Replication Flashcards
(20 cards)
What happens if a mistake is made during DNA replication?
- Cell may not function
- Cell may not do its job correctly
- If it does, causes a mutation
Reason for evolution?
- An advantage to the survival rate, reproduction, sexual advantage (desirability),
How does gene splicing occur?
- Cutting DNA strands at specific spots by enzymes.
What determines variation in genes?
- Arrangements of base pairs
- Number of base pairs.
Shape of DNA?
Double Helix

“Rails” of DNA?
Sugar and Phosphate groups

“Rungs” (Footsteps) of DNA?
Bases joined with hydrogen bonds.

Nucleotide?

A base linked to a Phosphate group
The functioning unit of DNA
Purines?
One group of Bases - Adenine and Guanine
Always bonds to pyrimidines

Pyrimidines?
One group of Bases - Thymine and Cytosine
Always bonds to Purines
At The Gold Coast
Adenosine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine
Importance of hydrogen bonds?
- Simple splitting and reforming
- Specific bonding nature of A with T and G with C
- Mistakes in DNA duplication are difficult to make.
Late stages of Interphase (Mitosis and Meiosis)?
Genetic Material Duplicates

Role of Helicase?
Untwists and unzips DNA strand at the replication fork.

DNA Replication - First Step
DNA strand untwists and unzipps by Helicase (moves along DNA)
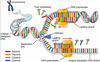
Role of DNA Polymerase?
Assembles new Nucleotides on original DNA arm.
Ensures that bases bond correctly.

DNA Replication - Second Step
New DNA formed by Polymerase glueing floating bases.

Semi Conservative Replication?
New DNA contains one of original DNA and one new strand.

DNA Replication - Third Step
- Assembled DNA re-twists into double helix.
- Double helix strands condense into chromatids.

Loci?
The position of a gene or mutation on a chromosome.


