cerebral hemisphere Flashcards
(34 cards)
Achicotex
- part of allocortex (ancient center)
- contains 3 layers of gray matter
- involved in memory and emtions
- HIPPOCAMPAL FORMATION
Paleocortex
- Part of allocortex (ancient cortex)
- made up of 3-5 layers of gray matter
- PARAHIPPOCAMPAL GYRUS, uncus and the lateral olfactory gyrus (olfactory system)
Mesocortex
- Part of allocrotex (ancient center)
- made up of 3-6 layers of gray matter
- cingulate gyrus and the insula
describe Neocortex
- is the evolutionarily newer cortex (makes up 90% of cerebral cortex)
- made up of 6-layers present with regional variation
–> HOMOTYPICAL CORTEX = association areas (all 6 layers are present)
–> HETEROTYPICAL CORTEX = PRIMARY AREAS
1) agranular = primary motor cortex
2) granular = primary sensory cortex
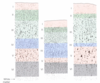
define pyramidal cells
- most abundant, 75% of cortical cells
- Long axons FORM WHITE MATTER TRACTS
Fusiform
- Modified pyramidal
- Located in the DEEPEST cortical layers
- Axons PROJECT TO THALAMUS
define Stellate (granule) cells
- Involved in integration
- Aspiny = INHIBITORY INTERNEURONS
- Spiny = EXCITATORY interneurons, located in layer IV of the gray matter
Horizontal cells of cajal
- located in SUPERFICIAL most layer of gray matter
- Seldom seen or completely lacking in adult brain
Cells of MARTINOTTI
- Interneurons
- located in DEEP LAYERS of the gray matter
Association fibers
- Intracortical fibers = superior longitudinal fasciculus, uncinate fasciulus, occipitofrontal fasiculus
- Send projections WITHIN SAME HEMISPHERE (IPSILATERAL)
Commissural fibers
- Commissural fibers = corpus callosum, anterior/posterior commissures
- TO/FROM OPPOSITE HEMISPHERE (CONTRALATERAL)
Projection fibers
- Ex = crus cerebri, internal capsule
- TO/FROM CORTEX and SPINAL CORD = corticobulbar, corticothalamic, corticopontine
- INTERNAL CAPSULE
Molecular layer (I)
- Synaptic area = axons and MOSTLY DENDRITES
- neuroglia and cells of cajal
- INTEGRATION (sends axons horizontally)
External granular layer (II)
- Small pyramidal and STELLATE CELLS
- Axons and dendrites from deeper layers
- INTEGRATION (sends cells horizontally)
External Pyramidal layer (III)
- Moderate size PYRAMIDAL cells
- EFFERENT LAYER (OUTPUT LAYER)
- Corticocortical fibers = association and commissural fibers
Internal granular layer (IV)
- STELLATE CELLS DENSLY PACKED
- outer band of baillarger = myelin staining
- AFFERENT LAYER = CHIEF INPUT LAYER (EXPANDED IN SENSORY CORTEXS)
- thalamic afferents = VPL, VPM-thalmocortical fibers
Internal pyramidal layer (V)
- GIANT PYRAMIDAL CELLS of betz, smaller number of stellate cells, cells of martinotti
- Inner band of baillarger- myelin staining
- EFFERENT LAYER (OUTPUT)
- PROJECTION FIBERS = corticofugal (striate), corticobulbar, corticospinal fiber
**EXPANDED IN MOTOR CORTEX**
polymorphic (multiform) layer (VI)
- small pyramidal cells, stellate cells, CELLS OF MARTINOTTI, Fusiform cells
- Efferent layer
- corticothalamic fibers
Precentral gyrus
- Brodmanns 4 = primary motor cortex
- Lesion = contralateral weakness, spastic paralysis, hyperreflexia (UMN lesion)
Premotor and supplementary motor area
- Brodmanns 6 = superior and middle frontal gyri
- Premotor and supplementary motor area = programming necessary for movements
- LESION = APRAXIA (inability to perform purposeful movements)
frontal eye field
- brodmanns 8 = superior and middle frontal gyri of pre-frontal cortex
- LESION = disruption of some of the most complex aspecs of behavior (e.g Phinaeus gage)
Brocas area
- Opercular and triangular parts of inferior frontal gyrus
- Brodmanns 44
- motor programs necessary for generation of language
- located in DOMINANT HEMISPHERE
- LESION = Brocas aphasia
define broca’s aphasia
- nonfluent, motor, expressive
- Comprehends language, difficult producing written or spoken words
Primary somatosensory area
- Brodmans 3,1,2 = post central gyrus
- Lesion = loss of tactile discriminatory and proprioception on CONTRALATERAL SIDE
- PAIN is not elicited, abolished or relieved


