Ch 7: EIGRP Flashcards
(30 cards)
EIGRP uses the protocol number _______ to identify its packets.
a. 87
b. 88
c. 89
d. 90
B. EIGRP uses protocol number 88.
EIGRP uses _______ packet types for inter-router communication.
a. three
b. four
c. five
d. six
e. seven
C. EIGRP uses the hello, request, reply, update, and query packet types
What is an EIGRP successor?
- The next-hop router for the path with the lowest path metric for a destination prefix
- The path with the lowest metric for a destination prefix
- The router selected to maintain the EIGRP adjacencies for a broadcast network
- A route that satisfies the feasibility condition where the reported distance is less than the feasible distance
- An EIGRP successor is the next-hop router for the successor route (which is a loop-free route with the lowest path metric).
Which of the following attributes does the EIGRP topology table contain? (Choose all that apply.)
- destination network prefix
- hop count
- total path delay
- maximum path bandwidth
- list of EIGRP neighbors
All except #4 are contained.
The EIGRP topology table contains the destination network prefix, path attributes (hop count, minimum path bandwidth, and total path delay), and a list of nearby EIGRP neighbors.
Which of the following destination addresses does EIGRP use when feasible? (Choose two.)
- IP address 224.0.0.9
- IP address 224.0.0.10
- IP address 224.0.0.8
- MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:0A
- MAC address 0C:15:C0:00:00:01
2 and 4. EIGRP uses the multicast IP address 224.0.0.10 or MAC address 01:005E:00:00:0A when feasible.
Which value can be modified on a router to manipulate the path taken by EIGRP but avoid having impacts on other routing protocols, such as OSPF?
- interface bandwidth
- interface MTU
- interface delay
- interface priority
- The interface delay can be modified to change the EIGRP path calculations without modifying the path calculation of OSPF.
EIGRP uses a reference bandwidth of ________ with the default metrics.
- 100 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
- 10 Gbps
- 40 Gbps
- EIGRP uses a reference bandwidth of 10 Gbps with the default metrics.
The default EIGRP hello timer for a high-speed interfaces is ______.
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 60 seconds
- EIGRP uses a default hello timer of 5 seconds for high-speed interfaces.
When a path has been identified using EIGRP and in a stable fashion, the route is considered ______.
a. passive
b. dead
c. active
d. alive
A. EIGRP considers stable paths to be passive.
How does an EIGRP router indicate that a path computation is required for a specific route?
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with the topology change notification flag set.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with a metric value of zero.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP query with the delay set to infinity.
- EIGRP sends a route withdrawal, notifying other neighbors to remove the route from the topology table.
- EIGRP sends out a query packet with the delay set to infinity to indicate that a route has gone active.
True or false: EIGRP summarization occurs for network prefixes as it crosses all network interfaces.
a. True
b. False
B. False. Summarization of prefixes occurs as traffic is advertised out an interface with summarization configured.
T/F: A router can run multiple EIGRP processes.
True.
A router can run multiple EIGRP processes. Each process operates under the context of an autonomous system, which represents a common routing domain.
T/F: Routers within the same domain use the same metric calculation formula and exchange routes only with members of the same autonomous system.
True.
Note: An EIGRP autonomous system should not be confused with a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) autonomous system.
What is a Successor route?
The route with the lowest path metric to reach a destination.
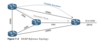
The successor route for R1 to reach 10.4.4.0/24 on R4 is R1→R3→R4.

What is a “Successor”?
The first next-hop router for the successor route.
The successor for 10.4.4.0/24 is R3.

What is FD (Feasible Distance)?
The metric value for the lowest-metric path to reach a destination. The feasible distance is calculated locally using the formula shown in the “Path Metric Calculation” section, later in this chapter.
The FD calculated by R1 for the 10.4.4.0/24 network is 3328 (that is, 256+256+2816).

What is Reported Distance?
The distance reported by a router to reach a prefix. The reported distance value is the feasible distance for the advertising router.
R3 advertises the 10.4.4.0/24 prefix with an RD of 3072.
R4 advertises the 10.4.4.0/24 to R1 and R2 with an RD of 2816.

What is a feasibility condition?
A condition under which, for a route to be considered a backup route, the reported distance received for that route must be less than the feasible distance calculated locally. This logic guarantees a loop-free path.

What is a Feasible Successor?
A route that satisfies the feasibility condition and is maintained as a backup route. The feasibility condition ensures that the backup route is loop free. (i.e. the RD < FD for the route)
The route R1→R4 is the feasible successor because the RD 2816 is lower than the FD 3328 for the R1→R3→R4 path.
T/F:
EIGRP’s topology table is a vital component to DUAL and contains information to identify loop-free backup routes. The topology table contains all the network prefixes advertised within an EIGRP autonomous system. Each entry in the table contains the following:
- Network prefix
- EIGRP neighbors that have advertised that prefix
- Metrics from each neighbor (for example, reported distance, hop count)
- Values used for calculating the metric (including load, reliability, total delay, maximum bandwidth)
False.
Almost…
EIGRP’s topology table is a vital component to DUAL and contains information to identify loop-free backup routes. The topology table contains all the network prefixes advertised within an EIGRP autonomous system. Each entry in the table contains the following:
- Network prefix
- EIGRP neighbors that have advertised that prefix
- Metrics from each neighbor (for example, reported distance, hop count)
- Values used for calculating the metric (for example, load, reliability, total delay, minimum bandwidth)
The minimum bandwidth is important for eliminating slow links.

With the command sh ip eigrp topology, what are the meanings of P and A?
The 10.4.4.0/24 route is passive (P), which means the topology is stable. During a topology change, routes go into an active (A) state when computing a new path.

T/F: EIGRP neighbors never exchange full routing tables, only incremental updates.
False.
EIGRP neighbors exchange the entire routing table when forming an adjacency, and they advertise only incremental updates as topology changes occur within a network.
The neighbor adjacency table is vital for tracking neighbor status and the updates sent to each neighbor.
What are the 5 packet types that EIGRP uses to communicate among routers?
EIGRP uses five different packet types to communicate with other routers, as shown in Table 7-3. EIGRP uses its own IP number (88); it uses multicast packets where possible and unicast packets when necessary. Communication between routers is done with multicast, using the group address 224.0.0.10 when possible.

In the EIGRP metric calcuation what is delay, exactly?
Delay is the total measure of delay in the path, measured in tens of microseconds (μs).


