CH10 Acids and Bases Flashcards
(22 cards)
Arrhenius Acid/Base definition
Acid: donates/dissociates H+ in solution (HCl, HNO3)
Base: donates/dissociates OH- in solution (NaOH, CaOH2)
Bronsted-Lowry acid/base definition
conjugate acid/base?
Acid: donates H+
Base: Accepts H+
Conjugate acid: the molecules that receive the H+
Lewis acid/base definition
Acid: accepts electrons
base: donates electro
one pair is shared in its entirety. (coordinate covalent bond formation)
Amphoteric species
i.e H2O
under acidic condition behaves life a base H3O
under basic condition behaves like an acid OH-
Oxygen suffixes and preffixes for quantity
suffixes for acids with o2
Hypo- =less HYPOchlorite (ClO)
ite=less Chlorite (ClO2)
ate= 1 more Chlorate (ClO3)
Per- = 1 more PERchlorate (ClO4)
ite = ous
ate = ic
pH and pOH formulas
pH= - log {H+] = log 1/[H+]
acid/base equilibrium constant Kw
what does affected?
only dependent on TEMP
changes in Conc, pressure or volume will NOT affected
how to get the P value from a concentration
[x] to pH
what is the pH of an acid with [H+] = 1.8 x 10-5 ?
-log(n x 10-m)
what is the pH of an acid with [H+] = 1.8 x 10-5
pH= -log (1.8 x 10-5) = 5 - log 1.8 = 5 - 0.18
Strong Acids, do they form unstable or stable conjugate bases?
- HCl
- HBr
- HI
- H2SO4 sulfuric acid
- HNO3 Nitric acid
- HClO4 Perchloric Acid
the stronger the acid the more stable the conjugate base
Strong bases
KOH
NaOH
and other soluble hydroxides with group 1 or 2
Ka of acid
and
which one is a stronger acid pka:10 or pKa:20
Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA]
the smaller the Ka the weaker the acid (there is more HA did not dissociate)
pKa:10 is a stronger acid. the smaller pka the stronger the acid
electronegativity and acidity what is the relationship?
Acid molecules with a highly electronegative element near where the H is attached will make it easier to donate
since its pulling e- away from the site of where the H is bonded
what is Kb x Ka
and what is pKa + pKb
= 1.0 x 10-14= Kw
Strong acid + Strong base
what happens
HCl + NaOH = H2O + NaCl
all salt, SB and SA neutralize each other
Strong acid + weak base
what happens increase or decrease pH?
HCl + NH3 = NH4+ Cl-
NH4 will react with H2O and donate its Hs making more H3O+ therefore decreasing the pH making it more acidic
Strong base + Weak Acid
what happens?
increase or decrease pH?
NaOH + CH3COOH = H2O + Na+ CH3COO-
CH3COO- will react with h2o
CH3COO- + H2O = CH3COOH + OH-
it will make the solution more basic it will increase pH
pH of a buffer solution Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH= pKa + log [B+]/[BOH]
Formula at equivalence for acid/base titration
NaVa=NbVb
N is the acid/base normalities
Titration Curve and labels, where is pKa, where is equivalence point
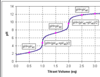
what is the gram equivalent of phosphoric acid?
problem

Normality problem

Titration what is it used for?
It is to determine the concentration (molarity) of a known solution. i.e solution with HCl is titrated with NaOH


