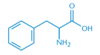
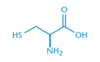
Chapter 1. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Flashcards
(93 cards)
What are the four properties of proteinogenic amino acids?
- There is a central carbon with an amino group, carboxyl group, side chain, and hydrogen atom.
- All are α-amino acids.
- All are chiral (except for glycine).
- All are L-isomers.
Is the following an L-amino acid or D-amino acid? Explain.

L-amino acid. The amino group is on the left side.
Is the following an L-amino acid or D-amino acid? Explain.
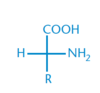
D-amino acid. The amino group is on the right side.
Which amino acids are nonpolar, nonaromatic?
- Glycine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Methionine
- Proline
Glycine is the only proteinogenic amino acid that is considered achiral. Why?
Its R-group is a hydrogen atom.
*Remember: A molecule is chiral if it has four different groups attached to it.
Which two amino acids contain a sulfur atom in their side chain?
Methionine and Cysteine
Methionine and cysteine both contain sulfur in their side chain. Why is methionine considered to be nonpolar, while cysteine is considered to be polar?
The sulfur in methionine has a methyl group attached to it, which makes it nonpolar.
Which amino acid has the amino group attached to the α-carbon?
Proline
The amino group in proline is only attached to the α-carbon, which creates a ring. What effects does the ring in proline have?
The ring causes flexibility constraints, which limits proline’s position on a protein and effects its role in secondary structures.
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for proline?
pro, p
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for alanine?
ala, a
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for valine?
val, v
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for leucine?
leu, l
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for isoleucine?
ile, i
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for methionine?
met, m
What are the 3-letter and 1-letter abbreviations for glycine?
gly, g
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Glycine
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Alanine
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Valine
What is the name of the following amino acid?
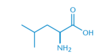
Leucine
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Isoleucine
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Methionine
What is the name of the following amino acid?

Proline
Which amino acids are considered to be aromatic? State whether each one is polar or nonpolar.
- Tryptophan (nonpolar)
- Phenylalanine (nonpolar)
- Tyrosine (polar)