Chapter 11 Flashcards
(101 cards)
John Maynard Keynes wrote that responsibility for low income and high unemployment in economic downturns should be placed on:
- low levels of capital.
- an untrained labor force.
- inadequate technology.
- low aggregate demand.
4
According to classical theory, national income depends on ______, while Keynes proposed that ______ determined the level of national income.
- aggregate demand; aggregate supply
- aggregate supply; aggregate demand
- monetary policy; fiscal policy
- fiscal policy; monetary policy
2
The IS–LM model takes ______ as exogenous.
- the price level and national income
- the price level
- national income
- the interest rate
2
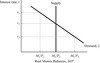
A variable that links the market for goods and services and the market for real money balances in the IS–LM model is the:
- consumption function.
- interest rate.
- price level.
- nominal money supply.
2
In the IS–LM model, which two variables are influenced by the interest rate?
- supply of nominal money balances and demand for real balances
- demand for real money balances and government purchases
- supply of nominal money balances and investment spending
- demand for real money balances and investment spending
4
Two interpretations of the IS–LM model are that the model explains:
- the determination of income in the short run when prices are fixed, or what shifts the aggregate demand curve.
- the short-run quantity theory of income, or the short-run Fisher effect.
- the determination of investment and saving, or what shifts the liquidity preference schedule.
- changes in government spending and taxes, or the determination of the supply of real money balances.
1
The IS curve plots the relationship between the interest rate and ______ that arises in the market for ______.
- national income; goods and services
- the price level; goods and services
- national income; money
- the price level; money
1
For the purposes of the Keynesian cross, planned expenditure consists of:
- planned investment.
- planned government spending.
- planned investment and government spending.
- planned investment, government spending, and consumption expenditures.
4
In the Keynesian-cross model, actual expenditures equal:
- GDP.
- the money supply.
- the supply of real balances.
- unplanned inventory investment.
1
In the Keynesian-cross model, actual expenditures differ from planned expenditures by the amount of:
- liquidity preference.
- the government-purchases multiplier.
- unplanned inventory investment.
- real money balances.
3
Planned expenditure is a function of:
- planned investment.
- planned government spending and taxes.
- planned investment, government spending, and taxes.
- national income and planned investment, government spending, and taxes.
4
When planned expenditure is drawn on a graph as a function of income, the slope of the line is:
- zero.
- between zero and one.
- one.
- greater than one.
2
When drawn on a graph with Y along the horizontal axis and PE along the vertical axis, the line showing planned expenditure rises to the:
- right with a slope less than one.
- right with a slope greater than one.
- left with a slope less than one.
- left with a slope greater than one.
1
The equilibrium condition in the Keynesian-cross analysis in a closed economy is:
- income equals consumption plus investment plus government spending.
- planned expenditure equals consumption plus planned investment plus government spending.
- actual expenditure equals planned expenditure.
- actual saving equals actual investment.
3
With planned expenditure and the equilibrium condition Y = PE drawn on a graph with income along the horizontal axis, if income exceeds expenditure, then income is to the ______ of equilibrium income and there is unplanned inventory ______.
- right; decumulation
- right; accumulation
- left; decumulation
- left; accumulation
2
According to the analysis underlying the Keynesian cross, when planned expenditure exceeds income:
- income falls.
- planned expenditure falls.
- unplanned inventory investment is negative.
- prices rise.
3
When firms experience unplanned inventory accumulation, they typically:
- build new plants.
- lay off workers and reduce production.
- hire more workers and increase production.
- call for more government spending.
2
The Keynesian cross shows:
- determination of equilibrium income and the interest rate in the short run.
- determination of equilibrium income and the interest rate in the long run.
- equality of planned expenditure and income in the short run.
- equality of planned expenditure and income in the long run.
3
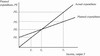
In this graph, the equilibrium levels of income and expenditure are:
- Y1 and PE1.
- Y2 and PE2.
- Y3 and PE3.
- Y3 and PE4.

2
In this graph, if firms are producing at level Y1, then inventories will ______, inducing firms to ______ production.
- rise; increase
- rise; decrease
- fall; increase
- fall; decrease

3
In this graph, if firms are producing at level Y3, then inventories will ______, inducing firms to ______ production.
- rise; increase
- rise; decrease
- fall; increase
- fall; decrease
2
The government-purchases multiplier indicates how much ______ change(s) in response to a $1 change in government purchases.
- the budget deficit
- consumption
- income
- real balances
3
In the Keynesian-cross model, if the MPC equals 0.75, then a $1 billion increase in government spending increases planned expenditures by ______ and increases the equilibrium level of income by ______.
- $1 billion; more than $1 billion
- $0.75 billion; more than $0.75 billion
- $0.75 billion; $0.75 billion
- $1 billion; $1 billion
1
According to the Keynesian-cross analysis, when there is a shift upward in the government-purchases schedule by an amount G and the planned expenditure schedule by an equal amount, then equilibrium income rises by:
- one unit.
- Delta-G.
- Delta-G divided by the quantity one minus the marginal propensity to consume.
- Delta-G multiplied by the quantity one plus the marginal propensity to consume.
3