Chapter 13 Flashcards
(13 cards)
Gyrus
is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. sulcus).
sulcus
is a depression or fissure in the surface of the brain
Gray matter vs White Matter
Grey matter (or gray matter) (lat. Substantia grisea) is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and myelinated as well as unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astroglia and oligodendrocytes) and capillaries. Grey matter is distinguished from white matter, in that grey matter contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons, while white matter is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axon tracts and contains relatively very few cell bodies.[1] The color difference arises mainly from the whiteness of myelin
What is the arbor vitae of the cerebellum?
is the cerebellar white matter, so called for its branched, tree-like appearance. In some ways it more resembles a fern and is present in both cerebellar hemispheres.[1] It brings sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum. The arbor vitae is located deep in the cerebellum.
What is the basal ganglia?
a group of structures linked to the thalamus in the base of the brain and involved in coordination of movement.

What is the limbic system?
a complex system of nerves and networks in the brain, involving several areas near the edge of the cortex concerned with instinct and mood. It controls the basic emotions (fear, pleasure, anger) and drives (hunger, sex, dominance, care of offspring).

ventricles of the brain.
The CNS is a hollow tube
Lined with ependymal cells
Two lateral ventricles in the cerebrum connected by the interventricular foramen of Monroe
The third ventricle is in the diencephalon
The cerebral aqueduct of sylvias passes through the midbrain
The fourth ventricle is in the superior part of the medulla
It is continuous with the central canal of the cord
It is continuous with the subarachnoid space via two latereal foramena of luschka and the medial foramen of the magendie
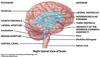
Name the ventricles of the brain.
There are two lateral ventricles, one on the left and one on the right. The other two ventricles are called the third and fourth ventricles.
Trace a drop of CFS from the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles to their place of absorption in the sagittal sinus of the venous circulation.

What is CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid
It is produced in the choroid plexus of the brain. It acts as a cushion or buffer for the brain’s cortex, providing a basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull, and it serves a vital function in cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.
What is the blood-brain barrier?
a filtering mechanism of the capillaries that carry blood to the brain and spinal cord tissue, blocking the passage of certain substances.
The blood-brain barrier allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function.
From a diagram locate the various arteries the make up the cerebral circulation.



