Chapter 13 Flashcards
(34 cards)
Define solvent
The majority component of a solution
Define solute
The minority component of a solution
What is spontaneous mixing and which way does water flow?
The tendency for soultions of different concentrations to mix when they come in contact. Water flows from less concentrated to more concentrated solution

For a liquid solution, the solvent is always ________
Liquid
Note: solue may be gas, liquid, or solvent

What factors determine solubility?
- Nature’s tendency toward mixing
- Intermolecular forces
Define entropy
Measure of energy dispersal in a system
When do solutions form and when do they not form?
When the solute-to-solvent attractions are weaker than the sum of the solute-to-solute and solvent-to-solvent attractions, the solution will form only if the energy difference is small enough to be overcome by the increase in entropy from mixing.

For make a solution, you must overcome what?
- all solute-solute attractive forces (endo +)
and
- some solvent-solvent attractive forces (endo +)
- Form new attractions between solute-solvent molecules (exo -)
ΔHsol’n = ΔHsolute + ΔHsolvent + ΔHmix
Define miscible
Two liquids that are always solube in each other
Miscible - Alcohol and water
Immiscible - Oil and water
What is solubility and what does it depend on?
Max amound of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent. Depends on Temperature and Pressure
What is dynamic equilibrium?
What rate of dissolution (dissolving) = rate of deposition (recrystalization)
What is ΔHsolution for aqueous solutions of ionic compunds?
ΔHsolution = ΔHhydration - ΔHlattice
*ΔHsolute = - ΔHlattice
*ΔHhydration = ΔHsolvent + ΔHmix
What is a solution considered saturated?
At the point of dynamic equilibrium
*Unsaturated < saturated
*Supersaturated > saturated
For most solids, how are solubility and temperature related?
As Temperature increases, Solubility increases
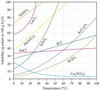
For gases, how are solubility and temperature related?
For ALL gases, as temperature increases, solubility decreases
For gases, how are solubiliy and pressure related?
For ALL gases, as pressure increases, solubility increases
Note: Liquids/Solids are independent of pressure
What is Henry’s Law?
Sgas = kHPgas
<span>Solubiilty of a gas is directly proportional to its partial pressure</span>
What are colligative properties?
Values depond ONLY on number of solute particles
The vapor pressure of a solvent above a solution is _____than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
Lower
Addition of a nonvolatile solute _____ the rate of vaporization, _____ the amount of vapor
reduces, decreasing
What is Raoult’s Law?
Psolvent in solution = χsolvent • P°
What is the difference between a volatile and nonvolatile solute?
A volatile solute will contribute to the vapor pressure, a nonvolatile solute will not contribute to vapor pressure.
What is Raoult’s Law for a Volatile Solute?
Ideal solution (similar structure eg. polar-polar)
Ptotal = Psolute + Psolvent
What is the difference between Ideal and Nonideal Solutions?
Ideal: solute-solvent interations = solute-solute + solvent-solvent
Nonideal: solue-solvent < or > solute-solute + solvent-solvent


