Chapter 14 Flashcards
(16 cards)
What happens to the rate of a reaction over time?
Generally slows down because concentration of reactants decreases
Compare order and order of reaction
Order: exponent of specific reactant
Order of reaction: sum of exponents on reactants
Name 4 factors that affect the rate of a reaction
- Temperature
- Reactant concentrations
- Catalyst
- Physical state
What is zero order (n=0)?
Rate of reaction is always the same
Doubling [A] has no effect on reaction rate

What is first order (n=1)?
Rate is directly proportional to reactant concentration
Doubling [A] will double reaction rate

What is second order (n=2)?
Rate is directly proportional to square of reactant concentration
Doubling [A] will quadruple rate of reaction
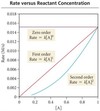
What is the units, slope and y-intercept of zero-order reactions?
Units: M • s-1
Slope: -k
y-intercept: [A]0

What is the units, slope and y-intercept of first-order reactions?
Units: s-1
Slope: -k
y-intercept: ln[A]0

What is the units, slope and y-intercept of second-order reactions?
Units: M-1 • s-1
Slope: k
y-intercept: 1/[A]0

For Arrhenius equation, what do A and Ea represent?
A: frequency factor - number of molecules that begin to form activated complex (transition from reactants to products)
Ea: activation energy - minimum energy need to start reaction (difference between reactants and activated complex)

What is the activated complex?
Chemical special with partially broken and partially formed bonds (transistion state)
If Ea increases, what happens to exponential factor and reaction rate in Arrhenius equation?
Decreases
The higher the energy barrier (larger activation energy), the fewer molecules that have sufficient energy to overcome it.
If Temperature increases, what happens to exponential factor and reaction rate in Arrhenius equation?
Increases
Increasing temperature will increase the number of molecules with sufficient energy to overcome the energy barrier.
What 2 terms can the frequency factor (A) be broken into?
Orientation factor (p)
Collision frequency (z)
What makes a mechanism valid?
- The elementary steps must sum to the overall reaction.
- The rate law predicted by the mechanism must
be consistent with the experimentally observed rate law.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that lowers rate of reaction by lowering activation energy without being consumed.
Note: It may be consumed in an early mechanism step then made up at a later step.


