Chapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Flashcards
(128 cards)
residue
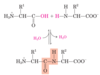
reflects the loss of the elements of water when one amino acid is joined to another
hydrolyzed
broken down
All 20 of the common amino acids are _____-amino acids. They have a _____ group and an _____ group bonded to the same carbon atom (the _____ carbon). They differ from each other in their _____ _____, or ______ groups, which vary in structure, size, and electric charge and and influence the solubility of the amino acids in _____. This structure is common to all but one of the α-amino acids. (_____, a cyclic amino acid)

- α
- carboxyl
- amino
- side chains
- R
- water
- Proline
For all the common amino acids except _____,
the α carbon is bonded to four different groups: (______). The α-carbon atom is thus a _____ center. Thefour different groups can occupy _____ unique spatial arrangements; thus amino acids have two possible _____. Since they are nonsuperposable mirror images of each other they are _____. In glycine, the R group is another _____ atom
- glycine
- carboxyl group
- amino group
- R group
- hydrogen atom
- chiral
- two
- stereoisomers
- enantiomers
- hydrogen
The absolute configurations of simple sugars and amino acids are specified by the _____ _____ system, based on the absolute configuration of the three-carbon sugar _____. L and D refer only to the _____ _____ of the four substituents around the chiral carbon, not to _____ properties of the molecule.
- D, L
- glyceraldehyde
- absolute configuration
- optical

For all chiral compounds, stereoisomers having a configuration related to that of L-glyceraldehyde are designated L, and stereoisomers related to D-glyceraldehyde are designated D. The functional groups of the amino acids are matched with those of glyceraldehyde by aligning those that can be interconverted by simple,_____ _____ chemical reactions. Then L-Amino acids are those with the α-amino group on the _____, and D-amino acids have the α-amino group on the _____. Explain…
- one-step
- left
- right
- In these perspective formulas
- C are lined up vertically, w/chiral atom in the center
- C are numbered beginning with the terminal aldehyde or carboxyl carbon, 1 to 3 from top to bottom
- R group is always below the α carbon
- L-Amino acids have the α-amino group on the left
- D-amino acids have the α-amino group on the right

Nearly all biological compounds with a chiral center
occur naturally in only one _____ form, either D or L. The amino acid residues in protein molecules are exclusively _____ _____. _____-Amino acid residues have been found in only a few, generally small peptides, including some peptides of bacterial cell walls and certain peptide antibiotics.
- stereoisomeric
- L stereoisomers
- D
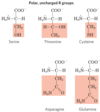
amino acids can be grouped into five main classes based on the properties of their _____ groups, particularly their ______, or tendency to interact with _____ at biological _____.
- R
- polarity
- water
- pH (near pH 7.0)
A few amino acids are somewhat difficult to characterize or do not fit perfectly in any one group, particularly _____, ______ and _____. Their assignments to particular groupings are the results of considered judgments rather than absolutes.
- glycine
- histidine
- cysteine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
______ has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive ______ structure. The secondary amino (imino) group is held in a _____ ______ that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing it
- Proline
- cyclic
- rigid conformation

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
_____, one of the two sulfur containing amino acids, has a slightly nonpolar ______ group in its side chain
- Methionine
- thioether

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
_____ has the simplest structure. Although it is most easily grouped with the nonpolar amino acids, its very _____ _____ _____ makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions
- Glycine
- small side chain

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
chains of _____, _____, _____, _____ tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of _____ _____.
- alanine
- valine
- leucine
- isoleucine
- hydrophobic interactions

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
- nonpolar
- hydrophobic

Glycine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Alanine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Proline
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Valine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Leucine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Isoleucine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Methionine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Aromatic R Groups
_____, _____, and _____, with their aromatic side chains, are relatively nonpolar (hydrophobic).
- Phenylalanine
- tyrosine
- tryptophan

Aromatic R Groups
The _____ group of tyrosine can form hydrogen bonds, and it is an important functional group in some enzymes
- tyrosine

Aromatic R Groups
Tyrosine and tryptophan are significantly more polar than phenylalanine, because of the tyrosine _____ group and the _____ of the tryptophan indole ring.
- hydroxyl
- nitrogen