Exam 3 Flashcards
(192 cards)
2009
In the structure below the orientation at which C atom would determine if this is a D or L sugar
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

4
2009
When two carbohydrates are epimers
- They differ in length by one carbon
- They rotate plane-polarized light in the same direction
- One is an aldose, the other a ketose
- One is a pyranose, the other a furanose
- They differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom
They differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom
2009
From the abbreviated name of hte compound Gal(B1→4)Glc, we know that
- the galactose residue is at the reducing end
- the glucose residue is the B anomer
- the glucose is in its pyranose form
- the compound is dextrorotatory
- the compound is lactose
the compound is lactose
2009
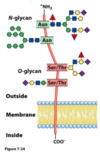
In glycoproteins, the carbohydrate moiety is always attached through the amino acid residue
- glutamine or arginine
- aspartate or glutamate
- asparagine, serine, or threonine
- glycine, alanine, or aspartate
- tryptophan, aspartate or cysteine
asparagine, serine, or threonine
2009
Which is found in glocogen?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E

E
2009
Which is a ketose?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E

D
2009
Which is an L-sugar?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E

C
2009
Which is a pair of epimers?
- A & B
- B & C
- C & D
- D & E
- C & A

B
2009
Which of the following statements about starch and glycogen is false?
- Both serve primarily as structural elements in cell walls
- Both starch and glycogen are stored intracellularly as insoluble granules
- Amylose is unbranched; amylopectin and glycogen contain many (α1→6) branches
- Both are homopolymers of glucose
- Starch is found in plants, glycogen is found in animals
Both serve primarily as structural elements in cell walls
2009
If glycogen is partially hydrolysed and all possible disaccharides are isolated, how many would be found?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2
2009
Neuraminic acid is a 9 carbon atom keose (i.e. nonose). The total number D diastereomers of neuraminic acid (ignore anomers is)
- 2
- 4
- i
- 16
- 32

16
2009
Neuraminic acid is formed from 2-acetamido-D and the metabolite phosphoennol pyruvate. How many 9C atom sugars can be formed?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16

2
2009
An unknown oligosaccharide is reduced at its reducing end with an appropriate reducing agent. It was found that 504 mg of the oligosaccharide consumed the equivalent of 1 millimole of hydrogen. The molecular weight of oligosaccharide is
- 126
- 252
- 378
- 504
- 1008
504
2009
An unknown oligosaccharide is reduced at its reducing end with an appropriate reducing agent. It was found that 504 mg of the oligosaccharide consumed the equivalent of 1 millimole of hydrogen. This oligosaccaride most like is.
- an aldo- or ketohexose
- an aldo- or ketodecanose (deca=10)
- a reducing disaccharide consisting of 2 aldohexoses
- a non-reducing disaccharide consisting of 2 aldohexoses
- a reducing trisaccharide consisting of 3 hexoses
a reducing trisaccharide consisting of 3 hexoses
2009
Ther term amphipathic means
- branched, with at least two branch points
- having one region that is positively charged and one region that is negatively charged
- different on the inside and outside of the lipid bilayer
- having one region that is polar and one that is nonpolar
- having two different types of bonds
having one region that is polar and one that is nonpolar
2009
The polar head group of cholesterol is
- the alkyl side chain
- glycerol
- the steroid nucleus
- the hydroxyl group
- choline
the hydroxyl group
2009
Required biological membranes are “self-sealing” due to all of the following except:
- The amphipathic character of the lipids
- hydrophobic interactions between lipids
- hydrogen bonding between the head groups of the lipids and H2O
- an increase in entropy of the system upon sealing
- covalent interactions among lipids
covalent interactions among lipids
2009
A cell has available deoxyribose molecules, inorganic phosphates and the standard purine and pyrimidine molecules with nothing attached to them. The cell makes a deoxytetranucleotide with a hydroxyl at one end and a phosphate at the other. How many water molecules does it remove to make the deoxytetranucleotide?
- none
- four
- eight
- nine
- eleven
eleven
2009
A cell has available deoxyribose molecules, inorganic phosphates and the standard purine and pyrimidine molecules with nothing attached to them. The cell makes a deoxytetranucleotide with a hydroxyl at one end and a phosphate at the other.
If the cell had ribose molecules instead of deoxyribose available, how many water molecules would it have had to remove to make the tetranucleotide with a hydroxyl at one end and a phosphate at the other?
- none
- four
- eight
- nine
- eleven
eleven
2009
Frederick Griffith injected mice with various strains of pneumococcus. Which of the following formulations would have caused the mice to die?
- live nonencapsulated nonvirulant bacteria
- live encapsulated virulent bacteria which are heat killed prior to injection
- a mixture of heat-killed nonencapsulated nonvirulent bacteria and heat-killed encapsulated virulent bacteria
- a mixture of heat-killed encapsulated virulent bacteria and live nonencapsulated nonvirulent bacteria
- none of the above
a mixture of heat-killed encapsulated virulent bacteria and live nonencapsulated nonvirulent bacteria
2009
Which of the following would be a violation of Chargaff’s rules with respect to the base composition of double stranded DNA?
- A = T
- C = G
- T + C = A + G
- A + T = G + C
- all of the above follow Chargaff’s rules
A + T = G + C
2009
Which of the following is not true of the following DNA sequence?
5’ … TGCGATACTCATCGCA … 3’
- it could form a hairpin
- it matched with its complementary strand, it could form a cruciform structure
- if matched with its complementary strand, it could be palindromic except for four bases
- if matched with its complementary strand, it would be a mirror repeat
- all of the above are true
if matched with its complementary strand, it would be a mirror repeat
2009
Hoogsteen base pairing can lead to formation of
- duplex DNA
- triplex DNA
- tetraplex DNA
- hairpins
- hatpins
triplex DNA
2009
The melting temperature, Tm of DNA is found to follow the expression
Tm = 81.5° + 0.41°(%GC) - 675°/(length of DNA in base pairs)
An oligonucleotide 15 basepairs in length is found to have a melting temperature of 65.2°. What is its GC content?
- 80%
- 70%
- 60%
- 50%
- 40%
70%