chapter 5 Flashcards
(39 cards)
what is a fluid?
- defined as a substance that can change its shape to correspond to that of the container (gases and liquids)
what is density?
- denoted using rho (p) is defined as mass divided by volume
- p = m/v
given the denisty of a material and its volume, you can easily calculate?
- how much mass it contains by multiplying density times volume
- pV = m
if you need to find out how many moles you have of something given concentration and volume, you can just?
- multiply molarity times volume
what are common units of density which are equivalent to eachother?
- g/mL
- g/cm3
- the actual SI unit for density is kg/m3
- 1000 kg/m3 = 1kg/L = 1g/mL = 1g/cm3 for the density of water at 4°C and 1 atm
- the actual SI unit for density is kg/m3
what is specific gravity?
- how dense something is compared to water
- specific gravity = rho/ rhowater
how is pressure defined?
- force divided by area
- P = F/A
- N/m2 and 1 N/m2 = 1 Pa
- P = F/A
what is atmospheric pressure?
- refers to the baseline pressure exerted on us by all of the air present between our location and the point where the Earth’s atmosphere transitions to space
- varies with elevation, becoming lower as you go higher
- 1 atm = 101 kPa, 760 mmHg, 1 Torr, 14.7 psi
the pressure ecerted on an object at any point submerged in a fluid is equal to the density of the fluid multiplied by g, multiplied by the depth of submersion:
- Psub = rho g h
- h indicates the depth of submersion (height of the fluid above the object)
if we are specifically interested in the pressure exerted by a liquid on an object submerged in it, we use the term?
- hydrostatic pressure, which is defined as Psub = rho gh
if we are interested in the total pressure exerted on such an object by both the hydrostatic pressure of the water and the atmosphere, we call this the?
- absolute pressure
- Psub = Patm + rho g h
what is guage pressure?
- situtations where we are clear that a given pressure reading does not reflect atmospheric pressure
- Pguage = Psystem - Patm
what is buoyancy?
- some objects float on the surface of water and others sink
- whether objects float or sink is a property of its density
- a low density object will will float on top of water
- higher density obkects sink
- the degree to which an object is submerged in water is proportional to its specific gravity
- whether objects float or sink is a property of its density
if the specific gravity of an object is greater than 1, it is denser than water so it will?
if the specific gravity is equal to 1, it will be?
if the specific gravity is less than 1 it will?
- sink
- be completely submerged but at equilibrium
- will float, but will be partially submerged in the water
- in fact, the percentage it will be submerged is equal to its specific gravity, expressed as a percentage
What if we’re not immersing the subject in water, or what if we’re using water with a non-standard density. In that case, we can use the following equation:
- % submerged = rhoobject/rholiquid x 100
- when an object is floating, the fluid it is floating in exerts an upward force on it. If the magnitude of this upward force, which is known as the buoyant force, exceeds that of the force of gravity that is pulling the object downward, then the object floats. If it does not, it sinks
what is Archimede’s principle?
- weight = rho V g
- the buoyant force is therefore directly proportional to the volume of displaced fluid as modified by the density of the water
what is Pascal’s law?
- states that a change in pressure made at any location within an enclosed fluid will be transmitted equally to all points throughout that fluid
- principle underlying hydraulic lift which ises this principle to generate mechanical advantage
- DeltaP = F1/A1 = F2/A2
- F2 = A2/A1F1
- DeltaP = F1/A1 = F2/A2
- principle underlying hydraulic lift which ises this principle to generate mechanical advantage

Work is therefore conserved:
- W = F1d1 = F2d2
what is surface tension?
- liquid is held together by the presence of intermolecular forces among molecules of the liquid
- each such molecule experiences attractive forces from all of the other water molecules around it, and we can assume they balance out. However, the intermolecular forces from other water molecules act unevenly on water molecules that are on the surface of the water. these molecules experience attractive forces from the water molecules deeper in the liquid, but virtually no compensating interactions with the air. this imbalance of forces acting on water molecules on the surface creates tension
surface tension has units of?
- force divided by lnegth
- or energy divided by area so more surface tension means more energy, so ssytems will want to minimize surface tension and the best way to do this is to minimize surfcace area
the effect of intermolecular forces within a given substance is known as?
- cohesion
- It is possible for a liquid to interact with a substance that it is in contact with. such forces are known as?
- adhesion forces
- can be used to analyze how objects do or do not stick to each other
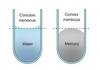
If the adhesive forces are stronger than the forces of surface tension, the liquid will crawl up the walls of the container to a slight extent. This results in the surface of the liquid becoming curved, which is knonw as a?
- meniscus
the meniscus formed by water is a?
- concave meniscus