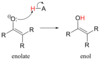Chapter 5 - Carbonyls and Alcohols Flashcards
(117 cards)
Acetal structure

Hemiacetal structure

Ketal structure
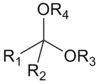
Hemiketal structure

Acid halide structure

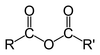
Acid anhydride structure
Amide structure

Imide structure

Lactone structure

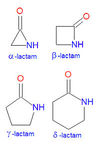
Lactam structure
Describe the signal present for a hydroxyl group on 1H NMR
broad peak between 1 and 5 ppm
Describe the general reactivity of alcohols
They are not good nucleophiles, but they can be deprotonated and converted into an alkoxide under basic conditions.
Describe the general reactivity of aldehydes and ketones
They are reactive with most nucleophiles , but not by a traditional nucleophilic substitution mechanism. The reactivity occurs mainly at the electrophilic carbonyl center, often forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Out of ketals, hemiketals, acetals, and hemiacetals, which can be formed and removed under acidic conditions?
acetals and ketals
Out of ketals, hemiketals, acetals, and hemiacetals, which can be formed only under basic conditions, but removed under any conditions?
hemiacetals and hemiketals
What are the 4 steps in an acid-catalyzed mechanism?
1) protonate (making the leaving group a better leaving group)
2) break bond (leaving group leaves)
3) make bond (nucleophile attacks carbocation)
4) deprotonate (molecule returns to natural state)
What are the 4 steps in a base-catalyzed mechanism?
1) deprotonate (make a strong nucleophile)
2) make bond (nucleophile attacks), break bond (leaving group leaves)
3) protonate (molecule returns to neutral state)
What charge do intermediates carry in an acid-catalyzed mechanism?
positive
What charge do intermediates carry in a base-catalyzed reaction?
negative
The addition of an alcohol to an aldehyde under acidic conditions yields what?
an acetal
The addition of an alcohol to a ketone under basic conditions yields what?
a hemiketal
What reactant is needed to form a ketal or acetal protecting group?
a 1,2-diol (OHCH2CH2OH) under acidic conditions

What is produced when an ester is reacted with a strong base in water?
Saponification: forms a carboxylate (deprotonated carboxylic acid) + alcohol

What is produced when an ester is reacted with an acid in water?
Ester hydrolysis: carboxylic acid + alcohol