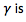chapter 6 Flashcards
(71 cards)
A flow is hydrodynamically unstable if
a small perturbation in the flow grows spontaneously, drawing energy from the mean flow.
It is useful to divide fluid instabilities into two types:
parcel instability and wave instability
Examples of parcel instability are
buoyant instability and inertial instability.
Buoyant Instability
If the atmospheric lapse rate (Γ) is more than the dry adiabatic lapse rate (Γ), an air parcel displaced upward will become buoyant and tend to move away from to its original level.
Inertial Instability
If an air parcel that is moving with the zonally directed geostrophic basic flow, is displaced across the stream, will accelerate further from that position
In buoyant and inerital instability an air parcel moved from its original position will
continue to accelerate away from where it started, instead of oscillating around its original position.
Most of the instabilities of importance in meteorology, are associated with
wave propagation
The wave instabilities important for synoptic-scale meteorology generally occur in the form of
perturbations to a zonally symmetric basic flow field
A


B


C


D


In general the basic flow is
a jetstream that has both horizontal and vertical mean-flow shears.
Examples of wave instability are:
barotropic and baroclinic instability.
Barotropic Instability is
a wave instability associated with the horizontal shear in a jet-like current.
Barotropic instabilities grow by
extracting kinetic energy from the mean-flow
Baroclinic instability, is associated with
vertical shear of the mean flow.
Baroclinic instabilities grow by
converting potential energy associated with the mean horizontal temperature gradient that must exist to provide thermal wind balance for the vertical shear in the basic state flow.
Wave Instability Assessment
Step 1:

Wave Instability Assessment
Step 2:

Wave Instability Assessment
Step 3:

Wave Instability Assessment
Step 4:

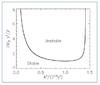
If N is real then the fluid is
stable, and a parcel disturbed vertically from rest would oscillate about its original position.
If N is real then the fluid is stable, and a parcel disturbed vertically from rest would oscillate about its original position. However, if N is imaginary then
we know a parcel will be unstable