Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes Flashcards
(19 cards)
Hydrohalogenation across an alkene

Markovnikov Product
H will go to carbon with more H’s on it, and the other substituent will go on the carbon with fewer H’s on it
List carbocation stability from greatest to least

Which types of reactions will add OH or OR to alkenes?
acid catalyzed hydration
oxymercuration - demercuration
acid catalyzed alcohol addition
Describe what is added, regioselectivity, and whether a rearrangement is possible in acid catalyzed hydration
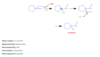
Describe what is added, regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and whether a rearrangement is possible in oxymercuration-demercuration

Describe what is added, regioselectivity, and whether a rearrangement is possible in acid catalyzed alcohol addition

Adding a halogen across an alkene will have what type of stereoselectivity?
anti

T/F? Rearrangements when adding halogens across a double bond are not possible.
true
What will give products in anti-markovnikov fashion when doing reactions with alkenes?
hydroboration-oxidation and hydrobromination with peroxide
In hydroboration-oxidation, the product will have ____ stereoselectivity
syn

When adding nucleophiles to an epoxide under acidic conditions, attack will occur at the ____ ___ position.
In basic conditions, it will attack at the most ___ ____ position
What type of stereoselectivity will it have?
acidic = most substituted
basic = least substituted anti
syn
In ozonolysis, a workup containing Zn, water, or (CH3)2S will form what kind of product?
If a workup contained just H202, what will the product look like?
Zn, H2O, (CH3)2S = one oxygen per carbon
H2O2 = one OH will replace one H
In catalytic hydration of alkenes, describe which reagent is used to create an E alkene or a Z alkene
E = Na or Li, with NH3
Z = H2 and lindlar catalyst
*E and Z are referring to the H’s being on the opposite or same sides, respectively
Differentiate between hydrohalogenation of terminal vs. internal alkynes
terminal - addition of HX markovnikov style
internal - two products
Describe the product of di-halogenation of an alkyne with one equivalent of the halogen, then with excess.
one equivalent - alkene with E addition of the halogen
excess - tetra halide
Acid catalyzed hydration of an alkyne will form what kind of product?
enol - will tautomerize to form a ketone

If an alkyne underwent a hydration through hydroboration-oxidation, what product will form?
How about if the same alkyne underwent an acid catalyzed hydration reaction?
hydroboration-oxidation = antimarkovnikov enol, which will tautomerize to an aldehyde
acid catalyzed hydration = markovnikov enole, which will tautomerize to a ketone
Alkylation of an alkyne uses ____ as a reagent, which will do nucleophilic attack on a terminal alkyne to create a ______
NaNH2, acetylide


