Chapter Four: Special Topics Flashcards
(28 cards)
equations of a vertical parabola
(x - h)2 = 4p(y - k)
y = a(x - h)2 + k
note: a = 4p
equations of a horizontal parabola
(y - k)2 = 4p(x - h)
x = a(y - k)2 + h
note: a = 4p
where is the focus of a parabola located?
- ±p distance away from the vertex
- y = cx2 –> (0, 1/4c)
- x = cy2 –> (1/4c, 0)
where is the directrix of a parabola located?
- ±p distance away from the vertex (in the opposite direction of the focus)
- y = cx2 –> y = -1/4c
- x = cy2 –> x = -1/4c
how can you determine the axis of symmetry of a parabola?
it is the equation of the horizontal or vertical line through the vertex and the center of the parabola
(ie: if the vertex is (-3, 2) and the parabola opens up, the equation for the axis of symmetry is x = -3)
what is the standard equation of an ellipse?
note: the term with the larger denominator comes first
(the larger denominator denotes the major axis)
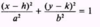
where are the intercepts of an ellipse that has a center of (0, 0)?
the x-intercepts are at ±a
the y-intercepts are at ±b
where are the foci of an ellipse?
- if the x term is first –> (±c, 0)
- c2 = a2 - b2
- if the y term is first –> (0, ±c)
- c2 = b2 - a2
- c2 = larger denominator - smaller denominator
what is the equation of a standard hyperbola? what are the intercepts of this hyperbola?
- will never cross y-axis
- x-intercepts at ±a
- foci at (±c, 0)
- c2 = a2 + b2

what is the standard equation of a vertical hyperbola? what are the intercepts and foci of this hyperbola?
- will never cross the x-axis
- intercepts at ±b
- foci at (0, ±c)
- c2 = a2 + b2
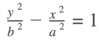
what is the equation for the asymptotes of a hyperbola?
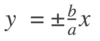
binomial theorem
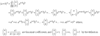
binomial coefficient

factorial
n!
the product of all the natural numbers that are less than or equal to n
sequence
an ordered collection of numbers, where an describes the location of a number in that sequence
inductive/recursive sequence
a sequence where the next term depends on the value of the previous term (ex: fibonacci)
arithmetic sequence
- a sequence with a constant difference between terms
- an = a1 + (n - 1)d
geometric sequence
- a sequence with a constant multiplicative ratio
- an = a1rn-1
- r = (an + 1)/(an)
sum of a finite arithmetic sequence
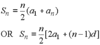
sum of a finite geometric sequence
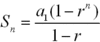
induction
if the first statement is proven true –> the next statement must be true –> all statements are true
steps to prove by induction
- prove that the statement is true for n = 1
- the base case does not have to be for n = 1
- assume that the statement is true for n = k
- prove that the statement is true for n = (k + 1)
permutation
an arrangement of distinct objects in a definite order
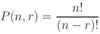
combination
a way of selecting things from a collection when order does not matter
(also the binomial coefficient formula)



