Chapters 1-4 Flashcards
(51 cards)
chemical element
pure subtance(a substance with constant composition that can’t be broken down by physical processes) that can’t be decomposed into other substances by ordinary means
atom
- the smallest particle of an element that cannot be chemically or mechanically divided into smaller particles
- smallest representative unit/particle of an element
- size- 10-10 m and spherical
compound
- a pure substance that is composed of 2 or more elements linked together in fixed proportions that can be broken down to those elements by some chemical process
- elements combine to form compounds
molecule
- 2 or more atoms chemically bonded together in characteristic proportions by forces called chemical bonds
- smallest representative unit of a compound
- some elements also exist as molecules (O2)
solid
- particles are in a fixed pattern
- vibrate
- definite shape and volume
liquid
- particles are close together
- arranged randomly and free to move
- definite volume
- flows to assume the shape of its container
gas
- particles are far apart
- move at high speeds
- no definite volume or shape
- expands to fill its container but is also compressible
- can be squeezed into a smaller volume if there is applied pressure and container is rigid
- aka vapor
chemical property
- a property of a substance that can only be observed by reacting it to form another substance
- Ex: high flammability
physical property
- property that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance
- don’t change the substance’s identity (ex. density)
intensive property
- independent of amount of substance present
- pure substances have distinctive properties
- shiny, dull, malleable, hard, colors
- sometimes we use several extensive properties to find an intensive one
- Ex: density
extensive properties
- dependent on amount present
- Ex: mass, volume, length, width
mixture
- any matter that is not a pure substance
- a combination of pure substances in variable(not definite) proportions in which the individual substances retain their chemical identities and can be separated from one another by a physical process
homogenous mixture
- a mixture in which the components are distributed uniformly throughout and have no visible boundaries or regions
- can also be called a solution if it is made of liquids(usually), or they may also be solids or gases
- Ex: sugar water
mass
the property that defines the quantity of matter in an object
matter
- anything that has mass and occupies space
- all matter is made up of either pure substances(very few exist in nature) or mixtures
substance
matter that has a constant composition and cannot be broken down to simpler matter by any physical process; aka pure substance
physical process
a transformation of a sample of matter, such as a change in its physical state, that does not alter the chemical identity of any substance in the sample
determining types of matter


element
- a pure substance that can’t be broken down into simpler substances
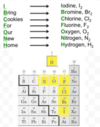
- Some elements exist as diatomics in nature
- H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (H plus the 7 shape)
compounds
- a pure substance that is composed of 2 or more elements bonded together in fixed proportions and that can be broken down into those elements by a chemical rxn.
- typically have properties very different than those of the elements of which they are composed
heterogenous mixture
- a mixture in which the components are not distributed uniformly, so that the mixture contains distinct regions of different compositions.
- to identify, you can look for boundaries between the liquids in a liquid mixture OR check that it is not clear/transparent(light can’t pass through such liquids b/c it is scattered by tiny solid particles that are suspended(not dissolved) in the liquid)
- Ex: salad dressing
energy
the capacity to do work
law of constant composition
every sample of a particular compound always contains the same elements combined in the same proportions
Ion
- a particle consisting of 1 or more atoms that has an overall positive or negative electrical charge
- are electrostatically attracted to one another
- may consist of single atoms(Ca2+, Cl-) or can contain 2 or more atoms bonded together







