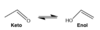Chem-Phys Flashcards
(318 cards)
Do cell membranes made with phosphatidyl-choline/-ethanolamine require a counter ion? why or why not?
No. they are charge balanced b/c (+) charge of choline/ethanolamine group offsets (-) charge of phosphate grp
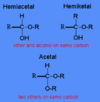
“Difference between isomers…
- structural
- geometrical
- conformational
- optical”
- structural: different connectivity
- geometrical: cis vs. trans.
- conformational: interchangable structures by rotation abount a bond
- optical: enantiomers—»same connectivity, different spatial orientation about chiral center”

treatment of Oleic acid with D2/Pd would yield a compound with how many chiral centers?

what factors increase membrane rigidity?
1) inc. degree of saturation
2) inc. # of carbons
which of the following alcohols are oxidized by Na2Cr2O7?
- phenols
- methyl/1º alcohols
- 2º alcohols
- 3º alcohols
methyl, primary, & secondary alcohols
How can you quickly identify whether a change in oxidation state is an oxidation or reduction? (i.e. S–S —» S–C)
If an atom is bound to a more electronegative atom —» oxidation
If an atom is bound to a less electronegative atom —» Reduction
what is the difference in structure of an enamine vs. imine

What forms when an aldehyde is treated with a grinard reagent?
a 2º alcohol is formed
Pinacol Rearrangement
Pinacol Rearrangement: converts a vicinal diol (OH groups on neighboring carbons) into a ketone via an alkyl shift.

of the 4 types of compounds, which are/are not reduced by NaBH4?
- phenol
- 3º alc
- ketone
- ester
- phenol —» no
- 3º alc —» no
- ketone —» yes
- ester —» no


if a food molecule (i.e. carb, fat, protein, etc.) isn’t metabolized by the digestive system, how many dietary calories are contributed to the consumer?
0 Cal are contributed to the consumer b/c anything that isn’t metabolized cannot provide any energy & ∴ no calories.
why is a solution of NaNO2(aq) basic?v
NO2- reacts w/H2O to form OH- ions, thereby inc. pH of solution
if there are 60 million nuclei of a radioactive atom (half-life of 430 years), how many years would it take before there are 3.75E^6 nuclei remaining?
- 1 half-life = [(# nuclei) / 2]
- (3.75E6)/(60E^6) = 1/16 = [4 half-lifes]
- 4(430) = 1720
What are 2 different units for electric field?
- Newton/Coulomb (N/C)
- Volt/Meter (V/m)
– 1(V) = 1 (J/C)
what type of interference occurs when two waves are out of phase by 180º?
Destructive Interference: occurs when two waves that meet when they are half a wave difference out of phase (180º)
how does the period of a waveform change as you move up through the 1st, 2nd, & 3rd harmonic? what about wavelength? frequency?
- the period (T) DEC. as you move up a harmonic level (i.e. 1st—»2nd)
- the wavelength DEC. as harmonic level increases
- if 1st harmonic = [100 Hz], 2nd = [200 Hz], 3rd = [300 Hz], etc.
what is the only effect that the photon frequency has on ejected electrons?
- photon frequency only affects the ejected e-‘s KE —» ∴ inc. in frequency = inc. in KE = inc. speed of ejected e-
- photon energy = cathode work function + KEelectron
if someone drinks an extremely hypertonic/hypersaline solution, why would this person be at risk of death?
ingested salt would be absorbed into the blood, creating a hypertonic environment outside the cells of the body—»causes water to flow out of the cell causing it to shrivel
How does adding salt to water affect it’s boiling point & vapor pressure?
1) adding salt inc. BP of water
2) adding salt dec. VP of water—»∴ as solute inc., the rate of water molecules breaking the liquid surface dec.
•BP—»the temperature at which VP of solution = VP of the atmosphere
what allows H2O to exhibit the unique property where it’s solid state (ice) is less dense then the liquid (water)
• the bent structure of H20 (bond angle ~104.45º) & the high degree of hydrogen bonding yields a hexagonal crystalline structure w/alot of space between molecules
1) Β- Decay
2) What is the product of I-131 B- decay?
1) conversion of neutron to proton & loss of 1e-
• element undergoing B-decay will convert to an element w/1 additional H+
2) Xe-131
What are the 4 main types of radioactive decay?
1) α-Decay: emission of alpha particle (2 protons & 2 neutrons [2+])
2) B- / B+ Decay:
- B- = neutron converted to H+ and B- particle (e-) ejected
- B+ = H+ converted to neutron and B+ particle (positron) emitted
3) Gamma Decay: emission of gamma ray (high energy photon) and release of ionizing radiation
4) Electron Capture: nucleus “grabs” an e- —» converts H+ to a neutron
if a child and an adult are exposed to the same contamination levels of I-131, would the child, compared with the adult, recieve a higher, lower, or equal relative dose?
- B/c children weigh less, the same quantity of external I-131 results in a higher concentration of the isotope in the body
- higher concentration = inc. likelyhood of DNA damage & cancer