Chemistry/Physiology Recap Flashcards
(170 cards)
Chemical energy
- Stored in bonds of chemical substances
- ex. Glucose (C6H12O6)
The energy is stored in the covalent bonds between carbon atoms

Some bacteria require energy in the form of the _______________.These bacteria cannot manufacture food like ___________ nor absorb nutrients from the environment like _________.
- Organic Molecules
- photosynthetic organisms
- fungi
The organic ___________ some bacteria take up are broken down to make _______.
- molecules
- ATP
________ provides the energy cells need to stay alive.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
_________ in molecules is stored in the ___________between _________ that make up the molecules.
- energy
- bonds
- carbon atoms
definition of chemistry
Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules
definition of atom
The atom is the smallest unit of matter and cannot be subdivided into smaller substances
Atoms interact to form ___________.
molecules
Atoms are composed of ____________.
subatomic particles
what are the 3 subatomic particles?
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Protons
positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutrons
neutrally charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electrons
negatively charged particles that orbit nucleus in an electron cloud
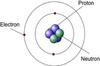
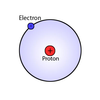
planetary model of an atom
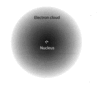
orbital model
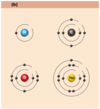
what are the 3 smallest elements?
- hydrogen
- helium
- lithium
- hydrogen (H)
- 1 proton, 0 neutrons, 1 electron

- helium atom (He)
- 2 protons, 2 neutrons, 2 electrons

- lithium atom (Li)
- 3 protons, 4 neutrons, 3 electrons
outer layer of e- is called the ________, and the e- in that layer are called __________.
- valence shell
- valence electrons
Only ___________are involved in ____________between any two atoms.
- valence electrons
- chemical bonding
what are the 4 chemically reactive elements?
- hydrogen
- carbon
- sodium
- oxygen
Most atoms chemically combined with other atoms to form __________________.
molecules and compounds
definition of a molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together (e.g., H2 or C6H12O6)