Chromosomes and their abnormalities Flashcards
(38 cards)
Only have 23 nuclear chromosomes
Gametes- oocytes and sperm cells, have only 23 nuclear chromosomes (haploid)
designate this karyotype

46,XY
designate this karyotype for male or female

47,XY,+21 or 47,XX,+21
designate the karyotype for robertsonian translocation downsyndrome
female and male
46,XX,rob(14;21), +21
46,XY,rob(14;21),+21
designate the karyotype edwards syndrome for female and male
47,XX,+18 or 47,XY,+18
designate patau karyotype
47,XX,+13 or 47,XY,+13
designate the karyotype for cri du chat
46,XX,del(5p) or 46,XY,del(5p)
designate karyotype for klinefelter syndrome
47,XXY
designate the karyotype for turner syndrome
45, X and 45,X/46,XX mosaics
what are the following types of chromosomes?
- P and q arms are clearly different lengths
- p and q arms are ~ equal lengths
- centromere is near one end
- submetacentric
- p and q arms are clearly different length
- metacentric
- ~equal length of p and q arms
- acrocentric
- centromere is near one end

what is the segragation of sister chromatids?
disjunction

abnormal chromosome seperation during meiosis
non-disjunction

meitotic crossover ocurrs during what time of meiosis?
meitotic cell division - production of haploid gametes
- meitotic crossover (genetic recombination)
- increases genetic diversity
- occurs during meiosis1- P1
describe autosomal deletion syndrome:
- cause
- type of cry
- phenotypic expression
cri du chat
- caused by deletions in the p arm of chromosome 5:
- 46,XX,del(5p) or 47,XY,del(5p)
- cat like cry
- phenotypic expression
- intellectual disabilities
- growth retardation
- speech impairment
- heart problems
- small head
- narrow eyes , with greater than normal distance between them
- low-set ears

- what are the increases in incidence of edwards?
- what are the phenotypic expressions?
47,XX,+18
- incidence increases with mother’s age
- phenotypic expression
- intellectual disabillities
- failure to thirve
- congenital hear problems
- receding jaw
- low-set, malformed ear
- specifically clenching fist
- rocker-bottom feet
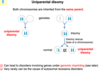
what chromosomes are considered for uniparental disomy? generate a flow chart examplifying the act of the UPD
take notice that a phenotype may be rescued from a UPD
what can be expected with most chromosomal abnormalities?
intellectual disabilities
developmental problems
cancers
what are the types of chromosomal abnormalities?
- abnormal chromosome number
- structural abnormalities
- balanced
- normal complement of chromosomal material
- ex: uneaqual crossover between chromosomes
- normal complement of chromosomal material
- unbalanced
- there is missing or additional chromosomal material
- deletions or insertions
- there is missing or additional chromosomal material
- balanced

total chromosome number is not a multiple of 23. What are the two types? discuss the compatability for life.
aneuploid
- trisomy
- abnormal (extra chromosome)
- most common:
- x
- 21
- 18
- 13
- monosomy
- abnormal (missing chromosome)
- only turner syndrome patients are viable
- 45,X
most common genetic cause of intellectual disability.
what 5 ways to generate this phenotype?
down syndrome
- 47,XY,+21 or 47,XX,+21
- 46,XX,rob(14;21),+21 or 46,XY,rob(14;21),+21
- 46,XX,i(21q21q) or 46,XY,i(21q21q)
- isochromosome
- the logn arms of two chromosome 21s join together
- 46,XX/47,XX+21 or 46,XY/47,XY,+21
- occurs during embryonic develeopment. some cells are wild type and others are downs
- partial trisomy 21
- only part of chromosome 21 is present in triplicate
- one c’some is structural unbalanced
describe the sex-specific differentiation and phenotypic sex, pertaining to gonadal development
- p arm
- tetis dependent factor: expression of the SRY GENE ON THE Y CHROMOSOME induces male gonadal development
- SRY is a transcription factor for TDF
- very close to the telomeres and homologous region where gentic information between X and Y is shared
- tetis dependent factor: expression of the SRY GENE ON THE Y CHROMOSOME induces male gonadal development
- q arm
- makes sperm and other genes

- what is increases the incidence of patau
- what are the phenotypic expressions
47,XX,+13
- incidence increases with mothers age
- phenotypic expression
- intellectual disabillities
- failure to thrive
- congenital heart problems
- sloping forehead
- cleft-lip
- polydactyly
- rocker bottom feet

describe the normal crossover and abnormal structural transnlocation between sex chromosomes. generate the genetypes and phenotypes
-
Sex reversal-
- transfer of SRY from Y to X in sperm cells can produce XX male (gain of SRY) or XY female (loss of SRY) offsprings
- loss of function mutations in SRY also produces XY female offspring
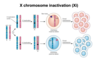
What happens if there are more than one X c’somes in the human genome?
if more than two X c’somes are present, all but one will be inactivated.
If one of the X c’somes is aberrant (substandard), it will be preferentially inactivated