Circulatory Disturbances Flashcards
(179 cards)
Ground substance of ECM consists of
Glycoproteins (Fibronectin and Laminin), Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, etc
Edema can be classified as
Inflammatory
Non-Inflammatory
Water distribution between plasma and interstitium is primarily determined by
Hydrostatic and Osmotic pressure differences between the two compartments
Thrombosis
Clot (thrombus) forms within a vessel which is not injured or only mildly injured
Endothelin released from vascular endothelium has what effect
Vasoconstriction
Coagulation Factors
Plasma proteins produced by the liver
Interstitial fluid accounts for ________% of total water weight
15%
Starling Equation
Illustrates the role of hydrostatic and osmotic forces in the movement of fluid across capillary membranes
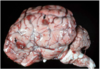
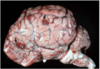
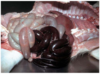
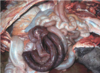
Common name for this disease

“Mulberry Heart Disease”
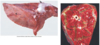
Nutmeg Liver
Appearance of the parenchyma with animal suffering from chronic hepatic congestion
Coagulation Cascade
Amplifying series of enzymatic conversions; each step proteolytically cleaves an inactive proenzyme into an activated enzyme, culminating in thrombin formation
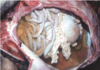
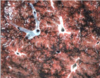
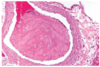
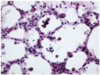
Histological appearance of what circulatory disorder

Edema
Interstitium is composed of
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Supporting Cells
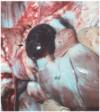
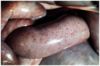
Condition

Submandibular edema
_______________________
“Bottle Jaw”
Fat Embolsim can be the result of
long bone fractures
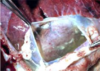
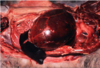
Pericardial Effusion
“Mulberry Heart Disease”
Inflammatory edema
Fibrin strands and cloudy appearance of pericardial fluid
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Reddening - Rubor
Edema - Tumor
Heat - Calor
Pain
Loss of Function
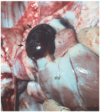
Example of what circulatory disturbance
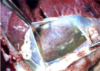
Edema
________________
Inflammatory Edema
Pathogenesis of septic shock
- Endotoxin - producing gram negative bacilli
- LPS and other microbial substances induce injury and activation of the vascular endothelium
- Stimulate WBCs to release cytokines
- Vasodilation and prothrombotic diathesis
Describe what happens during the primary hemostasis step of normal hemostasis
- Endothelial injury exposes highly thrombogenic subendothelial ECM allowing platetlets to adhere and be activated
- Activation of platelets results in a dramatic shape change and release of secretory granules lead to further platelet aggregation to form the primary hemostatic plug
- Secreted products recruit additional platelets
Hemostasis
Arrest bleeding by physiological properties of vasoconstriction and coagulation or by surgical means
Anti-coagulation factors secreted by endothelium
Prostacylin
Nitric Oxide
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
Thrombomodulin
Condition

Hydrothorax
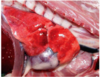
Gingivitis and blood shot eyes are an example of what circulatory disturbance
Hyperemia