Skin Flashcards
(325 cards)
Cause of pustules
Leukocyte infiltrate
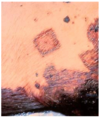
Characteristics of equine melanomas
Grey horses - lesions are usually progressive and mulicentric
Chemical Burns
Caused by body or wound secreations, application of drugs, exposure to acids, alkalies, soaps, detergents, or irritant plants
Type IV Hypersensitivity
Cell-Mediated Hypersensitivity
Manifestation = contact dermatitis, tubercular leasion and graft rejections
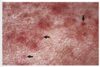
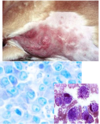
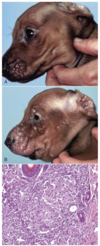
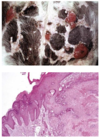
Melanoma
Dog, Horse, Angora Goat
Usually dark brown
Location, size, mitotic index, and cell morphology may help predict behavior
Suppurative/Pustular/Exudative/Neutrophilic lesions are associated with what types of disease
Bacterial
Auto-Immune
Disease and cause

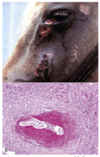
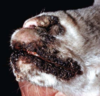
Sarcoptic Mange
Sarcoptes scabiei
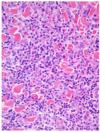
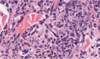
Histologic characteristics of allergic skin disease
Lymphocyte and eosinophillic dermatitis
Scale
Gross appearance of Discoid Lupus Erythematosis
Depigmentation
Erythema
Scaling
Erosion
Ulceration
Crusting
Pathological processes that could cause scale
Inflammation and Repair
Disorders of growth
MDx

Ulcerative/Exudative dermatitis
MDx

Neutrophilic dermatitis/folliculitis
Pathogenesis of sarcoptic mange
- Burrow into stratum corneum
- Intesnse pruritis through hypersensitivity mechanism
- Self trauma, chronic irritation
- Hyperkeratosis, lichenification, alopecia
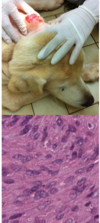
Histological appearance of acral lick dermatitis
Not really a granuloma!
Epidermal hyperplasia
Granulation tissue
Fibrosis
Disease

Collagen Dysplasia
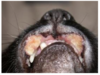
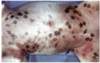
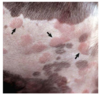
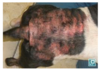
Gross appearance of insect bite hypersensitivity
Often includes papules
Disease

Zinc Responsive Dermatosis
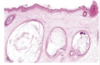
Vesicle / Bulla
Palpable elevation filled with clear fluid
Vesicle - < 1cm
Bulla - > 1cm
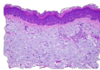
Histological appearance of callus
Epidermal hyperplasia
Calcificaion of skin
Most common forms observed int he skin are both classified as dystrophic calcification
Chalky white, gritty to hard texture
Calcinosis cutis vs Calcinosis circumscripta
Disease

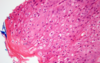
Hemangioma / Hemangiosarcoma
Hemangioma - Hemangiosarcoma
Young adult dogs
Due to solar radiation
Pox Virus Infections
Have gene product similar to epidermal growth factor → epidermal hyperplasia
Many cutaneous lesions only, some systemic and fatal