Clinical Flashcards
(617 cards)
Fragile X repeat cutoffs
normal <50,
Pre 56-200,
Path = 200 (methylated)
Fragile X premutation phenotypes
Female: Premature Ovarian Failure.
Males and females: Ataxia/Tremor
Coffin Lowry
X-linked - RPS6KA3
ID
Broad hands with tapered fingers
Frontal bossing, flat nasal bridge, downslanting PF, wide mouth
Transcription Coupled Repair disorder
Cockayne syndrome
Gene: CSA, CSB
Face: Sunken eyes RP, SNHL, ID, Intracranial calcifications, short stature, photosensitive
Think: similar to XP but no cancer + dysmorphci facies
Syndromes with nuchal translucency
>3.4mm cutoff
Turner, Down Syndrome, Noonan
Most common genes in non-syndromic HCM
MYBPC3, MYH7
Down syndrome dysmorphic features
Upslanting PF
Burshfield spots
Small ears
Short 5th digit
Sandlegap toes
epicanthal folds
Single palmar crease
Ddx: epicanthal folds
Asian descent
Down syndrome
Fetal Alcohol
Zellweger
Down Syndrome association
Endocardial cushion defect (AV canal)
Duodenal atresia
Hirschsprungs
Leukemia
Alzheimers
hypothyroidism
Marfan diagnostic criteria
GHENT criteria:
If no FHX:
root dilation + lens,
FBN1,
systemic score >7,
OR lens + FBN1
If positive FHX: lens, root, or systemic score
Homocystinuria vs Marfan
AR inheritance,
rigid joints,
strokes,
ID
Turner syndrome dysmorphic features:
Webbed neck
low hair line
low set ears
lymphedema
cubitus valgus
Madelung deformity
Noonan Dysmorphology
Downslanting PF
low set, posteriorly rotated ears with creases
Turner features (webbed neck, board chest, pectus, short, cubitus valgus)
Noonan associations
Pulmonic stenosis
HCM
Bleeding/clotting
Trisomy 18 dysmorphology
microcephaly with prominent occiput
rocker bottom feet
short sternum
thumb/radius agenesis/hypoplasia
clenched fist with overlapping fingers
horseshoe kidneys
Trisomy 13 dysmorphology
cutis aplasia
holoprosencephaly
midline cleft
polydactyly
Cutis aplasia associations
Trisomy 13
Adams Oliver
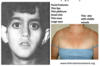
Fragile X dysmorphology
Long, triangular face
flattened nasal bridge
protruding ears
macro-orchidism
Treacher collins dysmorphology
Downslanting PF
eyelid coloboma
absent bottom eyelashes
microtia
conductive hearing loss
NORMAL intellect
22q11 Dysmorpohlogy
tubular nose with hypoplastic nares
long tapering fingers
Cleft
CDLS dysmorpology
hirsutism
Synophrys/arched eyebrows
down-turned corners of mouth
Limb reduction defects
Achondroplasia dyrmorphology/associations
Trident Hand
Macrocephaly
Frontal bossing
Mid face hypoplasia
Foramen magnum stenosis
OSA
Beckwith Wiedemann Dysmorphology
Macroglossia
umbilical hernia
ear pits/creases
hemihyperplasia
BW Syndrome Cancer risks
Wilms
hepatoblastoma
embryonal