Cornea Degeneration and Ectasia Flashcards
(71 cards)
which layer of the cornea is capable of regeneration? which ones are not?
epithelium is the only layer to undergo mitotic division (Bowman’s, stroma, Descemet’s and endothelium do not regenerate)
what are the cell junctions present in the corneal epithelium?
desmosomes and gap junctions and connect to Bowman’s layer via hemidesmosomes
what type of pumps are in the corneal endothelium and what is the purpose?
Na-K-ATPase pumps to keep the stroma from having too much fluid
what is a degneration?
a process in which normal elements of corneal tissue are converted (age-related or metabolic diseases) - can be benign or detrimental to normal function
what are 7 corneal degenerations that are non-sight threatening?
crocodile shagreen, arcus, limbal girdle of vogt, farinata, terriens marginal degeneration, moorens ulcer and amyloid
what are 2 non-sight threatening corneal degenerations that have the possibility of turning to sight threatening?
mooren’s ulcer and amyloid
what are 3 exmples of degenerations that are opacificiations and sight threatening?
salzmanns nodular, spheroidal and band keratopathy
what is crocodile shagreen?
age related, benign, common condition, easily seen with slit lamp = plaques of fibrous tissue

where is crocodile shagreen located anteriorly and posteriorly?
anterior = bowman’s layer
posterior = posterior corneal stroma and descemet’s
what are the symptoms and treatment for crocodile shagreen?
no symptoms and no treatment required
what is arcus?

lipid/cholesterol deposits in Bowman’s (not common under age 40)
why does arcus have a lucid interval between the limbus?
the lipid deposition ends at bowman’s - it has an abrupt ending
what does type 1 limble girdle of vogt look like?
has a lucid interval - deposition ends at bowman’s swiss cheese holes and sharp edges centrally early form of band keratopathy

what does type 2 limble girdle of vogt look like?
goes to limbus - elastoid degeneration of sub-epithelial collagen extensions centrally

what is farinata?
white dust-like particles, pre-descemet’s and occurs with aging (may resemble pigment dispersion syndrome)

what is the leading line of a pterygium called?
stocker line (iron line)

what is a hudson-stahli line?
occurs in the interpalpebral zone from tear stagnation (iron deposits in tear film) = typically after chronic inflammatory condition

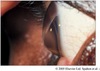
what is Terrien’s marginal degeneration?
thinning of the cornea (starts superiorly then circumferential), asymptomatic, bilateral and epithelium stays intact, fine line of lipid deposit, superficial vascularization, males >> females and 40+

what is a differential diagnosis for Terrien’s marginal degeneration?
Mooren’s ulcer
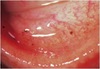
what symptoms will patients have with Mooren’s ulcer?
non-infectious (unknown etiology - autoimmune likely), painful, red, photophobia
where does Mooren’s ulcer begin?
near limbus, typically progressive (circumferentially and centrally) = thinning, stromal melting, potentially perforation (epithelium is not intact)

what is Mooren’s ulcer type 1?
typically seen in older patients, unilateral and better responses to treatment
what is Mooren’s ulcer type 2?
seen in younger (african descent) 20-30 y/o, bilateral and poor response to treatment (rare)
how do you differentiate between Mooren’s and Terrien’s?
Terriens has intact epithelium, no NaFl staining, rarely painful/inflammatory, and rarely perforates