Cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Disease Flashcards
(69 cards)
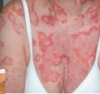
discoid LE (lupus erythematosus)
- has what other name
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- dx
- complications
= chronic cutaneous LE
- pathogenesis: UVB radiation triggers a exlusively cutaneous reaction
- demographics: AA women
- presentation:
- indurated erythematous plaques on face/neck/scalp ears with:
- scarring
- surrounding hair loss
- follicular plugging
- NO systemic sx!
- indurated erythematous plaques on face/neck/scalp ears with:
- dx: only 5% ANA positive
- complications: can progress to -> SLE

subacute cutaneous LE (SCLE)
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- dx
- complications
- pathogenesis: sun exposure triggers cutaneous disease + some internal involvement
- demographics: female caucasion
- presentation:
- polycyclic plaques on sun-exposed areas that are:
- annular with central clearing
- no scarring
- polycyclic plaques on sun-exposed areas that are:
- dx:
- 60-80% ANA
- anti-Ro/SSA (overlaps with sjogrens)
- complications: can progress to SLE

compare and contract discoid LE and SCLE in terms of
- location of lesions
- presence of scarring
- presence of systemic sx
- lab findings
- progression to SLE
- discoid LE (chronic cutaneous LE)
- localized to face / neck / scalp / ears
- heals with scarring
- no systemic sx
- lab findings: 5% ANA
- less likely to progress to SLE
- subacute cutaneous LE (SCLE)
- lesions on sun exposed areas
- NO scarring
- mild systemic sx - arthalgia/arthritis
- lab findings: 80% ANA + anti-Ro/SSA
- more likely to progress to SLE
neonatal lupus erythema
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- dx
- complications
- pathogenesis: transplacental passage of maternal anti-Ro/SSA Abs
- demographics: neonates
- presentation: similar to SCLE, but more facial involvement
- annular lesions
- periorbital erythema
- dx: anti-Ro / SSA antibodies
- complications: heart block

acute cutaneous lupus (ACLE)
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- dx
- complications
- pathogenesis:
- demographics: AA women
- presentation:
- skin: malar erythema (“butterfly rash”) + dorsal hands
- malar erythema: overal nasal bridge & bilateral malar cheeks + spares nasolabial fold
- dorsal hands: spares the knuckles
- systemic: kidney, heart
- skin: malar erythema (“butterfly rash”) + dorsal hands
- dx: ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith
- complications: can progress to SLE (more likely than DLE or SCLE)

systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- dx
- complications
- pathogenesis: autoimmune, predipsposed by complement deficiency
- demographics: AA females
- presentation: SOAP-BRAIN MD
- S - serositis (pleuritis, pericardiits)
- O - oral ulcers
- A - alopecia
- P - photosensitivity
- B - blood
- R - reynauds / acronyanosis
- A - arthritis
- I - immune: ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith
- N - neurologic
- M - malar rash
- D - discoid rash
- dx: ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith
- complications:
drug induced SLE
- m/c causes?
- dx?
- drugs
- hydralazine
- procainamide
- isoniazid
- quinidine
- dx: anti-histone positive & dsDNA negative
which variations are lupus are most / least likely to progress to lupus?
in order of most to least:
acute cutaneous lupus (ACLE) > subacute cutaneous lupus (SCLE) > discloid lupus (DLE)
summarize the lab findings for each type of lupus
- DLE (chronic): 5% ANA
- SCLE/neonatal: 80% ANA, + anti-Ro/SSA
- ACLE/SLE: 99% ANA, + anti-Sm + anti-dsDNA
- drug induced SLE: + anti-histone, - anti-dsDNA
lupus - management
- prevention: sunscreen !!
- treatment: hydrochloroquine (systemic) + topical steroids (cutaneous)
what are the variations of scleroderma?
- localized scleroderma
- morphea
- linear
- systemic scleroderma
- limited aka CREST syndrome
- diffuse aka progressive
localized scleroderma
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- treatment
- pathogenesis: CT disease characterized by excess collagen deposition in skin/organs
- demographics: female predominant
- presentation: plaques of expanding erythema -> become hairless
- morpheoa form: trunk + proximal extremities
- linear form: lower extremities (l for lower)
- “en coupe de sabre” is a linear lesion on the forehead
- treatment: steroids; if severe - METHOTREXATE
limited systemic sclerosis
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- diagnosis
- pathogenesis: excessive collagen deposition
- demographics: female predominant
- presentation: = CREST syndrome
- C = calcinosis cutis
- R = reynaud’s phenomenon
- E esophageal dysmotility
- S = sclerodactyolyl
- T = telagiectasia
- diagnosis: anti-centromere antibodies

diffuse scleroderma
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- diagnosis
- treatment
- pathogenesis: CT disorder characterized by excess collagen deposition
- demographics: female predomoinant
- presentation:
- skin:
- shiny, “leather like” skin - “loss of wrinkles”
- beaked nose
-
fingers:
- edema
- sclerodactyl
- digital pitting ulcers on tips
- systemic (more involvement than limited)
- esophageal dysfunction (m/c)
- renal & pulmonary
- skin:
- diagnosis: anti-Scl-70 (anti-topoisomerase)
- complications: bilateral basilar pulmonary fibrosis is the m/c cause of death
- treament: most important to control internal organ involvement

reynaud’s syndrome
- can present in what systemic-cutaneous disorders?
- is treated how?
- disorders
- SLE
- systemic scleroderma (limited & diffuse)
- treamtment:
- first line:
- AVOID COLD
- SMOKIN CESSATION
- next: vasodilating drugs (calcium channel blockers)
- first line:
what features do limited scleroderma and diffuse scleroderma and diffuse scleroderma share? what are their differences?
- both present with
- esophageal dysmotility
- reynaud’s
- sclerodactyl
- limited scleroderma only:
- calcinosis
- telangectiasis
- diffuse scleroderma only:
- finger edema w/ ulcers at the tip
-
significant renal & pulmonary involvement:
- m/c cause of death = bilateral pulmonary dibrosis
dermatomyositis (DM)
- pathogenesis
- demographics
- presentation
- diagnosis
- complications
- treatment
- pathogenesis: autoimmune CT disease
- demographics: biomodal distribution - juvenile, adult forms
- presentation: skin findings → muscle weakness
-
skin findings:
- grotton’s papules: lichenoid papules over IP joints including knukcles
- helitrope sign: red eyelids surrounded by white circle
- shawl sign: redness on neck
-
muscle weakness that is
- proximal
- painless
- disruptive of rising from seated position
-
skin findings:
- diagnosis:
- elevated CK (>1000)
-
antibodies
- anti-Jo L (histadyl tRNA synthetase) - specific
- Anti-Mi-2 (helicase) - if skin only, no muscle px
- treatment:
- skin only = photoprotection + topical steroids
- muscle = prednisone until CK normalizes (if skin also: add MTX & azahthioprine = steroid sparing)

what are the muscle dysfunctions seen in dermatomyotisis?
- proximal weakness
- painless
- diffuctly rising / walking up stairs
which antibodies are seen in dermatomyositis? explain.
- anti-Jo (histadyl tRNA syntase) - highly specific
- anti-Mi-2 (helicase) - in skin presentation only
how to tx dermatomyotisis with both skin & muscle presentation?
steroids (prednisone) + steroid sparing agents: MTX + azothioprine
peutz-jeghers syndrome
- pathogenesis
- presentation
- complications
- pathogenesis: STK11 mutation (tumor suppressor gene)
- presentation:
- skin: pigmented papules on oral mucosa
- systemic: harmatomatous GI polyps - esp in jejunem
- complications: increased risk of GI and non-GI malignancies

gardner syndrome
- pathogenesis
- presentation
- complication
- treatment
- pathogenesis: APC gene mutation (adenematous polypolsis coli)
- presentation:
- systemic: premalignant colon polyps by age 20 -> GI bleeding + abdominal pain
- skin: cysts:
- osteomas - in mandible
- odontogenic cysts
- epidermoid / desmoid cysts
- other: CHRPE (congenital hypertrophy fo the retinal pigment)
- complications: 100% risk of GI adenocarcinoma
- treatment: prophylactic total colectomy

what is the treatment for gardner syndrome?
prophylactic total colectomy
what two systemic-cutaneous diseases increase risk of GI malignancies?
- what mutations do they result from?
- what are their skin manifestations?
- what specific risks do they each pose?
- peutz-jegher:
- STK-11 mutation
- skin: pigemented macules on oral mucosa
- risk: inc risk of GI and NON-GI malignancies
- gardner syndrome:
- APC gene mutation
- skin: cysts - osteomas (mandible, maxilla), odontogenic cysts, epidermoid cysts
- risk: 100% chance of developing GI adenocarcinoma without total prophylactic colectomy