December 4 Flashcards
(27 cards)
Viruses
Acellular genetic element
Cannot copy itself without a host cell
Classified by whether they have DNA or RNA
Linear genome, sometimes circular
Viral Hosts
Bacterial virus (bacteriophage)
Animals
Plants (Tobacco Mosiac Virus)
Some only infect particular cells in particular organisms (HIV)
Viral Structure
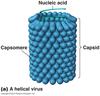
Capsid: protein covering viral genome composed of subunits called capsomeres
Viruses can also have an envelope around the capsid taken from the nuclear envelope
Enveloped virus
Have an envelope around the capsid taken from nuclear envelope or cell membrane of host

Viral Symmetry/Shape
Helical (rod shaped)
Icosahedral (20 sides)
Complex (other shapes including T4)
Helical Virus
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Icosohedral Virus
Roughly spherical viruses

Lysozymes
Make holes in cell walls common in phages
Nucleic Acid Polymerase
To replicate genome
Neuraminadases
Cleave glycosidic bonds, virus can leave host
Complex shape
Other virus shapes including the shape of T4 bacteriophage

Rabies
Broad virus, can infect most mammals
Complex shape (bullet), has no set size or shape

Animal viruses
Can grow in tissue or cell culture
Don’t need whole animal to reproduce virus
Bacteriophages
Easiest to grow
Model system for all viruses
Plant viruses
Most difficult to study
The entire plant is needed to reproduce virus
How are viruses quantified?
Plaque Assays: Analogues to bacterial colony, plaques are clear zones that develop on a lawn of bacteria, each plaque is a single virus particle
The number of plaques is usually lower than virus counts, inactive viruses
Plaque assay conditions are not always ideal

Titer
Number of infectious units per volume
Viral Replication
- Attachment
- Entry Phase
- Synthesis
- Assembly
- Release
T4 Entry Mechanism
Phage attaches via tail fibers, fibers interact with polysaccharides of outer membrane of E. coli
Lysozyme creates pore in peptidoglycan
Tail sheath contracts and inserts viral genome

Restriction modification systems
Many bacteria have restriction modification systems to help evade infection. Restriction enzymes cleave DNA at specific sequences, only effective against double-stranded DNA viruses
Attachment
The virus must first attach to a host cell (highly specific), complementary receptors on the host cell and its infecting virus, receptors on the host cell have a normal fuction (such as protein uptake), virus attaches to host cell, then it needs to get nucleic acids into the cell.
Entry Phase
Nucleocapsid (nucleic acid and capsid) or viral genome enters host cell, entry of bacteriophage T4 (E. coli virus)
Synthesis
Once a host cell has been infected, must make new copies of viral genome. First, mRNA must be generated, typically viral genome is a template for viral mRNA. In some viruses the viral RNA is the mRNA.
mRNA is either in the plus configuration, and its complement is the minus configuration
Positive RNA virus
Negative RNA virus
Retrovirus
Positive Strand RNA Virus
Single-stranded RNA genome with same orientation as mRNA


