Derm HX/PE/DX/Therapy Introduction Flashcards
(51 cards)
What are the three key factors that can be used to DX a skin condition?
1. The degree of pruritus
2. The distribution of the pruritus
3. The nature and distribution of any primary eruption.
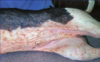
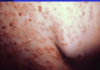
Primary skin lesions
Macule
Papule
Nodule
Plaque
Tumor
Pustule
Wheal
Vesicle
Bulla
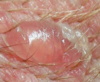
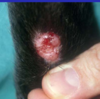
secondary skin lesions
Scale
Crust
Scar
Ulcer
Excoriation
Lichenification
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperkeratosis
Epidermal collarette
Large vesicle; an intraepidermal or subepidermal accumulation of serous fluid
bulla
Accumulation of keratin and dried sebum in a hair follicle
comedones (comedo)
Dried exudate for secretion ± epithelial or bacterial debris
crust
Inflammation of the skin.
Abnormal condition or disease of the skin
Dermatitis*
Dermatosis*
Epidermis (name the layers)
Outermost, nonvascular layer of the skin.
Made up from outward-in of 5 layers: 1) Stratum corneum, 2) S. lucidum, 3) S. granulosum, 4) S. spinosum, 5) S. basale.
Redness produced by capillary congestion
erythema
Superficial erosion or ulcer; usually implies scratching or abrasion
excoriation
Inflammation of hair follicles and associated adnexae
folliculitis
Thickening of the stratum corneum due to an increased number of keratinized cells. Maybe from increased production or decreased loss. Orthokeratosis is a form wherein in the nucleus is lost in normal fashion (vs. parakeratosis).
Hyperkeratosis
Cell of the epidermis
keratinocyte
Thickening of skin with exaggeration of normal markings. Consists of acanthosis, hyperkeratosis and dermal thickening.
Lichenification
Circumscribed, flat change in skin color. May be pale, hyperpigmented or erythematous.
macule
A large papule; a circumscribed lesion raised above the level of the epidermis. Often extends into dermis.
nodule
Circumscribed elevation of skin less than 1 cm in diameter.
papule
Raised flat‑topped lesion
plaque
Circumscribed epidermal or dermal accumulation of purulent exudate.
pustule
Purulent dermatitis
pyoderma
Flake of abnormal or compacted epithelial cells.
scale
A functional disturbance of sebaceous glands or of lipid metabolism of the epidermis. Accompanied by abnormal keratinization
seborrhea
Layer of epidermis composed of flattened cells with pyknotic nuclei and keratin granules
s. granulosum
Swelling or enlargement. Usually, but not always, neoplastic
tumor