Dermatology Flashcards
(209 cards)
3 Layers of the Skin
- Epidermis
- keratinocytes continuously produced and shed
- melanocytes- produce melanin to protect against UV rays
- langerhans- antigen presenting cells
- Merkel cells- pressure sensing cells (light touch)
- Dermis
- collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels, sensory, fibroblasts
- epidermal appendages: sebaceous glands, sweat glands, apocrine glands, mammary glands, hair follicles
- Subcutaneous tissue
- fatty layer on which the dermis and epidermis rest
Layers of the Epidermis
- Stratum corneum- dead keratinocytes
- size (thickness) depends on location
- Granular cell layer- keratinocytes produce lipids which create water barrier (lucidum) above
- Spinous layer- intercellular bridging hold keratinocytes together
- Basal layer- live cells
- melanocytes
- 28 days to migrate to stratum
Contents of the Dermis
- 2 layers
- Papillary- thin upper: unmyelinated nerve endings perceiving pain, itch, temp
- Reticular layer- thick collagen elastic fibers
- capillaries, muscles, cutaneous glands, hair follicles
- Meissner’s & Vater-Pacini corpuscles: touch and pressure
- autonomic nerve fibers- errector pili mm., blood vessels, sweat glands
Hair Follicle Anatomy
- outer root sheath- continuous with epidermis
- inner root sheath- protects and molds the growing hair
- one of the most rapidly dividing cell in the body
- hair shaft is dead protein
Dermal Gland Anatomy
- Eccrine sweat glands
- open directly to skin surface
- regulate body temp
- Apocrine sweat glands
- axilla, nipples, areolae, anogenital area, eyelids, external ears
- larger and associated with hair follicles (give off odor)
- Sebaceous glands
- surrounds and lubricates hair follicles
Contents of the Subcutaneous Tissue
- Fatty connective tissue
- thermal regulator
- protection from bony prominences
Nail Anatomy
- epidermal cells converted to hard plates of keratin
- structures:
- vascular nail bed
- lunula
- white crescent shape of proximal nail
- nail matrix- site of growth
- eponychium- cuticle
Medical Hx Items
- acute (<1wk) vs chronic (>1wk)
- fever
- systemic illness
- pain
- itching
- medications (incl self tx to relieve rash)
- malnourished (dietary issues)
- obesity (creases in skin)
- poor hygiene (skin infections or infestations)
- psychiatric illness
Physical Exam Points
- Inspection
- color
- morphology
- Palpation
- texture
- elevation
- Configuration
- Distribution
Fitzpatrick Skin Color Scale
(phototypes I-VI)
I white/freckled - always burns, does not tan
II white - burns easily, tans poorly
III beige/olive - mild burns, tans gradually
IV light brown - rarely burns, tans easily
V dark brown - very rarely burns, tans very easily
VI black - never burns, tans very easily
Lesion Color Interpretations
- erythema
- black
- blue
- brown
- gray
- purple
- white
- green
- salmon
- yellow
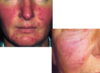
Erythema- dermatitis: any insult causing vasodilation- extra blood going to skin
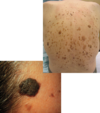
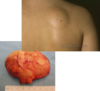
Black- necrosis (vasculitis; thrombosis; emboli; vasospasm; vascular compromise; eschar; melanoma)
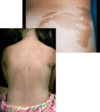
Blue- cyanosis; ecchymosis; venous congestion; Mongolian spot (dermal melanocytosis)
Brown- pigmented lesions; seborrheic keratosis; melanoma, melasma, metabolic (Addison’s disease; hemochromatosis); café-au-lait macules
Gray- drugs; silver accumulation- argyria
Purple (violaceous)- palpable and non-palpable purpura (palpable purpura- small vessel vasculitis); lichen planus
White- absences of melanocytes; vasospasm (Raynaud’s phenomenon); deposits (gouty tophi); scarring (leukoplakia)
Green- pseudomonas infection; tattoo
Salmon- pityriasis rosea
Yellow- xanthomas (accumulation of lipids/cholesterol deposits)
Morphology
(general appearance of lesions)
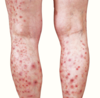
Macule- < 1 cm, flat, circumscribed; hypo or hyperpigmented; other colors- pink, red, violet (“freckle”)
Patch- flat, circumscribed; > 1 cm; hypo or hyperpigmented; other colors- pink, red, violet
Papule- elevated, circumscribed; < 1 cm; Elevation d/t increased thickness or epidermis and/or cells/deposits in the dermis
Nodule- elevated, circumscribed; > 2 cm; involves the dermis and can extend to subcutis; greatest mass below skin surface
Vesicle- elevated, circumscribed; < 1 cm; filled with clear fluid; can become pustular, umbilicated or an erosion
Bulla- elevated, circumscribed; > 1 cm; filled with clear fluid
Pustule- elevated, circumscribed; < 1 cm; filled with purulent fluid
Crust- dried serum, blood, pus (“scab”)
Scale- hyperkeratosis; accumulation of stratum corneum
Fissure- linear cleft in skin; painful; d/t drying, skin thickening, loss of elasticity
Erosion- partial loss of epidermis (superficial)
Ulceration- full-thickness loss of epithelium; can include dermis and subcutis (deeper)
Excoriation- exogenous injury to all or part of epidermis
Atrophy- thinning of the epidermis- leads to wrinkling, shiny appearance
Dermal atrophy- loss of dermal collagen leading to a depression
Lichenification- thickening of the epidermis
Palpation Descriptions
Flat- macule/patch
Smooth raised- cyst, module, papule, plaque
Surface Changes- crust/scale
Fluid-filled- vesicle, bulla, pustule
Red blanchable- erythema, erythroderma, telangiectasia
Purpuric- ecchymosis/petechiae/palpable purpura
Sunken- atropy/erosion/ulcer: Depth- epidermis, dermis, fat layer below the dermis, more than 1 layer
Necrotic- eschar/gangrene
Configuration
(arrangement of skin lesions)
- annular
- group/clustered
- linear
- scattered
- serpenginous
Distribution Descriptions
- body region
- unilateral vs bilateral
- gereralized vs localized
- symmetric vs asymmetric (dermatomal)
- discrete vs confluent

Clinical Aids and Test
- magnifying lens
- Wood’s lamp- UV long wave light
- find dermatophytosis (fungus)
- Diascopy- blanching of skin lesion with microscope slide
- erythema (blanches) vs petechiae (non-blanching)
- inspect deep layers and distinguish malignant vs benign
- Dermoscopy / Dermatoscopy (10-30x magnification)
Procedures
- skin testing
- patch- contact allergy testing
- photopatch- patch with UV radiation
- prick- determine type I allergy
- cultures
- gram stain: G+/-
- Tzanck smear: multinucleated giant cell (HSV)
- fungal cultures: KOH rapid for fungus
- biopsy
- shave: superficial thin disk of tissue (warts, skin tags, superficial BCC/SCC)
- saucerization: thick tissue disk (mid-dermis to subcutaneous fat)
- punch: core of skin to subcutaneous fat, 2-8mm diameter
- incisional/excisional: length 3x lesion, width 2x lesion
- Mohs surgery
- microscopic evaluation of tumor and excision near margins
- remove visible -> remove deeper/divide/map -> observe -> remove any CA
Topical Therapies
- soaks (good for large surface areas)
- whirlpool for debridement
- seitz bath
- wet dressings (soaked gauze)
- NO antiseptic solutions
- wet to dry dressings for wound debridement
- other:
- biological dressings w/ keratinocytes
- skin grafts
- platelet-derived growth factor
Terminology
- spongiosis
- parakeratosis
- hypergranulation
- acantholysis
- dyskeratosis
- tachyphylaxis
- id reaction/autoeczematization
- Koebner phenomenon
- Auspitz sign
- Wickham striae
- spongiosis- intercellular edema in epidermis; inflammation (eczema, psoriasis, bullous)
- parakeratosis- incomplete maturation of keratinocytes in epidermis (thin/loss granular)
- hypergranulation- increased prolif of granular cells (seen in overgrowth during healing)
- acantholysis- loss of intercellular connections, leads to development of vesicles
- dyskeratosis- abnormal development of keratinocytes below stratum granulosum
- tachyphylaxis- decreased response to meds with repeated administration
- id reaction/autoeczematization- acute rash developing distant from primary rash
- Koebner phenomenon- skin lesions appearing along trauma lines
- Auspitz sign- signs of punctate bleeding spots after psoriasis scales removed
- Wickham striae- fine white lines seen in plaques of lichen planus
Types of Dermatitis
- contact
- irritant
- allergic
- atopic
- nummular
- dyshidrotic
- seborrheic
- periorbital
- stasis

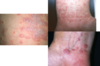
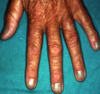
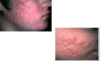
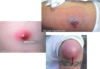
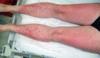
Irritant Contat Dermatitis
- reaction to exposure to toxic substance - can lead to necrosis
- Etiology
- agents, skin type, occupation
- Patho (3 main changes):
- disruption of skin barrier
- epidermal cellular changes
- cytokine relase
- cytotoxic damage to keratinocytes
- Manifestations
- acute presentation (w/in 48hr of exposure): burning, itching, stinging, pain
- physical:
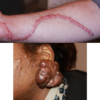
- erythema, vesicles, bulla, burns, necrosis
- sharply demarcated
- unusual configuration
- lesions at various stages
- lasts days to weeks
- Chronic presentation
- dryness, chapping, scaling, fissures (typically on hands)
- Tx:
- remove irritant
- barrier creams
- emolients (Vaseline, lanolin)- form oily layer trapping water on skin
- Ceramide creams- resore epidermal layer
- acute tx:
- wet dressings w/ Burrow’s solution: Al sulfate, acetic acid, Ca carbonate, water- astringent, antiseptic, antipyretic cools and dryes
- topical class I-II gluticosteroid preparations
- severe: oral prednisone
- topical steroids:
- hydrocortisone .5, 1, 2.5%- low potency
- clobetasol .05%- higher potency
- triamcinolone- .025, .1, .5%
- eruption: erythema and edema w/ papules or vesiles/bulla
- evolution: erosions, crusts, scaling
- chronic: papules, scaling, lichenification-excoriations

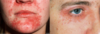
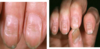
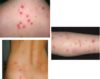
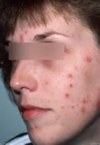
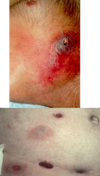
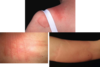
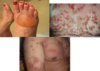
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Patho:
- sensitivity rxn after cutaneous contact - systemic T-cell mediated reaction
- can be delayed up to 2-4d
- id/autoeczematization- acute rash distant primary rash (due to immunologic stimuli)
- Etiology:
- NICKLE/metals, preservatives, topical abx, formaldehyde, pentadecylcatechols (poison ivy), latex, etc…
- Epidemiology:
- 9%, w > m
- S/s:
- INTENSE PRURITIS, pain, burning, stinging, +/-constitutional symtoms
- confined to site of exposure then spreads
- PRURITIC PAPULES, VESICLES on erythematous base
- Tests:
- patch test
- KOH test to r/o fungal infection
- Tx:
- avoid agents
- topical steroids
- clobetasol
- hydrocortisone
- systemic steroids
- prednisone taper over 1-3w: 60mg bid x 3d; 50mg bid x 3d…10mg bid x 3d
- injectable steroids for widespread
- triamcinolone
- antihistamines
- hydroxyzine 25mg po q6-8h prn pruritis (6x ben)
- benadryl 25mg po q 8h prn pruritis
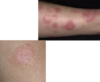
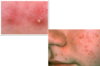
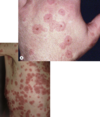
Nummular Eczema
- dry skin, “coin-shaped” lesions
- winter months
- more common in adults
- men- legs
- women- arms
- chronic pruritic round lesions
- Tx:
- skin hydration
- topical corticosteroids
- phototherapy

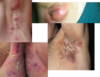
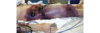
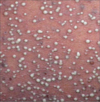
Dyshidrotic Eczyma
- pruritic, vesicular eruptions
- “tapioca” like
- bulla- pompholyx (small blisters on fingers, palms and feet)
- painful erosions/fissuring
- cause unknown
- Tx:
- high potency topical corticosteroids
- +/- oral steroids