MSK Flashcards
(218 cards)
1
Q
Bone Cell Types
A
- osteoprogenitor cells
- unspecialized that develop into osteblasts
- osteoblasts
- form new bone, role in calcification and protein synthesis
- osteoclasts
- resorbing and breaking down bony matrix
- osteocytes
- mature osteoblasts in the bony matrix
2
Q
Medical History
A
- age- problems vary by age (dislocation, overuse, etc)
- gender
- occupation/recreation
- family history (autoimmune, CA, osteoporosis)
- onset and progression of symptoms
- injury vs. “wear and tear”
- joint symptoms (stiffness, movement limitations)
- muscular symptoms
- skeletal symptoms (limb length discrepancy)
- joint pattern (how many affected, symmetrical or not)
- inflammatory vs non-inflammatory
- warmth and swelling
- morining stiffness (“gel phenomenon”)
- non: worsening w/ activity
- extra-articular vs. systemic
- usually autoimmune
- lung, kidney, etc. problems
- how disabling- ADLs
3
Q
Physical Exam Components
A
- evaluate symmetrically and systematically
- inspection- deformity, swelling, erythema, asymmetry
- look at skin!
- palpation- tenderness, crepitation, warmth, synovial thickening
- ROM- active and passive, limited d/t muscle/nerve injury
- manual muscle testing- strength/resistance
- special testing
4
Q
9 Categories of MSK Disorders
A
- local and regional
- cartilage degeneration
- inflammatory synovitis
- crystalline arthropathies
- enthesopathy
- joint space disease
- osteoarticular disease
- inflammatory myopathy
- general conditions
5
Q
Local and Regional Conditions
A
- tendonitis, bursitis
- sprains- injury to ligaments
- I: partial tear, no instability
- II: partial tear, some instability
- III: complete tear
- strains- injury to muscle
- I: few torn fibers, fascia intact
- II: moderate amount of m. fibers torn, fascia intact
- III: tear all m. fibers w/ fascia intact
6
Q
- loss of articular cartilage
- formation of osteophytes
A
cartilage degeneration
- primary
- biomechanical abnormalities leading to micro-fisures in the articluar cartilage
- secondary
- infection, autoimmune
- trauma or hypermobility of joint
7
Q
- pigmented vilonodular synovitis (PVNS)
- thickening vascular swelling and infiltration of synovia
- autoimmune disease
A
inflammatory synovitis
8
Q
- monosodium urate
- calcium pyrophosphate
- hydroxyapatite
A
crystal-induced synovitis
- gout
- pseudogout
9
Q
- disorder of transition zone where tendons, ligaments and joint capsule attach
A
enthesopathy
- hallmark: spondyloarthropathies
- enthesis affected
10
Q
- microorganisms in the joint
- extremely painful
A
joint space disease
- septic arthritis
- perform joint aspiration and fluid analysis, gram stain, cultures
- hemarthrosis
- blood in joint (can occur w/ ACL tear)
11
Q
Osteoarticular Disease
A
- osteopenia
- osteoperosis
- osteonecrosis (typically w/ joint separation)
- periostitis
12
Q
- painless inflammation and weakness of proximal skeletal muscles
A
inflammatory myopathy
- increased creatine kinase (CK) levels
- abnormal electromyography (EMG)
- histological abnormalities w/ biopsy
13
Q
General Conditions
A
- polymyalgia rheumatic
- fibromyalgia
- complex regional pain syndrome
14
Q
Initial Imaging Technique
A
x-ray
- tissue densities:
- air- black or dark gray
- fat- gray (lighter than air and darker than muscle or blood)
- water (blood and soft tissue)- shades of gray
- calcium in bone- white
- metal and contrast agents- bright white
- 2 views at right angles
- compare with old or bilateral views
15
Q
X-ray Requirements
A
- Pt identification
- name, age, sex, birth date, medical record number
- location to image
- technical quality
- positioning of body part
- quality
- contrast
16
Q
- continuous x-ray imaging
- used w/ procedures
- assess joint motion
A
flouroscopy
17
Q
- used to evaluate joint soft tissue, muscle pathology, marrow structures, tumors
A
MRI
- expensive
- difficult to see bone, actually seeing fat in marrow
- T1:
- fat- bright
- water- dark
- T2:
- fat- dark
- water- bright
- blood, edema, CSF- white
18
Q
MRI with contrast
A
MRI Arthrogram
- Gadolinium conatrast injected IV or intra-articular
- helps visualize small structure damage- labral tear
- C/I
- cochlear implants, some heart valves, pacemakers, spinal implants, brain aneurysm clips, metalic fragments in eye (some joint prosthesis- some made of non-magnetic materials)
19
Q
- imaging joints not seen well with x-ray
- SI joint, vertebral bodies
- intra-articular fractures
- bony abnormalities in joint
- high radiation
- 360 degree x-ray 3-D reconstructions
A
CT scan
- contrast used to determine if mass is solid or cystic
20
Q
Other Imaging
- test to measure bone mineral density (lumbar spine and proximal femur- T score and Z score)
- measure muscle function w/ needle inserted into muscle
- stimulate sensory/motor nerve w/ electrical impulse to measure conduction
- sometimes used to evaluate disc herniation or spinal cord compression
- increased blood flow w/ radionucleotide to ID tumors, fracures
A
- DEXA scan
- electromyography test
- nerve conduction study test
- myelogram
- nuclear medicine (Bone/PET scan)
21
Q
- imaging using sound waves
- typically for prodedures- injections
A
Ultrasound
- images are grayscale
- high water = darker image (hyperechoic)
22
Q
Common Ortho Labs
- inflammation markers
- autoantibody test
- antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
- cryoglobulins
- metabolic markers
A
- inflammation:
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)- sed rate
- CBC w/ diff
- autoantibody
- Rheumatoid factor (RF)
- antibodies to anti-cyclic citrulinated proteins (anti-CCP)
- anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA)
- Abx to DNA or pospholipids
- cryoglobulins (normally done by rheumatology)
- metabolic markers
- calcium, phosphorus, Vit D 25-dihydroxy, alkaline phosphatase
23
Q
Synovial Fluid Analysis
A
- to ID cause
- septic arthritis, hemarthrosis, crystal arthritis, differentiate inflammatory vs. non-inflammatory arthritis
- r/o infection
- analyze:
- appearance (color)
- normal- clear, straw, wbc <200, PMN <25%
- noninflamm- clear, straw+, wbc 200-1000, PMN <50%
- inflamm- cloudy, yellow/green, wbc 1K-75K, PMN >50%
- septic- opaque, variable, wbc >50K, PMN >90%
- hemorrhagic- red
- volume
- wet prep
- cells, fibrin, collagen, cartilage, synovial fragments, rice bodies, crystals
- polarized light microscopy: ID crystals
- monosodium urate- gout
- calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD)- pseudog
- hydroxyapatite- osteoarthritis
- RBCs, WBCs
- gram stain (an/aerobic, fungal)
- gonococcal (most common young adults)
- G+ s. aureus, s. pyogenes, s. pneumonia
- G- enterobacterieae, pseudomonas
- fastidious hemophilus, neisseria meningitides
- crystals
- appearance (color)
24
Q
Joint Injection for Inflammation Reduction Drugs
A
Glucocorticoids
- stop production of inflammatory mediators: leukotrienes and prostaglandins
- max 3 injections per year
- increases pts blood sugar
- dexamethoasone sodium phosphate
- 1-2h onset, 12d duration
- hydrocortisone acetate
- 1-2d onset, 1-4w duration
- methylprednisone acetate (Depo-Medrol)
triamcinolone acetonide (Kenalog)
triamcinolone hexacetonide (Aristospan)
- 1-3d onset, 2-4m duration
25
Steroid Injection Contraindications
* joint infection
* overlying skin infection
* systemic bacteremia
* thrombocytopenia/bleeding disorders
* prosthetic joints
* osteonectrosis or fracture
* uncontrolled DM
* psoriatric plaques
* steroid allergy
26
Joint Injection for OA Pain
hyaluronate preparation
* hyaluronic acid is in synovial fluid- provides shock absorption
* brand names:
* Synvisc, Orhovisc, Euflexxa
* C/I
* infection
* overlying skin disease
* chicken/egg allergy
27
Complications of Corticosteroid Injections
* joint
* infection, hemorrhage, flare, steroid arthropathy (joint breakdown w/ too much steroid use)
* systemic
* facial flush
* worstening diabetic control
* supression of HPA axis
* iatrogenic Cushing syndrome
* local
* leakage along steroid tract
* atrophy of subcutaneous fat, depigmentation
* misplaced injections
* tendon rupture, nerve damage, cartilage injury, abscess
* rare
* pancreatitis
* hypersensitivity rxns
* uterine bleeding
* osteonecrosis
28
MSK Treatment Approaches
* conservative
* RICE- rest, ice, compression, elevation
* rehab
* meds
* Rx: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, pain relievers
* herbal: glucosamine and conjointin
* topical (except over surgical sites!)
* aspiration/injection
* bracing
* activity modification
* surgical
29
inflammation in subacromial space
(subacromial bursa, suprapsinatus tendon, acromion, coracoacromail ligament, biceps tendon)
* d/t overuse, repetition
* extremely common
* increases w/ age \>30
- s/s, tests, dx
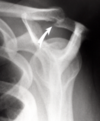
shoulder impingement
* s/s
* insidious onset or mild trauma
* deltoid/upper arm aching; dull at rest or sleeping
* rc pain referred to deltoid
* normal/near normal ROM
* full strength or mild weakness d/t inflammation
* tests
* Neer sign
* Hawkins-Kennedy sign
* x-ray (+/- bone spur), MRI (r/o tears, tendinosis)
* diagnosis: clinical
30
inflammation of long head of biceps
(frequently diagnosed w/ rotator cuff or superior labral patho)

bicipital tendinitis
* role of bicep: supination
* unknown cause
* s/s
* pain in bicep through bicipital groove
* rupture causes "Popeye muscle" deformity
* tests
* Speed's sign
* Yerganson's test
* tx
* conservative: PT, ice, subacromial/bicep injection, activity modification, NSAIDs
* surgical: arthroscopy w/ 6-8w recovery
31
impingement signs
* age \>40-45
* +/- injury
- s/s, tests, dx

rotator cuff tear
* supraspinatus muscle torn typically- cuff arthropathy: humeral head rides up superiorly
* s/s
* gradually worsening pain, NIGHT PAIN
* +/- weakness
* tests
* drop arm
* empty can
* x-ray (+/- spur, cuff arthropathy)
* MRI
* possible US
* tx
* based on size, acuity, dysfunction, activity level
* no symptoms = no tx
* conservative
* rest, ice, NSAIDs, +/- injection, PT
* NO SLING- will get frozen shoulder
* surgery
* arthroscopic or open repair
32
shoulder pain, unable to move arm, deformity
- s/s, tests, dx
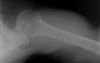
glenohumeral instability/dislocation
* s/s
* dislocation/subluxation vs. generalized- doesn't affect just the shoulder
* may be trauma or genetic (adolescent)
* may have numbness or tingling
* check axillary n. (CN XI) - feel for deltiod contraction
* ALWAYS do neurovascular check before reduction/procedure
* **Bankart Lesion**- labrum torn w/ dislocation
* tests
* x-ray pre/post reduction to check for fractures- MUST HAVE AXILLARY VIEW
* for recurrent instability
* apprehension test (anterior/posterior)
* sulcus sign (inferior)
* load and shift test (anterior/posterior)
* tx
* traction/counter traction
* Stimpson hanging arm technique
* 1st- immobilize 2-3w, PT \>4w, maybe surgery
* recurrent- arthroscopy vs. open surgery
33
common injury w/ overhead/throwing athletes, fall on outstreched arm or traction injury, increased tension on bicep tendon
- s/s, tests, dx

SLAP tear (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior)
* s/s
* pain anterior and deep
* +/- clicking
* weakness/pain w/ overhead activity
* normal ROM and strength
* tests
* O'Brien test
* Crank test
* GIRD: glenohumeral internal rotation deficit- lose ROM
* MR arthrogram (gold standard)- plain films will be normal
* tx
* grade 1-2: rest, ice, PT w/ scapular stabilizers, throwing protocol, core strengthening
* grade 3+: SLAP repair if \<30-35; tenotomy or tenodesis if \>35
34
progressively worsening pain, pain with ACROSS BODY ADDUCTION, rest of exam normal
- s/s, tests, dx

AC joint sprain/dislocation, OA/osteolysis
* sprain
* always lateral shoulder trauma (AC joint +/- CC ligs)
* tx:
* immobilize w/ sling ~2d, rest, ice, NSAIDs, PT
* surgery rare (grade 4+ only)
* OA/osteolysis
* conservative vs. open or arthroscopic excision/resection
35
pain, freezing and _loss of motion_ of arm (external rotation)
- s/s, tests, dx

adhesive capulitis
* s/s
* freezing -\> plateau -\> thawing
* trauma, immobilization, thyroid disease, diabetics, women
* adhesions and thickening of joint capsule
* tests
* x-ray to r/o other causes
* NO MRI
* tx
* conservative: rest, ice/heat, PT, GH injection, NSAIDs, pain meds
* surgery:
* manipulation under anesthesia
* arthroscopy for lysis of adhesions
36
Shoulder Joint Injections
* subacromial space
* seated w/ forearm on lap
* inject **~1cm** below posterior border of acromion
* directed medially, anteriorly, slightly superiorly 2-3cm
* glenohumeral joint
* posterior **2 fingers** medial and posterior acromion border
* directed anteriomedial toward coracoid process
* bicipital tendon sheath
* sitting or supine
* externally rotate arm and mark point of max tenderness
* insert 30-45 deg into sheath AVOIDING tendon
* AC (acromioclavicular) joint
* seated w/ forearm in lap
* superior approach insert ~.5cm
* SC (sternoclavicular) joint
* sitting or supine
* anterior approach ~0.5cm
37
compression of brachial plexus +/- subclavian vessels
- s/s, tests, dx
thoracic outlet syndrome
* s/s:
* women 20-50
* trauma or mechanical stress, conginital: cervial rib, long C7 transverse process, fibrous tissue in thoracic outlet
* vague: neck, trapezious, shoulder/arm, supraclavicular pain or aching
* parasthesia (ulnar nerve commonly)
* color changes in arm
* fatigue
* WORSENING w/ ARM OVERHEAD
* bruits
* tests
* Adson's maneuver
* elevated arm stress
* tx
* conservative
* rest, meds: NSAIDs, muscle relaxers, PT w/ postural awareness
* surgery- rare
38
Elbow Physical Exam
* inspection
* edema, deformity, ecchymosis, atrophy
* palpation
* bony landmarks
* ROM at elbow
* flexion, extension, supination, pronation
* strength testing
* special tests
39
pain w/ use and TTP over tendon origin, pain with grip strength
- s/s, tests, dx
medial/lateral epicondylitis
* s/s
* overuse injury
* +/- weakness
* lateral pain- tennis elbow (common extensor)
* medial pain- golfer's elbow (common flexor)
* tx
* conservative
* rest, ice, NSAIDs, +/- cortisone, injection bracing
* surgery (not common)
* drill holes in bone to advance healing
40
pain in medial joint line
- types, s/s, tests, dx
collateral ligament injury
* radial collateral ligament (LCL)
* rare, usually associated w/ fracture or dislocation
* ulnar collateral ligament (MCL)
* repeated valgus stress (pitching), injuries rare
* s/s
* acute- pop then medial elbow pain
* chronic- no specific injury, just progressing pain
* **ulnar paresthesia** (ring/little finger)
* pain w/ ecchymosis
* tests
* valgus stress test
* MR arthrogram
* tx
* conservative: rest, NSAIDs, PT, throwing mechanics
* surgery- "Tommy John" UCL repair
41
tender mass at tip of elbow
- s/s, tests, dx
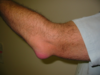
olecranon bursitis
* s/s
* acute or gradual
* direct blow, gout or crystalline deposits (gritty on palpation), infection (septic) bursitis requires surgery
* swollen, painful, sometimes red posterior elbow
* warm to touch
* remainder of exam benign
* tests
* aspirate and analyze WBC, crystals, gram stain/culture
* tx
* I&D and Abx
* NSAIDs, elbow pad, cortisone injection if no infection
* surgical excision (not common)
42
aching over medial elbow, numbness/tingling, claw hand
- s/s, tests, dx
cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar neuritis)
* s/s
* medial elbow aching
* atrophy of hand
* direct blow vs. leaning on elbows or holding flex position
* check for deformity/carrying angle
* tests
* elbow flex test
* positive Tinel's sign
* vibration and light touch perception- 2pt discrimination
* manual muscle testing
* finger abduction and adduction
* x-rays
* EMG/NCS
* tx
* conservative
* rest, avoid flexion, night extension splint
* surgery
* ulnar nerve decompression
* transposition- move nerve out of cubital tunnel
43
pain and ecchymosis in antecubital fossa, "pop",
"reverse Popeye" deformity
- s/s, tests, dx

distal bicep tendon rupture
* s/s
* pain and palpable defect in antecubutal fossa
* musce belly retracts w/ elbow flexion
* weakness w/ supination
* tests
* x-ray
* MRI
* tx
* **surgery w/in 2 weeks of injury**
* consider conservative if elderly, nondominant, partial
44
extreme swelling, pain, and inability to move elbow
- s/s, tests, dx
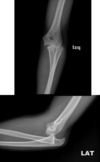
elbow dislocation
* s/s
* FOOSH
* terrible triad- dislocation w/ fracture of coronoid and radial head
* 80% posterior
* LCL always disrupted
* brachial a., median and ulnar nn. injured
* tests
* neurovascular check
* x-ray
* +/- CT scan
* tx
* reduction and splint under conscious sedation
* ROM start in 5-7d
45
Elbow Injections
* olecranon bursa
* elbow flexed, poserior 1cm distal to olecranon bursa
* 18g needle w/ 10ml syringe
* grasp bursa w/ other hand
* elbow joint
* seated w/ 45 degree elbow flex
* palpate center of lateral epicondyle, radial head, tip of olecranon triangle
* lateral epicondylitis
* seated w/ elbow flexed 90 degrees
* 1cm distal to epicondyle, point of max tenderness
* 22g needle
* medial epicondylitis
* seated w/ elbow extended 20 degrees
46
Wrist and Hand Exam
* inspection
* scars, atrophy, edema, erythema, deformity
* palpate
* bony and soft tissue
* ROM- active and passive
* especially if suspect tendon injury
* strength
* special testing
47
compression of median nerve
- s/s, tests, dx
carpal tunnel syndrome
* s/s
* female, repetition, DM, thyroid, RA, pregnancy
* 1st, 2nd, 3rd finger numbness and tingling
* worse at night
* muscle weakness- loss of grip and motor dexterity
* tests
* Tinel's sign
* Phalen's sign (\*most useful)
* 2pt discrimination loss
* muscle atrophy
* EMG and nerve conduction studies
* tx
* conservative
* NSAIDs, activity modification, bracing, injection
* surgery
* open vs endoscopic
48
swelling/stenosis in tendon sheath of snuff box
(abductor pollicis longis/extensor pollicis brevis)
-s/s, tests, dx
DeQuervain's Tenosynovitis
* s/s
* pain +/- mild edema
* tests
* Finkelstein test
* tx
* injection, +/- bracing, PT
* rarely surgical release
49
"bump" on dorsum of wrist, volar radial wrist, base of finger
- s/s, tests, dx

ganglion cyst
* s/s
* fluid leaks from joint capsule/tendon synovial sheath
* vary in size +/- pain
* transilluminate
* can compress medial nerve and radial artery
* tx
* conservative
* NSAIDs, rest, wrist splint
* aspiration- WATCH radial artery
* surgical
* if recurrent painful cyst or N/V compromise
50
finger/thumb deformity with pain, swelling, ecchymosis after injury
- s/s, tests, dx
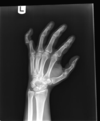
thumb/finger dislocations
* s/s
* tearing of collateral ligament/volar capsular ligament
* check for joint stability 1-2w later
* tests
* x-ray to r/o fracture
* tx
* conservative- taping
51
forced abduction of thumb
- s/s, tests, dx
gamekeeper's (skier's) thumb
* s/s
* tear of ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of MC joint
* pain, swelling, ecchymosis
* tests
* valgus stress test
* x-ray to r/o fracture
* +/- MRI if suspect rupture
* tx
* conservative vs. surgical if UCL ruptured
52
finger "feels locked" and palpable nodule with flex/extension
- s/s, tests, dx
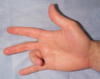
trigger finger
* s/s
* pain and catching
* thickening of flexor tendon sheath- a1 pulley
* mostly long and ring finger
* female, RA/DM
* worse after inactivity
* tx
* conservative vs. surgical
53
finger flexion weakness following injury
- s/s, tests, dx

flexor tendon injuries
flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) & digitorum sublimis (FDS)
* s/s
* "Jersey finger"- ring finger most common
* swelling, ecchymosis
* TTP at distal phalanx
* associated w/ RA/OA
* tests
* test flexion at PIP and DIP
* tx
* surgical repair
* \*\*\* DOCUMENT evaluation with every finger/hand cut \*\*\*
54
flexed PIP and hyperextended DIP
- s/s, tests, dx

boutonniere deformity
* s/s
* rupture extensor central slip
* tests
* x-ray to r/o fracture
* tx
* extension splint to PIP
* 6w if youger, 3w if older
55
blunt trauma to finger tip w/ swelling, ecchymosis, deformity
- s/s, tests, dx

mallet finger
* s/s
* rupture to extensor tendon at DIP
* tests
* x-ray to r/o fracture
* tx
* RICE
* extensor splint all times for healing
* surgery for large avulsion
56
hyperextension of PID/flexion of DIP
- s/s, tests, dx
swan neck deformity
* s/s
* weakening of volar plate
* RA/nerve disorders
* pain and swelling
* tests
* x-ray
* tx
* conservative vs. surgical

57
infection of soft tissue around fingernail
- s/s, tests, dx

paronychia
* s/s
* pain and swelling around nail
* tx
* digital block and drainage
* oral abx
* cephalexin (Keflex) 500mg po q6h 10d
* tmp/smx (Bactrim DS) 1 po q12h 10d
* clindamycin (Cleocin) 300mg 1 po q8h 10d
58
finger pulp infection
- s/s, tests, dx

felon
* s/s
* puncture wound (usually thumb or index)
* sever pain and swelling
* tense, red, swollen, very tender
* tests
* S. aureus pathogen
* tx
* digital block w/ surgical drainage
* abx: Keflex or Bactrim
59
fight bite in index, middle, ring finger
- s/s, tests, dx
septic flexor tenosynovitis
* s/s
* puncture wound
* **Kanavel's 4 cardinal signs**
1. intense pain w/ extension
2. flexion posture
3. fusiform swelling
4. tenderness along flexor tendon sheath
* tests
* CBC, ESR, sed rate
* x-ray
* tx
* call hand service
* SURGICAL EMERGENCY \*\*DO NOT MISS
* Abx
* poor prognosis- usually residual stiffness, loss of ROM
60
clear fluid filled vesicles on finger
- s/s, tests, dx

herpetic whitlow
* s/s
* pain, swelling
* tests
* herpes simples 1 or 2
* tx
* conservative- DO NOT DRAIN these
* +/- antivirals
61
Lower Extremity Physical Exam
* inspection
* LL length/alignment, deformity, muscle atrophy, pelvic obliquity, Q-angle
* Q-angle:
* female 17 deg, male 14 deg
* angle of ASIS to middle patella to mid tibia
* stresses medial side of knee + foot pronation
* gait analysis
* palpation
* bony prominences, soft tissue, joint line
* ROM
* manual muscle testing (MMT)
* special tests
62
Hip Anatomy Terminology
* ischial tuberosity
* anterior tilt- downward tilt w/ hip extension
* posterior tilt- hip flexion
* lateral tilt
* pelvic rotation w/ walking
* diarthroidal- movement in 3 planes
* hip pain- anterior to seam line of pants
* back pain- posterior to seam line of pants
* femoral neck angle
* anteversion- smaller angle than normal (foot in)
* retroversion- larger angle than normal (foot out)
* coxa vara- inclination \<125 degrees
* coxa valga- inclination \>125 degrees
63
Hip Exam Special Tests
* Trendelenburg Test/Sign
* hip drop opposite affected gluteus medius/minimus
* Thomas test
* hip flexor contracture/psoas tightness (knee to chest)
* log roll test
* pain w/ internal leg rotation- acetabular/femoral neckpathology
* FABER (Patrick) test
* flexion-abduction-external rotation (cross leg while lying)
* SI joint or hip problem
* Hamstring flexibility
* passive SLR 80 degrees
* knee extension should be 5-15 degrees of straight
64
pain and swelling of thigh, +/- ecchymosis, +/- palpable defect
- s/s, tests, dx
hip strain
* s/s
* TTP
* pain with stretching or resistance to MMT
* tx
* RICE, NSAIDs, pain relievers, PT
* surgery- avulsion injuries
65
lateral hip/thigh pain
- s/s, tests, dx
hip bursitis - trochanteric bursitis
* s/s
* most common hip bursitis
* lumbar spine OA/scoliosis, length discrepancy, trauma
* runner, female, middle age to elderly
* pain at rest and activity
* difficulty ambulating
* TTP greater trochanter
* pain w/ abduction
* tx
* RICE
* cortisone injection
* NSAIDs, pain reliever
* weight loss
* rehab: stretch/strengthen gluteus medius and IT band
66
buttock, labial/scrotal pain
- s/s, tests, dx
piriformis syndrome
* s/s
* pain w/ sitting or getting out of bed
* pain w/ hip adduction
* difficulty sitting
* absent neurological signs
* TTP SI joint, gluteal muscles, greater sciatic notch
* tests
* piriformis test
* Lasegue sign- leg lifted and straight, flex knee and cross
* x-ray, MRI, CT to r/o other causes
* EMG to differentiate btw piriformis and herniated disk
* tx
* NSAIDs, PT, +/- injection
* surgery?
67
clicking, popping, locking hip with lateral pain
"C sign"
- s/s, tests, dx
femoral acetabular impingement
* s/s
* osseous deformity of acetabular rim, femoral head/neck junction
* causes labral tear and articular cartilage microtrauma
* from overuse
* tests
* decreased flex and IR
* +FIDDIR
* x-ray (AP and lateral)
* MR arthrogram
* tx
* conservative vs. surgical
68
high trama impact to leg in seated position
- s/s, tests, dx
hip dislocation
* s/s
* obvious deformity
* tests
* check distal pulses and nerve status, knee
* x-rays (AP and lateral)
* CT if fracture suspected
* tx
* reduction ASAP
* if no fracture w/ PWB and advance as tolerated
69
pain in groin, lateral hip or buttock; worse w/ weight bearing; catching/popping sensation
- s/s, tests, dx
osteonecrosis
* s/s
* bone death- collapse of femoral head
* risks: corticosteroid use, alcohol abuse, trauma, sickle cell, RA, lupus
* Trendelenburg gait
* decreased/painful ROM
* tests
* pain w/ straight leg raise
* +log roll
* x-ray, MRI or CT
* tx
* w/out collapse
* core decompression
* vascularized fibular grafting
* w/ collapse
* arthroplasty (replacement)
70
loss of articular cartilage in hip
- s/s, tests, dx
hip osteoarthritis
* s/s
* childhood disease, trauma, osteonecrosis, infection
* anterior groin/thigh pain (worse at night)
* pain w/ activity and progresses to constant pain
* popping, catching grinding
* fixed external rotation and flexion contracture
* tests
* x-rays
* tx
* conservative
* pain control, activity modification, assistive devices
* surgery
* osteotomy
* total hip arthroplasty
71
ASIS compression
- s/s, tests, dx
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment
* s/s
* pain and dysethesia of lateral thigh
* decreased sensation but pressure or tapping over nerve increases symptoms
* no muscle or abnormal reflexes
* tests
* plain films- r/o abnormalities
* CT/MRI- r/o pelvic or abdominal masses
* tx
* weight loss, loosening tigh clothing
* meds
* cortisone injection
* surgical release of nerve rarely done
72
Knee Physical Exam Technique
* inspection
* gait, alignment, feet, discoloration, effusion, atrophy
* palpation
* quad/patellar tendon, joint line, MCL/LCL, bursa, popliteal fossa
* ROM
* knee flexion 0-130 degrees (up to 10 percent of hyperextension)
* manual muscle testing
* grading scale
* special test
73
Knee Special Tests
* apprehension test
* move patella laterally: +if pain, apprehension, quad contraction
* J sign
* excessive lateral patellar shift in terminal extension (up and out)
* McMurray's test- meniscus
* leg lifted w/ knee at 90 degree angle then...knee out/foot in to knee in/foot out
* try to catch popping or catching
* anterior drawer/Lachman's test- ACL
* ACL prevents anterior translation of tibia and posterior translation of femur
* posterior drawer/posterior sag sign- PCL
* valgus stress test- tests MCL
* knee pressed in, ankle pressed out
* varus stress test- tests LCL
* knee pressed out, ankle pressed in
74
swelling, redness, pain decreased ROM, +/- atrophy in knee
- s/s, tests, dx
bursitis
* s/s
* **pre-patellar-** inflamed (trauma related) or septic
* **pes anserine-** early medial compartment OA
* overuse, injury, break in skin
* tx
* aspirate to r/o infection
* NSAIDs, activity modification, compression
* surgery rarely to resect (normally resolves on own)

75
anterior knee pain w/ running, jumping, kicking
tendinitis
* quadriceps tendon- above patella
* patellar tendon- "jumper's knee", inferior patella
* s/s
* TTP on bony prominences/tendon
* pain w/ resisted knee extension
* full ROM
* +/- swelling
* tests
* plain films
* tx
* RICE, NSAIDs, activity modification, PT (hamstring stretches), knee strap/sleeve

76
knee effusion (giving off liquid), palpable defect, can't extend leg against gravity when seated or straight leg raise when lying
- s/s, tests, dx
tendon ruptures (quad, patella fracture, patellar)
* s/s
* fall on partially flexed knee
* pain, swelling, inability to ambulate
* discoloration
* tests
* plain films to r/o fracture
* MRI
* tx
* surgery
77
diffuse anterior knee pain, worse after long sitting, stairs, jump/squat, catching or grinding behind patella
- s/s, tests, dx
patellofemoral syndrome
* s/s
* overuse of overloading of joint
* worse w/ activities the load front of joint
* **chondromalacia**- pathologic changes of articular cartilage (softening of cartilage)
* observe alignment while weight bearing- foot pronation, femoral anteversion, genu valgum, vastus medialis oblique atrophy
* tests
* Q-angle, J sign, patellar apprehension sign
* assess hamstring tightness and quad strength- weak quads put more sheer force across patellofemoral joint
* plain films
* tx
* activity modification, NSAIDs, bracing
* PT- flexibility and strengthening
78
severe knee pain, inability to ambulate, patella lateral
- s/s, tests, dx
lateral patellofemoral instability
* s/s
* direct contact or sudden change in position
* usually spontaneously relocates
* deformity, swelling
* tests
* + apprehension sign
* TTP medial patella
* plain films
* MRI to r/o soft tissue damage
* tx
* conservative
* RICE
* +/- aspiration
* braced in extension
* NSAIDs, pain meds
* PT- quad strengthening, flexibility
* surgery
* if recurrent dislocation or conservative failure
* MPFL repair
79
intermittent pain in knee w/ catching, locking, popping, giving out that can come and go
- s/s, tests, dx
meniscus tears
* s/s
* acute w/ twisting, squatting, change in position
* swelling
* joint effusion and joint line tenderness
* decreased ROM- **EMERGENCY IF CANNOT EXTEND**
* +/- quad atrophy (quad shuts down w/ knee injury)
* +/- locked knee
* tests
* + McMurray test
* plain films- weight bearing
* MRI
* tx
* conservative
* RICE, pain control, PT
* surgery
* meniscectomy vs. meniscal repair
* inner cut out (no circulation) while outer stitched

80
excessive joint fluid tracts to popliteal bursa
- s/s, tests, dx
baker's cyst
* s/s
* most common cyst in knee
* **associated w/ degenerative meniscal tears**
* popliteal swelling/fullness and pain
* calf pain and swelling if ruptures (may think DVT)
* tests
* plain films
* MRI other pathlology suspected
* tx
* conservative
* rarely surgery for fear of transecting popliteal nerve

81
knee pain, immediate joint effusion, instability, decreased ROM, hemearthrosis - deceleration, hyperextension
- s/s, tests, dx
ACL tear
* s/s
* effusion
* decreased muscle strength
* antalgic gait
* +/- "pop"
* tests
* +Lachman's exam
* pivot shift test
* anterior drawer
* plain films, MRI
* tx
* RICE, ROM
* surgical reconstruction if younger, active (need full ROM before surgery)
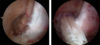
82
force to anterior tibia w/ flexed knee
- s/s, tests, dx
PCL tear
* s/s
* pain, joint effusion, +/- instability
* decreased ROM
* tests
* + posterior drawer test
* posterior sag
* x-ray/MRI
* tx
* depends upon degree of instability
83
valgus or varus grade I / II / III
evaluated and 0 and 30 degrees extension (more play at 30 deg)
- s/s, tests, dx
collateral ligament sprain
* s/s
* pain, swelling, stiffness, +/- instability or mechanical symptoms
* TTP over ligament/attachment
* tests
* plain films, MRI
* tx
* MCL- conservative if isolated or grade 1-3
* LCL- conservative grade 1-2, surgical grade 3
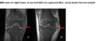
84
pain, mechanical symptoms, creptius in knee, +/- effusion
- s/s, tests, dx
chondral/osteochondral defect (OCD)
* s/s
* direct trauma, articular cartilage injuries
* tests
* plain films to check for loose bodies, MRI
* tx
* conservative
* surgical
* microfracture- punch holes in bone
* OATS- punches of outer articular cartilage place on points of greater weigth bearing
* autologous chondrocyte implantation
85
Foot and Ankle Exam
* inspection
* gait analysis, hindfoot analysis
* palpation
* anterior joint line, malleoli, sinus tarsi, achilles tendon, metatarsals, peroneal tendons, posterior tibial tendon
* ROM
* manual muscle testing
* special tests
* anterior drawer test
* draw foot anteriorly
* Thompson test
* feet hanging off bed, calf squeezed, foot should move if achilles intact, torn if no movement
* inversion stress test
* foot inverted while holding ankle
* eversion stress test
* foot everted while holding ankle
* interdigitation neuroma test
* foot squeeze test
* web space compression tenderness test
86
pain, swelling, ecchymosis in ankle w/ inversion or eversion
- s/s, tests, dx
ankel sprain
* s/s
* inversion: anterior/posterior talofibular lig, calcaneofibular lig, tibiofubular lig, subtalar lig
* eversion: deltoid lig
* TTP
* **palpate/assess 5th MT ALWAYS**- don't miss Jones fx
* **palpate/assess achilles tendon ALWAYS**
* tests
* anterior drawer
* squeeze test
* external rotation test
* x-ray, MRI, MR arthrogram (looking for uniformity around talus)
* tx
* goal: prevent chronic instability and pain
* conservative- rehab
* surgical- rare
87
sudden/severe pain near heel, "someone kicked me in the ankle"
- s/s, tests, dx
achilles tendon rupture
* s/s
* swelling, ecchymosis, difficulty ambulating
* **palpable tendon defect**
* tests
* Thompson's test (most reliable w/in 48 hrs)
* plain films, ?MRI
* tx
* non-surgical: serial casting
* surgical
* tendon retraction- based on activity level, age, risk

88
vague paresthesis of plantar foot, compression of tibial nerve
- s/s, tests, dx
tarsal tunnel syndrome
* s/s
* worse after walking/exercise
* relieved w/ rest
* night pain
* TTP over tarsal tunnel (posterior to medial malleolus)
* decreased sensation
* tests
* + Tinel sign
* plain films
* MRI to r/o other patho/space occupying lesions
* EMG/NCS not accurate at ankle and below
* tx
* conservative
* injection, orthotics
* surgical- poor outcomes
89
insideous onset heel/foot pain w/ worse "start up pain"
- s/s, tests, dx
plantar fasciitis
* s/s
* increased pain w/ standing and walking
* TTP medial calcaneal tuberosity
* toe dorsiflexion increases pain
* tests
* plain films
* entheseophyte- heel spur (but not source of pain)
* tx
* conservative
* orthotics, night splint, PT, NSAIDs, injections, acupuncture
* rarely surgical
90
posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
- s/s, tests, dx
pes planus - flat foot
* s/s
* classic presentation- mid 50, female, overweight
* RF: corticosteroid injections, DM, HTN, prev foot injuries
* insidious onset pain and swelling in media ankle
* ankle rolls and lost arch
* sinus tarsi pain
* hindfoot valgus- **"too many toes"**
* unable to toe raise
* tests
* plain films, ?MRI - thickening of tendon
* tx
* conservative
* casting, orthotics, PT
* surgical
* tendon transfer / osteotomy

91
forefoot pain
- s/s, tests, dx
metatarsalgia
* s/s
* abnormal metatarsal lengths, toe deformities: claw/hammer
* pain w/ activity
* callus formation- intractable plantar keratosis
* pain, swelling, MTP joint stability
* digital nerve function
* ddx
* plantar wart: anywhere on sole, punctate hemorrhage, fibrillated texture
* tests
* plain films
* tx
* conservative
* metatarsal pad, removal of callus, orthotics, PT, shoe wear
* surgical
* realign toes and/or metatarsal heads

92
perineural fibrosis of common digital nerve
- s/s, tests, dx
interdigital (Morton) neuroma
* s/s
* 3rd-4th toe webspace
* plantar forefoot pain
* dysesthesias of 2 affected toes
* rarely at night
* "feels like walking on marble"
* tests
* + squeeze test
* assess MTs
* sensory exam (ANYTIME a nerve is involved)
* plain films, MRI/US to r/o other causes
* tx
* conservative
* metatarsal pad, shoe change, corticosteroid injection
* surgical
* excision

93
lateral deviation of great toe at MTP joint
- s/s, tests, dx
hallux valgus ("bunion")
* s/s
* pain, swelling, numbness or tingling
* tests
* plain films
* tx
* conservative
* shoe wear, orthotics, PT- biomechanical evaluation
* surgery

94
1st MTP joint sprain
- s/s, tests, dx
turf toe
* s/s
* pain, swelling, ecchymosis
* +/- ligamentous
* common in athletes
* hyperextension of MTP
* tests
* plain films
* MRI to r/o other causes
* tx
* conservative
* orthotic devices, stiff soled shoes
* surgical (rare)
* only if displaced intra-articular or avulsion fracture
95
Toe Deformities
* hammer toe
* PIP flexion deformity (no DIP or MTP deformities)
* claw toe
* MTP extension w/ PIP flexion
* mallet toe
* DIP flextion
* s/s
* swelling, pain, deformity, shoe calluses
* tests
* evaluate sensory and motor of lower extremity
* tx
* conservative
* shoe wear, splints
* surgical
* fix deformities
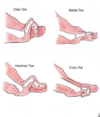
96
brachial plexus innervations
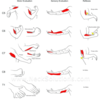
97
lumbar plexus innervations

100
cervical spine test
spurling test
* narrows neural foramen
* increases/reproduces redicular symptoms
101
* pain
* base of skull to thoracic region
* SCM / trapezious muscles
* \< ROM
* headache
* sleep disturbances
* fatigue
* difficulty concentrating
* +/- radicular symptoms
* pain, numbness, tingling
cervical sprain / strain
* PE
* +/- swelling, tenderness, limited ROM
* neurologic exam usually normal
* tests
* x-rays
* Tx
* meds: NSAIDs, pain meds, muscle relaxers, steroids
* +/- cervical collar or neck roll
* massage, stretching, PT
* DISCUSS tx options (time off, rest, ice/heat, chiro)
* self limited (4-6w)
* whiplash (6-12m)

102
lumbar spine tests
* straight-leg raise
* check for herniated disk
* pain w/ lifting **asymtomatic** leg
* seated straight leg raise
* creates sciatic tension
* patient will lean back to reduce pain (+)
* __FABER test
* flexion-abduction-external rotation (figure 4 postion)
* hip and SI joint pathology
103
tests for "non-organic" pain
Waddell signs
* non-organic tenderness
* axial simulation/torso rotation
* seated straight-leg raise
* sensory examination
104
neural foramen narrowing, disc herniation, bone spur
* limited mobility
* chronic neck pain - worse w/ upright activity
* paraspinous muscle spasm
* headaches
* radicular symptoms
* interference w/ ADLs
* myelopathy symptoms
PE, tests, Tx
cervical spondylosis
* PE
* tenderness, decreased ROM w/ pain, gait/sensory analysis
* tests
* Spurling, Babinski, Brudzinski-Kernig, ankle clonus
* x-ray, MRI, CT myelogram
* Tx
* degeneration will continue w/ time
* conservative vs. surgical
* decompression and fusion

105
* LBP
* radicular pain to buttocks/posterior thigh
* difficulty ambulating, sleeping, finding comfortable position
* **bowel or bladder dysfunction** (S2-S4)
* **saddle anesthesia**
* **weakness in lower exremeties**
PE, tests, Tx
cauda equina syndrome
(compression of n. roots distal to conus medullaris)
* PE
* **unable to heel toe walk**
* anal sphincter tone
* tests
* MRI, CT myelogram
* Tx
* IMMEDIATE decompression surgery

107
neurogenic pain in nerve roots
* +/- associated numbness, weakness, loss of reflexes
* neck and radiating pain w/ numbness and tingling
* muscle spasms
* muscle weakness
* headaches
* **relief when hand raised over head**
cervical rediculopathy
* can be caused by disc herniation or degenerative changes
108
* abrupt vs. insidious
* LBP w/ unilateral radicular leg pain
* exacerbated w/ walking, sitting, standing, coughing
* radiates **from buttocks to foot** or follows dermatome to **anterior aspect of thigh not past knee**
PE, tests, Tx
lumbar herniated disk
* PE
* list/trunk shift
* **sciatica**
* + seated asymptomatic leg raise (specific to herniated disk)
* tests
* plain films - degenerative changes
* MRI if neurologic changes/intolerable pain
* Tx
* conservative
* NSAIDs, rest, PT
* epidural steroid injections
* manipulative therapy, traction, acupuncture
* surgical
* microdiscectomy, laminectomy

109
neurological deficit d/t compression of spinal cord
* gradual onset
* long-tract signs
* **palmar** parathesia
* decreased **finger dexterity**
* subtle **gait** disturbances
* abnormal **urinary** function
* **lack of pain**
* loss of **vibration/position** sense
tests, PE, Tx
myelopathy
* tests
* Babinski sign
* Brudzinski-Kernig test (head lift - leg lift/abduct)
* ankle clonus (foot dorsiflex)
* x-ray, MRI, CT myelogram, EMG/NCS (neuropathy vs compression)
* PE
* TTP, decreased ROM, decreased lordosis, +/- Spurling
* **shoulder pain does not radiate past elbow** (cervical)
* Tx
* delayed leads to paralysis, weakness, chronic pain
* conservative
* spontaneous resolution in 2-8w
* NSAIDs
* cervical traction
* **NO SPINAL MANIPULATION** (no chiropractor)
112
general low back or SI joint tenderness
* **doesn't radiate past the knee**
PE, tests, Tx
lumbar sprain/strain
* PE
* decreased ROM, motor/sensory exam (L4-S1), special tests to r/o other structures
* tests
* +/- plain films
* MRI not indicated
* Tx
* conservative
* pain control, PT/HEP, pt education
* provide options for shared decision
* get them back to work
113
LBP \> 90 days (3m)
* LBP radiating to 1 or both buttocks
* worse w/ bending, lifting, stooping, twisting
* stiffness
* intermittent pain down leg
* relief w/ lying
PE, tests, Tx
chronic low back pain
* PE
* TTP lumbar and/or SI joint, decreased ROM, normal motor/sensory exam, positive SLR
* tests
* plain films (look for degenerative changes)
* MRI (evaluate structural changes)
* Tx
* pt education
* pain management (watch narco abuse)
* psychological testing
* injections
* biofeedback
* cognitive/behavior conditioning
* psychotherapy
* detoxification programs
115
4 cervical vetabrae fractures
PE, tests, Tx
* Jefferson fracture / C1 burst fracture
* Hangman's fracture (C2 pedicles)
* Clay-shoveler's fracture
* C7 \> C6 \> T1
* Avulsion fracture
* PE
* MOI specific: severe neck/back pain, paraspinous muscle spasm, bony tenderness, +/- neurologic
* tests
* plain images: AP, lateral, odontoid
* Tx
* **immobilization**
* Methylprednisone 30mg/kg bolus, then 5.4mg/kg/h drip 23h
* conservative vs. surgical intervention

116
neurogenic claudication
* **fatigue and weakness from proximal to distal**
* sitting or lying relieves pain
* narrowing of lumbar spine w/ nerve root compression
* order of commonality: L3/4 -\> L4/5 -\> L2/3
PE, tests, Tx
spinal stenosis
* PE
* +/- proprioception, reflexes, urine/bowel (spincter tone rarely affected)
* tests
* **Romberg test** (balance lost w/ eyes closed)
* x-rays to T10
* MRI
* EMG/NCS
* Tx
* conservative
* pain control, PT, water therapy, body mechanics
* surgical
* quality of life
* decompression and spinal fusion
117
lumbar fracture

118
* stabbing, knife-like pain in buttocks/posterior leg(s)
* worse w/ prolonged sitting, twisting, rotating
* trauma, leg-length inequality, tight iliopsoas, scoliosis, hip OA, pregnancy
PE, tests, Tx
SI joint dysfunction
* PE
* TTP
* normal motor/sensory findings
* tests
* FABER test
* compression test (push on ASIS and rock patient)
* plain films
* CT scan
* Tx
* conservative
119
tailbone pain
* pain w/ sitting, BM, sexual intercourse
PE, tests, Tx
coccydynia
* PE
* TTP rectally
* GI/gynocological exams
* tests
* plain films
* MRI to r/o other
* Tx
* conservative
* PT, change activity, nerve block, 6m-1y recovery
* surgical
* coccygectomy
120
pars interarticularis defect / forward translation of vertebrae
* repetetive hyperextension
* back pain w/ movement
* radiculopathy
PE, tests, Tx
spondylolysis / spondylolisthesis
* PE
* loss or lordosis
* decreased strength after walking
* + SLR
* tests
* x-ray
* Tx
* conservative
* weight loss
* surgical
* stabilize defect if skeletally immature
121
lateral curvature in spine
* +/- pain
* radiculopathy (L4/5 common)
* extensor hallicis longus weakening
* getting shorter/developing hump
* cardiopulmonary decompensation rarely
PE, tests, Tx
scoliosis
* PE
* neuro exam for reflexes, motor, sensory function
* gain analysis
* tests
* full-length PA and lateral films
* EMG (radiculopathy vs. neuropathy)
* Tx
* skeletally immature
* observation, bracing (25-45 deg), fusion (\>45 deg)
* Milwaukee or Boston brace
* mature
* conservative tx, surgical if curve \>50-60 deg
122
* back pain w/ weight bearing activities relieved by rest
* pain a night
* +/- constitutional symptoms (weight loss, fever, decreased appetite, night sweats, fatigue)
PE, tests, Tx
metastatic disease
* PE
* inspect for deformity
* TTP
* neuro exam
* tests
* AP/lateral plain films
* bone scan to ID other areas of mets
* Tx
* dependent on tumor
* decompression and stabilization w/ postop radiation
124
these spinal fracture uccur mostly d/t osteoporosis/weakening
thoracic vertebral fractures
126
vertebral fracture goal, type, tx
* goal - prevent neurologic injury, restore stability/normal fx
* types
* avulsion
* compression
* fracture/dislocation
* tx
* spinal fusion
* cervical
* soft collar, Philadelphia collar, rigid orthosis, halo
* thoracic
* corset, 3-point orthosis, clamshell
* lumbar
* elastic belt, corset, rigid orthosis
127
crystal deposition disease characteristics & 2 types
* sudden onset of severe joint pain and swelling
* usually 1 joint
* crystals found in synovium, cartilage, surrounding tissue
* types
* gout - monosodium urate crystals (MSU)
* calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate crystals (CPPD)
* pseudogout - synovitis
* chondrocalcinosis - deposits in soft tissue
128
disease / 4 phases / causes
* **urate** saturation in blood/body fluids
* hypertension, metabolic syndrome, obesity
* thiazide diuretics / low dose ASA
* diet:
* high purine: organ meat, select seafood
* high-fructose corn syrup
* excessive alcohol: beer/distilled liquors
* protective:
* Vit C, coffee, cherries
hyperuricemia
* phases
1. asymptomatic (\>7mg/dL)
2. acute gouty flare
3. intercritical gout (intervals between attacks)
4. chronic tophaceous gout
* causes
* underexcretion (90%)
* kidney, HTN, obesity, lead, drugs
* overproduction
* diet, obesity, psoriasis, nicotinic acid (B3)
129
gout
s/s, test, tx
* s/s
* sudden onset, cardinal signs inflammation, +/- constitutional
* 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (Podagra), ankle, midfoot, knee
* subcutaneous tophus: fingers, wrists, ears, olecranon bursa, achilles tendon
* tests
* synovial fluid analysis: crystal **negative birefringement**
* rod-shaped crystals
* +/- serum urate level
* x-ray (r/o fracture), US to look for crystals
* Tx
* lifestyle modifications
* acute: RICE, NSAIDs, **Colchicine**, corticosteroids
* meds
* xanthine oxidase inhibitor (overproduce/underexcr)
* **Allopurinol** 100mg PO daily
* Febuxostat 40mg po daily
* increase renal excretion (underexcr)
* Probenecid 250mg po daily
* Pegloticase 8mg IV q2w (warn: anaphylaxis, $$$)
130
calcium phyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease
(CPPD crystal deposition disease)
3 types, s/s, tests, Tx
* types (more common in women, gout in men)
* pseudogout - acute synovitis
* knee most common
* chondrocalcinosis - calcification in hyaline cartilage
* asymptomatic, incidental finding
* pyrophosphate arthropathy - OA w/ CPPD
* tests
* x-ray
* synovial fluid analysis
* postitive **bifringement** (square crystals)
* Tx (if symptomatic)
* RICE, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, +/- Colchicine
131
3 Hydroxyapatite Arthropathy Diseases
* crystals in joints, tendons, ligaments, bursa
* identified w/ electron microscopy
* species of basic calcium phosphate
* pts tend to be younger
1. calicific tendinitis
* sudden shoulder pain w/out MOI
* pain-\>plateaus-\>pain when resolving-\>no pain
* tx conservative or surgical (usually resolves on own)
2. Milwaukee shoulder
* crystals destroy RC and shoulder joint
3. DISH (diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis)
* bridging in cervical spine
132
MSK infection
* superficial \> deep
* olecranon, prepatellar, infrapatellar, 1st MTP
* redness, warmth, swelling
* typically **no ROM restriction** (if joint infection, pt will not move)
PE, tests, Tx
septic bursitis
* PE
* aspirate to r/o infection
* acute: S. aureus, B hemolytic strep, psuedomonas
* chronic (think systemic): B abortus, M. tuberculosis
* tests
* x-ray to r/o other, look for foreign body
* Tx
* outpatient
* PCN or 1st gen cephalosporin
* tri/sulfa (Bactrim) if MRSA
* Clindamycin or Linezolid if PCN allergy
* inpatient
* Nafcillin, oxacillin, cefazolin IV
* Vanco, daptomycin, linezolid if MRSA
133
MSK infection
* very painful, red, swollen, hot joint (knee typical)
* decreased ROM
* +/- fever
* IV drug use (SC or SI joint), diabetes, alcohol, immuno
* UTIs / indwelling catheters
* injury
PE, tests, Tx
septic arthiritis (infection to joint)
* PE
* tests
* x-rays: ususally normal, soft tissue swelling
* radiolucent lines if prosthetic infection
* MRIs
* identify osteomyelitis
* bone scan for associated osteomyelitis
* labs
* synovial fluid analysis
* WBC \> 50,000, low glucose, high protein
* ESR & CRP
* cervical/urethral cultures if +gonococcal
* Tx
* **surgery**
* IV antibiotics (4-6w)
134
infection of the bone
PE, tests, Tx
osteomyelitis
* PE
* trauma, surgery, immuno, systemic disease
* localized bone pain
* +/- sinus tract, swelling, abscess, constitutional
* tests
* biopsy/culture of affected area (GOLD standard)
* CBC - leukocytosis
* elevated CRP/Sed rate
* plain films
* MRI - marrow changes
* CT - early cortical erosions
* bone scan (highly sensitive, low specificity)
* Tx
* debridement and excision of infected bone
* abx spacer
* IV abx
* Abx impregnated methylmethacrylate beads
135
* loss of articular cartilage (trauma, obesity)
* extra-articular organs not affected
* pain affecting sleeping
* stiffness lasting \<30 min (worse w/ inactivity)
* swelling
* joint instability
* locking and grinding
PE, tests, Tx
osteoarthritis
* PE
* joint effusion, crepitus, antalgic gait, decreased ROM, muscle atrophy
* +/- deformity
* knees: genu varum (bow) vs. valgum (knock)
* hands:
* Bourchard nodes (PIP)
* Heberden nodes (DIP)
* tests
* x-ray: joint space narrowing, osteophytes, sclerosis
* MRI: r/o other sources of pain (not routinely used in OA)
* no US
* no specific labs
* Tx
* conservative as long as possible
* RICE, bracing, corticosteroid injections
* meds
* NSAIDs, tramadol, glucosamine/chondroitin
* NO opiates
* PT
* patient education- activity, occupation, weight loss
* CAM: accupuncture, Tai Chi, supplements
* surgical
* NO arthroscopy
* joint replacement
136
autoimmune attack of synovial tissue/joints
* genetics (+ family history)
* female
* age, smoking, coffee 3+/day
PE, tests, Tx
rheumatoid arthritis
* PE
* **symmetric polyarthritis, deformities**
* **morning stiffness**
* isidious onset w/ distal joints first - **MCP, PIP** (spares DIPs, toe IPs)
* swelling, tenderness, fever, malaise, weakness
* nodules anywhere
* improves with pregnancy then flares after
* C1-C2 articulation can affect surgery
* swan-neck; boutonniere deformity; hammer toes
* **Felty's syndrome**: RA, splenomegaly, neutropenia
* tests
* Rheumatoid factor
* anti-CCP (anti-cyclic citrulinated peptide antibody)
* Tx
* lifelong - no cure, just management/remission
* NSAIDs, low-dose prednisone, steroid injections
* disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (target inflammation/antibodies)
* Sulfasalazine, hydryoxychloroquine
* Methotrexate/Leflunamide
* Cyclophosphamide
* anti-TNF drugs
* inflixamab, entanercept
* adalimumab, golimamab
* surgery - joint replacement

137
RA scoring system

138
4 phases of fracture healing
1. cellular callus
* mesenchymoid cell proliferation
2. mineralized callus
* collagen to cartilage
3. bony callus
* lamellar bone replaces mineralized callus
4. remodeling

140
fracture complications
* acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
* fat embolism to lungs
* atelectasis (partial or complete collapse of lung)
* DVT, PE
* compartment syndrome (5 P's)
* nerve/blood vessel injury
* failure of normal healing
141
5 P's of compartment syndrome
1. pain out of proportion
2. paresthesia
3. pallor
4. paralysis
5. pulselessness
142
fracture description

* bone side and name, position
* proximal, mid, distal
* line: transverse, spiral, oblique
* type of fracture
* open (no skin break) / closed (bone protruding)
* complete / incomplete
* greenstick, buckle (Torus) - "squished can"
* simple / comminuted (w/ or w/out butterfly fragment)
* angulation (bent- change in anatomical position)
* direction apex is pointing, location of distal fragment
* ex.: angulated 45 deg apex dorsal
* displacement (distance apart)
* anterior, posterior, lateral, medial
* 100% = no contact at fracture site
* other:
* distraction- amount of separation
* shortening- overriding, impacted
* # of pieces
* fragments
* joint disruption- intra-articular
* % subluxation- dislocation laterally, medially...
143
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

clavical fracture
* mechanism
* direct blow, fall on outstretched arm
* presentation
* pain, deformity, grinding at fx site, sagging shoulder
* CHECK SKIN for necrosis
* tx
* based on displacement
* conservative
* immobilize: sling, brace 4-6w
* surgery
* ORIF: open reduction w/ internal fixation
* IM nail (intermedulary)
144
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
\*what nerve affected

proximal humerus fracture
(axillary nerve)
* high energy injury: fall, MVA
* Neer classification: 2, 3, 4-part (head, shaft, greater/lesser tuberosity)
* tx
* conservative: sling 6w, passive ROM after 3w
* surgery
* ORIF
* hemiarthroplasty
145
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
\*what nerve affected

humeral shaft fracture
(radial nerve)
* mechanism: trauma, fall
* tx
* varies by severity
* malunion common
146
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
\*artery injury to watch
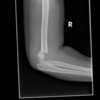
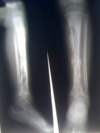
supracondylar fracture
(brachial artery)
* mechanism: fall w/ elbow extended
* tx
* surgery
147
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

epicondyle/condylar fractures
(medial/lateral condyle)
* mechanism
* fall on outstreatched arm (valgus/varus force)
* tx
* conservative
* rest, splint, delayed, ROM
* surgical
* percutaneous pinning
* ORIF
148
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

radial head/neck fracture
* mechanism
* fall w/ elbow extended
* most common elbow fx in adults
* tx
* long arm splint 2-3w (must go beyond wrist)
* rarely surgery
* DO NOT immobilize too long
* PT
149
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

olecranon fracture
* mechanism
* fall onto posterior elbow
* active tricep avulsion
* tx
* displacement & triceps guide treatment
150
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

MUGR "gruesome murder"
* Galeazzi
* radial fracture w/ distal radioulnar joint dislocation
* fall on outstreatched arm w/ elbow flexed
* surgical fixation
* Monteggia
* ulnar fracture w/ radial head dislocation
* fall on outstretched arm
* surgery
151
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
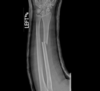
radial shaft fracture
* mechanism
* high energy injury, MVA
* usually w/ ulnar fracture/dislocation
* tx
* surgery
152
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

ulnar shaft fracture
* mechanism
* usually direct blow
* tx
* spint
* rarely surgery
153
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
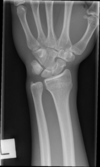
distal radius fracture
* mechanism
* **Colles**: low energy FOOSH
* **Smith**: fall on _flexed_ wristh (reverse Colles)
* most common fx of upper extremity
* presentation
* deformity, swelling, ecchymosis
* tenderness over fracture site
* tx
* buckle/minimal displacement - immobilize
* colles/smith/angulation/displacement - reduction or surgery (6w: 2 splint, 4 cast)
154
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
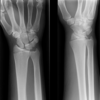
chauffeur fracture (radial styloid fracture)
* mechanism
* direct blow to back of wrist
* forced ulnar deviation and supination
* tx
* surgery
155
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

scaphoid fracture
* mechanism
* FOOSH
* often misdiagnosed as sprain
* "snuff box pain"
* most common carpal fx
* tx
* when in doubt- tx as fx: thumb SPICA splint
* splint 12w
* surgery rarely
156
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

metacarpal fracture - boxer's fracture
* mechanism
* hitting object with closed fist
* neck, shaft, or base fx
* 5th metacarpal neck most common
* presentation
* pain, swelling, **rotational deformity**, depressed knuckle
* CHECK for open wounds
* tx
* acceptable angulation: 10-20-30-40 rule from 1st digit
* rotational deformity NOT acceptable
* conservative
* ulnar gutter splint/cast
* 4-6w immobilization
* referral
* unstable fractures/rotational deformity
* closed reduction vs. surgeryd
157
1st metacarpal fractures

fracture at base of 1st metacarpal
* types:
* **Bennett** fracture: intra-articular avulsion fx - CMC joint
* sublux/dislocation
* **Rolando** fracture: "Y" or "T" shaped comminuted, intra-articular fx
* same mechanism, less commom
158
failures of healing
* malunion
* incomplete or faulty healing that affects function
* delayed union
* slower than normal healing
* non-union
* lack of bony reconstituion - bone remains at callus stage
159
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
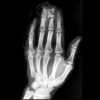
phalange fractures
* mechanism
* most common MSK injury
* presentation
* pain, swelling, deformity
* CHECK open wounds, nail bed injury - ortho referral
* tx
* budding taping
* surgery: angulation, displacement, open fracture
* complications:
* loss of motion, malunion, nonunion
160
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
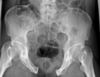
pelvic fracture
* mechanism
* high energy, MVAs
* presentation
* check for GU injuries: bladder, prostate
* fall - unable to bear weight
* leg shortened and externally rotated
* tx
* stabilize
* most need surgery
161
3 hip fracture types

1. femoral neck
* types:
* subcapital, transcervical, basicervical
* intracapsular
* blood flow to femoral head disrupted
* tx
* femoral neck w/ no/minimal displacement - pinning
* w/ displacement - arthroplasty (replacement)
2. intertrochanteric
* tx
* intramedullary nail/gamma nail
* dynamic hip screw (DHS)
3. subtrochanteric
* tx: screws
162
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

femur shaft fracture
* mechanism
* high energy, MVA
* tx
* nonsurgical
* non-displaced or multiple comorbidities
* surgical
* displaced/unstable
163
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

supracondylar fracture
* mechanism
* load to flexed knee
* presentation
* assess **popliteal artery**, ACL
* pain, swelling, inability to flex/extend knee, +/- deformity
* tx
* conservative vs. surgical
164
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

tibial plateau fracture
* mechanism
* extreme load or fall
* 60% lateral
* tx
* non-operative
* nwb w/ close follow-up
* surgery
* cannulated screw fixation or plate/screw, NWB
165
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

patella fracture
* mechanism
* direct trauma
* forceful quadriceps contraction
* presentation
* deformity, swelling, can't SLR
* tx
* non-operative:
* nwb 6w, gradually increase PROM
* surgery if displacement \>3mm
166
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

tibial shaft fracture
* mechanism
* high energy, often open, twisting mechanism
* most common long bone fracture
* presentation
* pain, deformity, wounds, fracture blisters
* **compartment syndrome** - 5 P's, fasciotomy
* assess n/v status
* tx
* conservative - LLC w/ progressive weight bearing
* surgical
* unstable, open fracture
* presentation after reduction
* IM nail
168
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

Maisonneuve fracture
* mechanism
* eversion injury - **Mortise widening**
* proximal 1/3 fibula fracture
* w/ fibular neck - think **peroneal nerve** palsy
* tx
* surgery
* ORIF
169
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

ankle fracture
* mechanism
* twisting (inversion/eversion), MVA
* most common bone + joint injury
* smoking and habitus
* presentation
* pain, swelling, deformity, inability to ambulate
* tx
* conservative
* avulsion: treat like ankle sprain
* posterior splint vs. walking cast vs. walking boot
* surgical
* if any mortise widening/suspicion
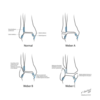
170
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

medial malleolus fracture
* mechanism
* usually high impact: MVA, fall, tackled
* considerations:
* displacement (\<2mm in joint acceptable)
* joint involvement (\<25% joint surface acceptable)
* tenderness elsewhere
* tx
* referral
* non-operative
* nwb short leg splint vs. wbat short leg cast
171
Dx, Tx
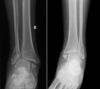
bi/tri-malleolar frature
* unstable, refer for surgery
172
3 types 5th metatarsal fractures
Stress, Jones, Avulsion
* mechanism
* IMPORTANT: sudden vs. aching over time
* inversion - Jones
* eversion - other fracture
* tx
* stress - nwb cast 6-8w
* Jones - surgery vs. short-leg walking cast vs nwb cast 6-8
* avulsion - most common, short-leg walking cast/boot 4-6

173
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx

stress fractures
* mechanism
* overuse
* presentation
* insidious pain that progressively gets worse
* MRI for inflammatory stress
* tx
* eliminate the stress - REST
* nwb 6-12w, immobilize, PT, pain control
174
Physeal Fractures Typing
| (pediatric/growth plate)
SALTER
* Type I: S- straight across
* Type II: A- above
* Type III: L- lower
* Type IV: T- through/transverse
* Type V: R- ruined (cRushed)

190
metacarpal fracture complications
* loss of grip strength
* residual dorsal deformity
* loss of knuckle prominence
199
Mechanism, Presentation, Dx, Tx
| (fibula fracture - no pic)
fibula fracture
* mechanism
* direct blow, inversion/eversion injury
* presentation
* limping or uable to bear weight due to pain, edema, ecchymosis
* tx
* non-weightbearing
* dependent on location, ankle stability
200
4 Spondyloarthopathies
share predisposing factors and clinical features
* ankylosing spondylitis
* reactive athritis
* psoriatric arthritis
* enteropathic arthritis
201
Spondylarthropathies Common Features and Tx
* spine/joint pain
* chronic inflammation -\> new bone formation (joint ankyloses)
* asymetrical peripheral arthritis
* **ocular inflammation (acute anterior uveitis**
* **HLA-B27 gene**
* **sacroiliitis in imaging**
* Tx
* pt education
* exercise
* NSAIDs, corticosteroids, sulfasalazine, methotrexate, anti-TNF therapy
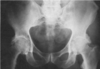
202
* most common axial skeleton inflammatory disease
* white males 15-40
* LBP \>3m: SI joint +/- buttocks
* early morning stiffness, fatigue
* asymmetrical polyarthritis
* entesitis: achilles tendinitis and/or heel pain
* ocular involvement
PE, tests, Tx

Ankylosing Spondylitis
* PE
* stooped posture (advanced)
* chest expansion
* tests
* **Schober test** - measure points on back (lumbar mobility)
* +/- FABER test (for SI joint)
* RF/ANA negative
* HLA-B27
* x-rays: "bamboo spine"
* MRI: inflammatory changes
203
* **develops 1-3w after systemic infection** (but aseptic)
* GI (salmonella, ersinia, shigella), GU (chlamydia)
* LE asymmetrical polyarthritis
* malaise, fever, fatigue
* enthesitis: achilles tendon or plantar fasciitis
* dactylitis: suasage fingers
* **Reiter's syndrome**
* conjuntivitis, urethritis/cervicitis, arthiritis ("can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree")
PE, tests, Tx

Reactive Arthritis
* PE
* mucocutaneous lesions
* papulosquamous eruptions on palms and soles
* diarrhea
* tests
* x-rays, MRI
* HLA-B27
* **synovial fluid analysis to dx septic vs. aseptic**
* Tx
* NO CURE - self limited
* NSAIDs
* +/- intra-articular injection
207
* papulosquamous disease w/ kertinocyte proliferation
* asymmetric polyarthritis in large and small joints w/ dactylitis
* DIP joints w/ nail dystrophy (pitting, oil drop stains)
PE, tests, Tx
Psoriatric Arthritis
* PE
* spondylitis - inflammation of vertabrae
* mimics RA but no nodules or RF
* tests
* x-rays
* Tx
* pain control
* anti-TNF
208
* nonerosive, assymtrical polyarthritis - large joints
* pt has Crohn's or ulcerative colitis
* inflammation of joints follow GI inflammation
PE, tests, Tx
Enteropathic Arthritis
* PE
* lower extremeties- peripheral arthritis not assoc. w/ HLA-B27
* spondylitis/sacroiliitis- assoc. w/ HLA-B27
* tests
* HLA-B27
* Tx
* control GI -\> controlled joint inflammation
209
autoimmune connective disease - thickening of skin/connetive tissue
3 cardinal processes
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
1. autoimmunity and inflammation
2. vascular injury and obliteration
* capillary loss
3. fibrosis and matrix deposition
* deposition of connective tissue matrix
210
3 Classifications of Scleroderma
* Systemic
* Diffuse
* all over, rapid progression
* swelling, erythema, pruritis, fatigue, stiffnesss, malaise, Raynaud later
* early pulmonary fibrosis and acute renal failure
* Limited
* peripheral (spares trunk)
* CREST
* Calcinosis cutis
* Raynaud's:
* primary cause: cold/stress = episodic vasoconstriction
* secondary: disease, B-blockers, chemotherapy
* Esophageal dysmotility (thickening)
* Sclerdactyly
* Telangiectasia
* Mixed Connective Tissue Disorder
* overlap of SLE, scleroderma, myositis
* Raynaud w/ hand edema, renal crisis later
* autoantibody against U1-RNP
* Localized
* more common in children
* **Morphea** - reddish/purple lesion of skin
* skin induration (hardening) spares digits, common on LE
* NO Raynaud, NO systemic involvement
211
Scleroderma Organ Involvement
* skin
* thickening, symmetrical/bilateral, starts @ fingers and works proximal, masklike facies, hyperpigmentation/vitiligo in dark skinned, calcium deposits
* GI tract
* periodontal disease; GERD; stomach-gastroparesis; small intestine-impaired mobility, malabsorption; colon-constipation, rectal prolapse
* lungs
* **honeycomb x-ray**; RF: AA, male, difuse skin, severe GERD, topoisomerase-I antibodies
* pulmonary HTN; RF: limited cutaneous, late disease onset, many telangiectasias, anticentromere autoantibodies
* kidneys
* life threatening; CKD; RF: AA, tendon rubs, RNA plymerase I & II autoantibodies
* cardiac
* diffuse disease; tachychardia; conduction abnormalities; regurgitation; diastolic HF; pericardial effusion
* MSK
* CTS; decreased joint mobility; tendon friction rubs (rupture)
* other
* dry eyes/mouth; hypothyroid; CNS spared
212
Scleroderma Tests, Dx, Tx
* tests
* labs
* CBC /w diff - anemia
* Sed rate/CRP/RA normal
* Vit deficiencies: folate, B12, D
* nailfold capillaroscopy
* Dx
* skin induration, Raynaud's, organ manifestations
* Tx
* No known regime to alter course
* immunosuppressants
* corticosteroids (sparingly in low doses)
* cyclophosphamide (slow lung disease)
* methotrexate (for skin manifestations)
* antifibrotic therapy
* D-penicillamine (prev. new organ involvement, improved survival)
* ACE inhibitors (for renal crisis)
* treat specific organ complications
213
Cells of Bone Remodeling
* osteoblasts - build
* osteoclasts - break down
* ostecytes - mature cells
* secrete and calcifies bone matrix material
* regulate bone reabsorption and formation
* release cytokines
* osteoprotogerin (OPG)
* receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand (RNAKL)
* regulate osteoclast production and rate of bone reabsorption
214
amount of bone acquired by modeling and remodeling / peak times
bone mineral density (BMD)
* peak bone mass
* 18-20 - proximal femur
* 25-30 - spine
* more loss than formation after this
215
bone physiology vs. pathology

217
primary / secondary causes of osteoporosis
* primary (idiopathic)
* juvenile (8-14 y/o)
* Stage I
* post-menopausal women (51-75)
* trabecular bone loss
* common fx: vertebral body, distal forearm
* Stage II (senile)
* men and women 70+
* trabecular and cortical bone loss
* common fx: wrist, vertebra, hip
* secondary
* men \> women
* environmental factors
* nutrition, Ca/Vit D deficiency, inactivity, meds (PPI, chemo), tobacco, alcohol, caffeine, trauma
* disease
* RA, cushings, DM, hyperthyroid
218
Who to DEXA Scan
DEXA - bone density scan
* 70+ y/o
* 50-70 postmenopausal
* 50-59 w/ wrist fracture
* 70's w/ vertebral fracture
* 50+ w/ hip fracture
219
Osteoporosis S/s, PE, tests, workup
* S/s
* NO s/s - must screen at risk
* PE
* measure height loss: \>4cm since young adult max suggests vertebral fx
* BMI
* kyphosis: **Dowager hump** (wedge shaped compression fx)
* +/- spinal TTP and percussion
* tests
* FRAX - fracture risk assessment tool: demographics, prev fx, parent fx, smoking, glucocorticoids, RA, alcohol, DEXA BMD #
* workup
* labs to assess secondary causes
* x-rays to check for fractures
* **duel energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) for bone mineral density**
* T-score: value of control peak BMD
* within 1 SD = normal
* -1.0 to -2.5 SD = osteopenia
* -2.5 SD and below = osteoporosis
* -2.5 and below + fragility fx = severe/established osteoporosis
* Z-score: value of age/sex match
* -2.0 and above = normal
* -2.0 and below = below expected
* Repeat testing
* normal - mild osteopenia: 10-15y
* moderate osteopenia: 3-5y
* advanced osteopenia: annually
* undergoing tx: annual to monitor response
* Not recommended
* premenopausal, men \< 70, women \< 65 w/out risk factors
220
Other Osteoporosis Screening Tests
* QCT-quantitiative CT (spine)
* pQCT (wrist and tibia)
* Finger DXA
* US of calcaneous or wrist
* 3D CT of bone biopsy microarchitecture
221
* softening of bone - decreased mineralization between calcified bone and osteoid
* rickets - defective mineralization of cartilage in epiphyseal growth plate
PE, tests, Tx

osteomalacia
* PE
* asymtomatic
* deformity over time
* muscle weakness
* fracture
* antalgic gait/difficulty ambulating
* tests
* Chvostek's sign: tap on facial nerve elicits twitch
* labs for underlying disorders: CMP, LFT, calcium, Vit D
* x-rays
* bone biopsy
* Tx
* Vit D replacement (\>18 6,000 IU qd or 50,000 qw x 8w, 1500-2000 qd maint.)
* patient education: dietary changes, fall risk
222
* _localized_ bone remodeling disorder:
* lytic phase: excessive reabsorption (osteoclasts)
* mixed phase: then increased bone formation of weaker, disorganized bony structure (osteoclast and osteoblast)
* sclerotic phase: disorganized bone becomes vascular, fibrous connective tissue
PE, tests, Tx

Paget Disease
* PE
* asymptomatic or specific bone pain
* increased hat size, hearing loss, tinitis (if skull)
* deformities: bowing, kyphosis, abnormal gait
* tests
* x-rays, +/- bone scan, No MRI/CT
* labs
* **alkaline phosphatase** (bone specific) - high sensitivity for diagnosis
* NOT a calcium/Vit D issue (osteoclast problem)
* urine: hydroxyproline, dexypyridinoline, C-telopeptide
* Tx
* goal: control activity, treat complications
* Bisphosphonates
* Zoledronate acid (Reclast) 5mg IV
* Alendronate (Fosamax) 40mg x 6m
* Risedronate (Actonel) 30mg qd x 2m
* neoplasm - refer for amputation, chemo
* joint disease (OA or fracture) - replacement/ORIF
223
Osteoporosis Treatment
* supplemental calcium (1000/1200 W\>50 & M\>70) and vitamin D (600/800 W/M\>70)
* Bisphosphonates
* inhibit osteoclasts to decrease turnover and bone loss
* oral
* **Alendronate** (Fosamax)
* Alendronate/cholecalciferol (Fosamax + D)
* Risedronate (Actonel)
* Iandronate (Boniva)
* Parenteral
* Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
* Ibandronate (Boniva)
* Expensive:
* Selective Estrogen REceptor Modulators (SERMs)
* decrease cytokines that activate osteopblasts - vertebral fx only
* **Raloxifene** (Evista) 60mg po qd
* Recombinant human parathyroid hormone
* **Teriparatide** (Forteo) 20mcg SQ qd (thigh or abdominal wall)
* high risk vertebral fractures, stimulates bone formation, no more than 2y, black box: osteosarcoma
* Human monoclonal antibody
* **Denosumab** (Prolia) 60mg SQ q6m
* Abx to RANKLE - inhibits osteoclast formation/activity
* Calcitrol
* nasal spray, inhibits osteoclasts
* Estrogen/progestin
* decreases bone turnover/loss
* Fracture treatment (total hip, hemiarthroplasty, vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty)
224
Bone Lesion Abbreviations
ABC, CMF, EG, GCT, FD, NOF, SBC
* ABC - aneurysmal bone cyst
* CMF - chondromyxoid fibroma
* EG - eosinophilic granuloma
* GCT - giant cell tumor
* FD - fibrous dysplasia
* NOF - non ossifying fibroma
* SBC - simple bone cyst
225
Benign vs. Malignant Lesions
benign types
benign typically have well defined borders
* bone forming (osteo-)
* osteoid osteoma, osteoblastoma, osteoma
* cartilage forming (chondro-)
* chondroma, osteochondroma, chondroblastoma
* fibrous bone lesions (fibro-)
* fibrous dysplasia, nonossifying fibroma
* radiolucent bone lesions
* giant cell tumor, unicameral bone cyst, aneurysmal bone cyst
227
* most common benign osteoid tumor
* most common in long bones - proximal femur
* most common in 2nd decade of life (10-30 y/o)
* **night pain**
* pain relieved w/ NSAIDs
tests, Tx
osteoid osteoma
* tests
* \<1cm **lytic nidus** w/ surrounding sclerosis
* HOT on bone scan, use CT to localize
* "cherry red" nidus histology
* Tx
* NSAIDs for pain
* curettage/burring
* radiofrequency ablation
228
* dnew bone depositied on skull, tibia, femur
* 2nd to 4th decade
* associated w/ Gardner's syndrome
* colonic polyps, desmoid tumors
PE, tests, Tx

osteoma
* PE
* firm mass w/ little to no pain
* tests
* xray: dense cortical bone, not contiguous w/ intramedullary canal
* Tx
* observation vs. marginal resection
229
* larger osteoid tumor (\>2cm and more aggressive)
* 1st to 3rd decades
* posterior spine, long bones (femur, tibia)
* night pain
* pain w/ activity NOT responsive to NSAIDs
tests, Tx
osteoblastoma
* tests
* x-ray: no sclerotic rim, NO **nidus**
* Tx
* biopsy
* surgical
* curettage and bone grafting
* tumor excision w/ bone reconstruction vs internal fixation
231
* **exostosis** - bony projection on surface of bone covered with cartilage
* most common benign bone tumor
* solitary or multiple (Multiple Hereditary Exostoses)
* femur (at knee), tibia, humerus
PE, tests, Tx

osteochondroma
* PE
* often asymptomatic
* pain or painful mass
* away from growth plate
* tests
* xrays
* Tx
* asymptomatic
* monitor
* symptomatic
* surgical excision
232
* tumor of hyaline cartilage **within medullary canal**
* \<5cm
* associated w/
* Ollier's disease
* Maffucci's syndrome
PE, tests, Tx
enchondroma
* PE
* asymptomatic - usually incidental finding
* pain w/ pathologic fracture
* tests
* plain films: stippled calcification
* Tx
* no tx if asymptomatic
* symptoms
* biopsy
* currettage w/ bone grafting
233
* tumor of hyaline cartilage on **surface of bone**
* usually metaphyseal (near tendon/ligament attachment)
PE, tests, Tx
periosteal chondroma
* PE
* painful, sometimes palpable mass
* tests
* xray: saucerization w/ sclerosis
* Tx
* excision
* need to r/o chondrosarcoma
234
* abnormal tissue formation in place of lamellar bone
* more common in femur
PE, tests, Tx
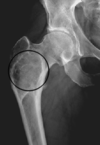
fibrous dysplasia
* PE
* pain
* tests
* xray: ground glass appearance
* Tx
* Bisphosphonates
* surgical management
* rigid fixation
236
* fluid filled cystic tumor w/ fibrous lining
* near physis and grows distally
* age 5-15 y/o
PE, tests, Tx
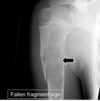
unicameral bone cyst
* PE
* incidental finding -or-
* mild pain, swelling, stiffness in joint
* sudding pain d/t pathologic fracture
* tests
* xray
* Tx
* r/o sarcoma!
* intralesional aspiration and corticosteroid injection
* surgery
* curettage w/ bone grafting
237
* aggressive **vascular lesion w/ cystic blood filled cavities**
* less frequent than GCT
* locally destructive
* d/t secondary lesion
tests, Tx
aneurysmal bone cyst
* tests
* MRI (instead of CT) to image fluid levels
* Tx
* surgery
* curettage and bone grafting

238
* most common malignant bone tumor
* common w/ other carcinomas:
* breast/prostate, lung, kidney, GI tract, thyroid

metastatic disease
239
* proliferation of interosseus plasma cells
* found in bone marrow
* more common in AA, men, 50+
PE, tests, Tx
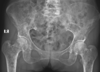
multiple myeloma
* PE
* bone pain, pathologic fractures, weakness/malaise
* neuro complaints - spinal cord compression
* tests
* plain films
* Tx
* surgical fixation of pathologic fractures
* chemotherapy
* radiation
240
* most common malignant bone tumor
* primitive mesenchymal bone forming cells produce malignant osteoid
* femur, tibia, humerus
* more common in 12-25 y/o
PE, tests, Tx
osteosarcoma
* PE
* variable: pain, swelling, night pain, no hx trauma
* palpable mass
* decreased ROM
* lymphandenopathy
* +/- respiratory mets
* primary (surface) vs. secondary (intramedulary) - variants
* tests
* labs: LDH, ALP, CBC w/ diff, CMP, urinalysis
* open biopsy
* plain xrays
* CXR to check for mets to lungs
* bone scan (evaluate metastatic disease)
* CT (location and staging)
* MRI (eval soft tissue involvement)
* Tx
* wide resection - limb sparing
* rotationplasty
* **amputation**
* chemo
241
* **cartilage** malignancy
* low grade/low mets - high grade/aggressive
PE, tests, Tx

chondrosarcoma
* PE
* **pain over time**
* night pain
* +/- mass
* symptoms near location of tumor
242
* arises from benign **cartilage lesion** (enchondroma, osteochondroma)
* pelvis, femur, humerus, ribs
tests

secondary chondrosarcoma
* tests
* plain films: scattered, irregular calcification
243
* endothelioma (internal surface) of bone
* associated w/ chromosomal translocation
* birth - 20's
PE, tests, Tx

Ewing sarcoma
(boards question - know osteo vs. ewing sarcomas)
* PE
* **progressively worse pain**
* night pain
* localized swelling/mass
* increased warmth over area, fever, incr sed rate/WBCs, anemia, malaise (mimics infection)
* tests
* plain films: destructive lesion w/ poor border, periosteal bone formation
* MRI for soft tissue involvement
* CT scan for staging
* Tx
* dependent on location and size
* chemo/radiation
* surgery
* limb sparing vs. amputation (rare)
244
* cartilage forming in epiphysis (d/t immature cartilage cell proliferation)
* ususally 2nd decade when growth plates open
PE, tests, Tx
chondroblasoma
* PE
* pain, tenderness, swelling, limp (if in LE)
* tests
* xray: well circumscribed/defined lytic lesion w/ surrounding sclerosis; +/- stippled calcification
* histology: "**chickenwire** calcification"
* Tx
* curettage (scrapping) and bone graft
* increased risk of osteoarthritis when joint involved
245
* proliferation of **fibrous tissue**
* fibrous cortical defect \<1 cm affecting **cortex** only
* children/adolescents
* **Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome** - multiple NOFs and cafe au lait spots
PE, tests, Tx
nonossifying fibroma
* PE
* asymptomatic to painful
* test
* xray: geographic, thick sclerotic rim, well circumscribed
* Tx
* usually heals spontaneously by 20's
* oberservation vs. surgical
* curettage and bone graft
247
* aggressive proliferation of benign multinucleated cells
* ages 20-50
* femur, tibia, radius
PE, tests, Tx
giant cell tumor
* PE
* pain, swelling, deformity w/ increasing size
* pathologic fractures
* **can metastasize to lung**
* tests
* xray: lucent, sometimes see bony destruction, can enter soft tissue
* Tx
* surgery
* curettage, ablation, bone grafting, fixation
248
* chronic multisymptom inflammatory autoimmune disease - autoantibodies
* frequent relapses, permanent organ damage, women of childbearing age
epidemiology, hx, systems, tests, Tx
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
* epidemiology
* unknown: genetics, environment (UV, drugs: procainamide, hydralazine, quinidine, isoniazid), viruses, diet (a.a.), hormonal
* Hx
* sunlight, hair loss, Raynaud's, FH
* systems
* fever, malaise, wt loss; skin; MSK: pain, stiffness out of proportion, non-erosive; kidneys; CNS: seizures, psychosis; cardio; GI; hematologic: anemia, thrombocytopenia; ocular
* tests
* CBC w/ diff, CMP, ESR, CRP, PT, PTT, ANA, urinalysis
* **anti-dsDNA**
* **anti-Smith**
* **anithistone** (drug induced SLE)
* plain films to r/o other
* CXR, ECG, echocardiogram to eval other systems
* Tx
* conservative vs. medicinal based on severity
* counseling/lifestyle - smoking cessation, sun, fatigue, sleep
* PT/OT
* meds
* antimalarials: hydroxycholoroquine (Plaquenil)
* NSAIDs
* corticosteroids: Prednisone (not w/ NSAIDs)
* supplement CA+Vit D if long-term
* DMARDs (immunosuppressants)
* Methotrexate (Trexall)
* Azathioprine (Imuran)
* Cyclophosphamide
* Mycophenolate
249
* autoimmune disorder **affecting exocrine glands**
* salivary and lacrimal glands
* **bilateral parotid gland swelling**
* women 40-60
* primary
* SICCA symptoms
* **keratoconjunctivitis**
* **xerostomia**
* mouth infections: dental carries, difficulty swallowing, pain, hoarseness, parotitis
* secondary
* associated w/ SLE, RA, scleroderma
etiology, systems, tests, Tx
Sjorgren's Syndrome
* etiology
* unknown: genetics, environment: viruses, hormones
* systems
* fatigue, fever; skin; pulmonary; MSK; renal; neuro: neuropathy, myelopathy; neoplasia: lymphandenopathy
* tests
* ocular/oral exams
* **Schirmer** test (strip from eye)
* Rose Bengal staining
* labs: CBC w/ diff, CMP, +RF, +ANA, +ESR
* **anti-Ro/SSA**
* **anti-La/SSB**
* Tx
* no cure - treat symptoms/systems
* fluid replacement, skin lotion, humidifiers, eye & dental exams
* rheumatology referral
250
* non-erosive inflammatory **affecting shoulders and pelvic girdle**
* typically 50+
* sudden onset muscle pain and stiffness
* morning stiffness \>45min
* **associated w/ giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis)\***
* extracranial blood vessels, can cause blindness
tests, Tx
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
* tests
* HLA-DR4
* ESR \>40, CRP, CBC w/ dif, -RF, -antiCCP, CPK
* **GCA (temporal artery biopsy) - gold standard**
* ****Tx
* Prednisone 12.5-25mg/d
* PPI to protect GI
* Ca+/Vit d
* giant cell arteritis
* Prednisone 40-60mg 4w then decrease 10mg q2w until at 20mg, then reduce by 2.5mg q2-4w to 10mg then decrease 1mg q1-2m as long as no relapse
251
* **systemic vascular syndrome that obliterates small/medium vessels**
* necrotizing inflammation occuring at bifurcations that weakens vessels (aneurysms, thrombi, hemorrhage, ischemia, infarction)
* men ages 40-60
etiology, systems, tests, Tx
Polyarteritis Nodosa
* etiology
* unknown: HBV/HCV, CECR1 gene mutation
* systems
* fever, fatigue, anorexia/weight loss, myalgia
* nervous system, cutaneous: Raynaud's, rash, purpura, **livido reticularis**; GI, renal failure, testicular tenderness
* tests
* CBC w/ diff, CRP, ESR, liver function, HBV/HCV, -RF, -ANA
* biopsy skin
* abdominal CT for ischemic/affected organs
* Tx
* refer to rheumatologist
* meds:
* Prednisone 1-2mg/kg/d
* antivirals for HBV
* tx HTN
252
* humoral **attack to muscle capillaries and small arterioles** - capillary infarctions/destruction
* abnormal T-cell activity, genetic HLA types DR3/5/7, infections, drugs (statins, interferon, quinidine)
S/s, tests, Tx

Dermatomyositis
* S/s
* **Gottron's papules**: raised scaly lesions on MCP, PIP, elbows, eyelids
* rash in V neck distribution
* arthralgias in knees, wrists, hands; fatigue, weight loss, fever; Raynaud's; GI; pulmonary; cardiac
* **proximal muscle weakness** - standing climbing, walking, lifting
* tests
* CBC, ESR, CK, AST/LDH
* +ANA (non specific)
* **anti-Mi2 & anti-MDA5** (specific)
* MRI, EMG
* **muscle biopsy** - definitive
* Tx
* non-med: high protein, exercise, consult system specialists
* skin: avoid UV, topical corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine
* oral meds:
* corticosteroids - Prednisone 1mg/kg/d 4-8w; d/c when CK level normal
* Methotrexate 7.5mg po weekly, increase as needed; take w/ folic acid
254
* T-cell mediated cytotoxic process against muscle antigens
S/s, tests, Tx
Polymyositis
* S/s
* arthralgias in knees, wrists, hands; fatigue, weight loss, fever; Raynaud's; GI; pulmonary; cardiac
* **proximal muscle weakness** - standing climbing, walking, lifting
* tests
* CBC, ESR, **elevated CK**, AST/LDH
* +ANA (non specific)
* **anti-Jo-1** (specific)
* MRI, EMG
* **muscle biopsy** - definitive
* Tx
* non-med: high protein, exercise, consult system specialists
* skin: avoid UV, topical corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine
* oral meds:
* corticosteroids - Prednisone 1mg/kg/d 4-8w; d/c when CK level normal
* Methotrexate 7.5mg po weekly, increase as needed; take w/ folic acid
255
* central sensitization - chronic widespread pain and tenderness
S/s, tests, Tx
Fibromyalgia
* S/s
* widespread pain and stiffness (neck, shoulder, low back, hips)
* fatigue, disordered sleep, cognitive function, depression, HA, IBS, TMJ, overactive bladder
* tests
* labs to r/o other diseases: CBC w/ diff, BMP, TSH, ESR, CRP, ANA, RF, CPK
* imaging for underlying pathology
* Tx
* focus on non-pharm: education, counseling, eliminate stressors, PT/OT
* meds (low dose, short term)
* acetaminophen, Tramadol 50mg q6-8h PRN
* muscle relaxers: Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) 5mg po q8h
* NO OPIOIDS
* anxiety and insomnia
* Alprazolam (Xanax)
* Zolpidem (Ambien)
* antidepressants
* Amitriptyline, Duloxetine (Cymbalta), Venlafaxine (Effexor)
* anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain
* Gabapentin (Neurontin), Pregabalin (Lyrica)
256
* pain, swelling, vasomotor dysfunction in **extremeties following trauma or surgery**
* soft tissue disorder, immobilization when pt should be getting better
S/s, tests, Tx

Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
* S/s
* pain out of proportion to event
* color changes
* skin dry, shiny, wrinkles w/ temp changes
* joint fibrosis: flexion contractures, frozen shoulder
* muscle weakness/tremors
* 3 stages: acute (3m), subacute (9m), chronic (1+y)
* tests
* no specific labs
* plain films for bone demineralization (DEXA scan)
* triple phase bone scan - increased uptake in articular structures
* Tx
* conservative
* education - screen for depression and suicide
* NSAIDs, corticosteroids
* sympathetic nerve block
* PT/OT
* surgical
* upper thoracic/lumbar sympathectomy
* chemical sympathectomy
* spinal cord stimulator implant
257
* cognitive difficulties and skeletal muscle fatigue
* myalgic encephalomyelitis
S/s, tests, Tx
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
* S/s
* sudden onset of abrupt, debilitating fatigue - impacts ADLs
* +/- flulike prodrome
* similar to fibromyalgia
* test
* r/o heart disease, thyroid, anemia, liver and renal disease, psych
* Tx
* supportive and symptomatic
258
* autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder
* multi-system: eye, skeleton, heart, aorta, lung, integument
S/s, tests, Tx
Marfan Syndrome
* S/s
* eye: lens displacement, retinal detachment; msk: ligament laxity, increased limb and finger length; mouth: arched palate, crowded detention; spontaneous pneumothorax; striae atrophy; cystic organs
* tests
* genetic testing
* opthalmic exam
* skeletal testing
* Tx
* education, tx of pathology
259
* heterogeneous disorder of connective tissue - affects structure, production or processing of collagen
* fragile tissues, joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility
S/s, tests, Tx
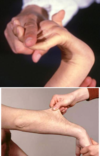
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
* S/s
* velvety skin/atrophy
* medium and large vessel rupture
* easily bruises
* organ rupture, premature rupture of fetal membranes
* Tx
* treat manifestations
* care w/ suturing
* B-blocker to protect vessels
260
* defects in bony matrix causes hereditary osteopenia
* blue sclera
S/s, tests, Tx

Osteogenesis Imperfecta
* S/s
* recurrent fx w/ bony deformity, impaired mobility
* short stature
* restrictive lung disease, compression of brain stem
* abnormal teeth
* **blue sclera**
* Tx
* fracture management
* **Risedronate** - increase bone mineral density


