Digestive System Flashcards
(70 cards)
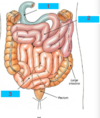
The digestive system includes…
- Oral Cavity
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
- Rectum
- Anal Canal
The oral cavity includes…
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary Glands
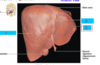
The intestinal area also include…
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
Digestive processes
- Propulsion/Motility
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Elimination
Propulsion
- Peristalsis
- Swallowing
Digestion
Mechanical
-Chewing
-Churning (stomach)
-Segmentation
Chemical
Identify 1-4
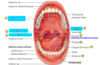
1- Hard palate
2- Palatoglossal arch
3- Palatopharyngeal arch
4- Soft palate
Identify 1-6
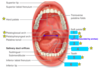
1- Uvula
2- Fauces
3- Tongue
4- Lingual frenulum
5- Gingivae
6- Vestibule
Identify 1-8

1- Vestibule
2- Gingiva
3- Hard palate
4- Palatoglossal arch
5- Soft palate
6- Uvula
7- Fauces
8- Palatopharyngeal arch
Teeth
The hardest substance in the body (made with calcium phosphate)
Contains pulp
Pulp consists of…
nerves, blood vessels and soft connective tissue
Identify 1-7

1- enamel
2- gingiva
3- dentin
4 - pulp cavity
5- root canal
6- cementum
7- periodontal ligaments
Identify 1-3

1- Crown
2- Neck
3- Root
How many teeth do children have? Adults?
20
32
1-4 bitches

1- (3) molars
2- (2) bicuspids
3- (1) cuspid
4- (2) incisors
Papillae - what are they? located where?
where taste buds are located
on tongue
Label 1-3

1- sublingual salivary gland
2- submandibular salivary gland
3- parotid salivary gland
Saliva has what in it to help with digestion?
Mucins, electrolytes, antibodies, enzymes
What enzymes are in saliva? What do they do?
Salivary amylase- begins chemical digestion of complex carbohydrates
lingual lipase- begins chemical digestion of triglcerides
1-5 :)

1- mucosa
2- submucosa
3- muscularis externa
4- serosa
5- lumen
Label the parts of the mucosa

1- epithelium
2- lamina propria
3- muscularis mucosae
1-4 (parts of the muscularis externa)

1- longitudinal
2- circular
3- longitudinal
4- circular
what are the circled things called and what layer are they in?

- glands in submucosa
- submucosa
1-4 of serosa

1- epithelium / visceral peritoneum
2- connective tissue
3- epithelium / visceral peritoneum
4- connective tissue