Earth Science Flashcards
As an inhabitant of Earth, you should probably know a thing or two about it! Maybe you forgot what Pangaea is, or what causes the tides. This deck should refresh your memory on the need-to-know Earth science topics. Special thanks to the Environmental Protection Agency, World Wildlife Federation, NASA, and National Geographic for helping us to select and comment on environmental facts and issues! (41 cards)
What supercontinent broke apart to create the continents we know today?
Pangea
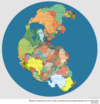
It is believed that similar fossil discoveries across continents can be attributed to Pangea’s existence. The supercontinent is believed to have broken apart around 200 million years ago.
What is the longest river in the world?
The Nile River

It is 4,258 miles long and spans 11 African countries.
What is the deepest area found in any of the world’s oceans?
The Mariana Trench
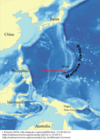
Located in the Pacific Ocean, the Mariana Trench is 6.8 miles deep.
What are the three layers of the Earth’s interior?
- Crust: The outermost layer of the Earth, this hard outer shell is made up of rock and is anywhere from a few miles to 20 miles thick.
- Mantle: The upper and lower mantle are located below the crust and are made up of solid and molten rock. The thickest of the 3 layers, the mantle is approximately 1,800 miles thick.
- Core: The core of the Earth is separated into two parts: outer and inner. The outer core is comprised mostly of liquified iron and nickel, and spans 1,400 miles. The inner core of solid, hot iron and nickel is about 750 miles in diameter.

What is an archipelago?
An archipelago is a chain of islands.

It is common for archipelagos to be volcanic. Indonesia is identified as the largest archipelagic state. Other well-known archipelagos include Japan, the Philippines, New Zealand, and the British Isles. Some well-known United States archipelagos include the Hawaiian Islands, the Outer Banks, and the Florida Keys.
- What causes a volcano to form?
- What are the three types of volcanos?
- Volcanos are caused by shifts in the Earth’s tectonic plates or hot spots that flare up underneath the Earth’s crust.
- Volcanos can be categorized in three ways:
- Active: Has erupted recently or is expected to in the future.
- Dormant: Has not erupted recently; may or may not erupt again in the future.
- Extinct: Not likely to erupt again.

What are the most common gemstones?
The most common gems include:
- diamonds
- sapphires
- rubies
- emeralds
- amethysts
What is an amber fossil?
An amber fossil is formed when an organism dies and is trapped in tree resin, which hardens and becomes amber over time, preserving the animal inside.

Organisms that would have otherwise decayed, such as early insects and plant life, have been found intact in amber fossils. Although some famous movies and real scientists helped us believe for most of the past 25 years that it may be possible to recover full DNA samples from amber fossils, it is now believed that the chances of such science are close to nil.
What large landform is comprised solely of densely packed layers of ice formed over time?
Glacier

The largest glacier in the world is Lambert Glacier. Located in East Antarctica, it spans 250 miles and is about 2,500 meters deep.
What is the tallest waterfall?
Angel Falls, located in Venezuela, is the tallest waterfall, with a height of 3,212 feet.

What is the Greenhouse Effect?
When energy from the sun hits the surface of the planet, infrared radiation is reflected back into space. Some of this energy is trapped by greenhouse gases, warming the Earth.
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are necessary for life, but elevated levels may result in overheating of the atmosphere (AKA global warming). Electricity generation and transportation are the two most common man-made sources of greenhouse gases. The most important greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide.

What landform is surrounded by water on three sides and connects to land on the remaining side?
Peninsula

Well-known peninsulas include the Arabian Peninsula, Alaska, and Cape Cod, Massachusetts.
Fill in the blank.
Any resource that is able to replenish over time is categorized as a _____ resource.
renewable
Renewable resources include wood, wind, and solar energy. Non-renewable resources include fossil fuels such as gasoline and coal, as well as minerals such as copper.
What are the major eras of the Earth and their milestones?
- Precambrian: The oldest era, 4,500 million years in length, includes the development of Earth’s oceans, early landforms, single-celled organisms, and first multi-celled organisms.
- Paleozoic: This era, 291 million years in length, brought the earliest forms of sea life, plants, insects, and eventually early reptiles and amphibians.
- Mesozoic: Also known as the Age of Reptiles, this 186 million year period included the dinosaurs, the first birds, and the first mammals.
- Cenozoic: The current era, referred to as the Age of Mammals, has spanned 66 million years thus far. Mammals and birds thrive and evolve, including the introduction of the first humans.
What is the difference between hail and sleet?
Sleet is frozen ice pellets that are generally larger than hail. While sleet occurs during winter storms, hail usually is seen during thunder storms and causes much more damage.
What is the composition of the air in Earth’s atmosphere?
- 78% nitrogen
- 21% oxygen
- 0.9% argon
- 0.03% carbon dioxide
- trace amounts of other gases including neon, helium, krypton, and xenon
Fill in the blank.
The movement of the Earth’s crust and upper mantle in large pieces is known as _____ ______.
plate tectonics
The crust and upper mantle make up tectonic plates. As these shift, so do pieces of the Earth and sea. The shifting of these tectonic plates can result in earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanic eruptions.
- What is a biome?
- What are the five major types of biomes?
- A biome is a way of classifying major ecosystems.
- Biomes are grouped by plant life and climate. There are a variety of biome classification schemes, but the five major types are:
- desert
- aquatic
- forest
- grassland
- tundra
What are the eight levels by which conservationists classify endangered species?
- Extinct
- Extinct in the Wild
- Critically Endangered
- Endangered
- Vulnerable
- Near Threatened
- Conservation Dependent
- Least Concern
What are the major layers of the atmosphere?
- Troposphere: the lowest level of the atmosphere, where weather and clouds form
- Stratosphere: the second lowest level of the atmosphere, where the ozone and highest clouds are located
- Mesosphere & Thermosphere: the upper layers of the atmosphere that merge with outer space
What are latitude and longitude lines?
Latitude and longitude are part of the coordinate system used to measure and navigate the Earth.

Lines of latitude run parallel to the equator (which divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres), tracing a circle around the Earth measuring how far north or south a location is from the equator.
Lines of longitude run vertically and measure a locations’s angle of difference from the Prime Meridian (which runs from the North to the South pole on a globe).
Both latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
What are some causes of deforestation?
Deforestation is caused by:
- commercial logging
- ranching
- agriculture
- climate change
- fires
- other forms of development
Approximately 36 football fields’ worth of forests are lost each minute worldwide.
Is there a difference between magma and lava?
Only a slight difference.
Magma refers to what is still underground, but lava is the term used for molten rock that is above ground due to a volcanic or seismic event.
Fill in the blank.
The preserved materials of a deceased organism, commonly bones and teeth, are called _____.
fossils
The biggest fossil ever discovered was the skeleton of the dinosaur titanosaur, measuring 130 feet long and 65 feet tall.


