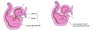Embryology Flashcards
(133 cards)
MSK:
• Mesenchyme is the same as_____ ______ _______
embryonic connective tissue
MSK:
What is mesenchyme?
a loosely organized, mainly mesodermal embryonic tissue which develops into connective and skeletal tissues, including blood and lymph.
From the mesoderm
MSK:
The mesenchymal cells migrate and differentiate into what?
into many different types of primitive cell lines
MSK:
Examples of 3 different types of primitive cell lines?
- Fibroblasts (adult connective tissue forming cells)
- Chondroblasts (cartilage forming cells)
- Osteoblasts (bone forming cells)
MSK:
What does the mesenchyme in the paraxial mesoderm do?
it will transform into osteoblasts that will form the bony elements of the vertebral column
MSK:
What does the mesenchyme in the somatopleuric mesoderm do?
will transform into osteoblasts that will form the pelvic/pectoral girdles and also the bones of the upper and lower limbs
MSK:
What is the process of bone formation known as?
Ossification
MSK:
Whw does bone start to develop?
develops during the intra uterine life through 2 types of ossification
- Membranous type (intermembranous)
- Intra cartilgainous type (endochondral)
MSK:
What is intermembranous ossifiction?
(mesenchymal tissue will directly transform into bone) eg: the flat bones of the skull
MSK:
What is endochondral ossifiction?
(mesenchymal tissue first gives rise to a hyaline cartilage model of the bone, then the osteoblasts will convert that model into bone) eg: long and irregular bones
MSK:
What is the entire muscular system of the body developed from?
mesoderm
• The entire muscular system of the body develops from the mesoderm (except from the muscles of the_____, which develop from the _______ of the optic cups)
iris
ectoderm
The cardiac muscles of the heart develop from the _________ ______ surrounding the primitive heart tube
splanchnic mesoderm
The smooth muscles of the GI tract develop from the _______ _______ surrounding the gut tube
splanchnic mesoderm
MSK:
How many pharyngeal arches are there in the human development?
5
MSK:
Each pharyngeal arch has its own:
Cartilage skeleton,
muscular component,
sensory nerve supply,
motor nerve supply
MSK:
Muscles of mastication are dervied from which pharyngeal arch?
Which nerve is the muscle innervated by?
derived from the 1st pharyngeal arch and are therefore innervated by the Trigeminal nerve (V)
MSK:
Muscles of facial expression are dervied from which pharyngeal arch?
Which nerve is the muscle innervated by?
derived from the 2nd pharyngeal arch and therefore are innervated by the Facial nerve (VII)
Uro:
What are the 3 stages in the development of the kidney:
- Pronephros
- Mesonephros
- Metanephros
Uro:
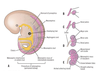
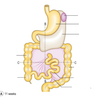
Embryology of the kidney


Uro:
Embryology of Kidney


Uro:
Embryology of Kidney


Uro:
When doe the pronephros develope?
It develops during the 4th week of uterine life in the cervical region of the intermediate mesoderm
Uro:
What does pronephros contain?
The pronephros contains lots of segmental vesicles and has the pronephric duct that grows caudally toward the cloaca
- The pronephric duct is in the embryo and thus cannot filter materials outside the embryo.
- Therefore it is said that the pronephros kidney is non-functional in humans thus it degenerates.