HARC - Foundation Flashcards
(83 cards)
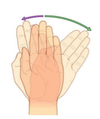
1
Q

A
orange: flexion
blue: extension
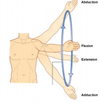
2
Q

A
aBDuction of arm C5
3
Q
A

4
Q

A

5
Q

A

6
Q
Which anatomical plane is this?

A
sagittal
7
Q
Which anatomical plane is this?

A
Coronal
8
Q
Which anatomical plane is this?

A
Axial/Horizontal/Transverse
9
Q

A

10
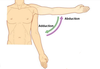
Q
What movement is this?
A
Circumduction
11
Q

A
12
Q

A

13
Q

A

14
Q

A
Flexion
15
Q

A
Extention
16
Q

A

17
Q

A

18
Q

A

19
Q

A

20
Q

A

21
Q

A

22
Q

A

23
Q

A

24
Q

A

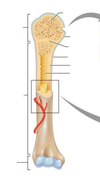
25
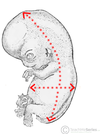
26
Which connective tissue covers in the bone?
periosteum
27
Name these sections:

28
Cartilage is avascular. What does this mean?
Does not have blood supply/blood vessels
29
What are the three types of joints?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
30
Examples of fibrous joints:
skull, tibiofibular joint, teeth
31
Examples of Cartilaginous joints:
vertebrae, pubic symphysis
32
Examples of synovial joints:
elbow, knee, hip, shoulder
33
How are fibrous joints formed?
by the firm interlocking of two bones and have a strong emphasis on stability rather than movement
34
Fibrous joints are.....
firm
35
synovial joints are......
freely moveable
36
Cartilaginous joints ....
permit some movement but not as much as synovial
37
What can you find in every joint?
Connective tissue
38
What is the only bone which does not articulate with another bone?
The hyoid bone
39
The 5 main characteristics of a synovial joint
1. Joint capsule
2. Ligaments
3. Joint cavity
4. Articular cartilage
5. Synovial membrane and fluid
40


41
What type of joint is the: Shoulder Joint
Synovial ball and socket
42
What type of joint is the: Joints of the sternum
clavicle (synovial saddle) versus the 1 st rib (primary cartilaginous)– what’s the difference?
43
What type of joint is in Pubic symphysis?
Secondary cartilaginous
44
Name the different types of synovial joints?
Ball and socket
Condyloid
Plane
Saddle
Hinge
Pivot
45
Example of ball and socket?
Hip joint
46
Example of pivot joint?
Between C1 and C2 verterbrae
47
Example of a hinge joint?
Elbow
48
Example of Saddle joint?
between trapezium carpal bones and 1st metacarpal bone
49
Example of plane joint?
joint between tarsal bones
50
Example of Condyloid joint?
Between radius and carpal bones of wrist
51
. Identify the following list of humeral features on the real humerus:
Head
Anatomical neck
Surgical neck
Greater tubercle
Lesser tubercle
Lateral epicondyle
Medial epicondyle
Trochlea
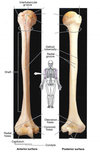

52
The nervous system splits into......
the central and preipheral nervous system
53
Name the missing labels


54
Name the missing labels
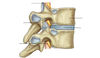

55
What is the PNS
Peripheral nervous system- it is any neural tissue that is outside the CNS
56
How many PAIRED spinal nerves are there?
31 (REMEMBER 8,12,5,5,1)
57
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
12
58
What is the difference between neruones and nerve?
REMEMBER: they are NOT the same
A nerve is composed of thousands of neurones collected together. A further point to understand is that the neurones in a nerve may have different functions to each other and may branch off to different muscles or sensory areas
59
What is a motor neurone and what is a sensory neurone?
Motor neurone travels to muscles to instruct them to contract. Sensory neurones are there to detect sensory innervation from the external or internal environment
60
What is the difference between a motor, sensory and mixed nerve?
A sensory nerve has purely sensory neurones. A motor nerve has purely motor nerves. A mixed nerve has both sensory and motor neurones within.
61
Identify the Brachial plexus and where the nerves are?


62
By tracing the nerves back give the root value for the femoral nerve?
L2-L4
63
What nerve is this?


64
Can you think about any processes that are controlled by the nervous system that are not under your conscious control?
Sweating,
blood vessel diameter,
Arrector pilli muscles,
heart rate,
rate of digestion,
arousal,
ejaculation,
salivation,
pupil diameter,
lens shape
65
What type of muscles do somatic motor nerves innervate and what type of muscles so autonomic motor nerves innervate?
Skeletal, smooth.
66
Sympathetic neurones only emerge from the spinal cord between \_\_\_\_
Levels T1 - L2/L3
67
What type of neruones do parasympathetic nervous system have?
long pre ganglionic neurone and a short postganglionic neurone
68
What type of outflow does parasympathetic nervous system have?
Craniosacral
69
Parasymlathetic system only emerges in \_\_\_of the ___ cranial nerves and in the spinal nerves \_\_\_\_
4
12
S2, S3 and S4
70
What is the longest parasympathetic nerve?
Vagus nerve
71
What are the three major functions of the lymphatic system?
1. it acts to maintain tissue fluid levels
2. it aids in fighting infection
3. it helps to transport fats from the intestines to the liver.
72
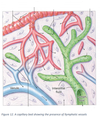

73
Into which veins do the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct drain into?
Right lymphatic duct into right subclavian vein. Thoracic duct into junction between left internal jugular vein and left subclavian vein (although can just be left subclavian vein).
74
What structures do lymphatic vessels have in common with veins?
They contain valves to help lymph ascend superiorly. Like veins a muscular pump system will also help with this.
75
. Which area of the body does the thoracic duct drain and which area of the body does the right lymphatic duct drain?
Thoracic duct = lower half and left part of upper half
Right lymphatic duct = Right part of upper half
76
This is a lymph node. Name all the missing labels


77
Function of Lymph nodes
The lymph nodes act to clean the lymph of any microorganisms that are present.
78
What could enlarged lymph nodes suggest?
In these cases the level of infection is too large for the node to cope with. In these cases the node itself will become infected. Metastatic cancer cells can invade the lymphatic vessels and find their way to lymph nodes
79
Where else is lymphoid tissue found in the body?
Peyer patches, tonsils, thymus, spleen and bone marrow.
80
The spleen is one of the major sites of lymphoid tissue within body. It has two parts; the white pulp and the red pulp. What is the function of the red pulp?
Break down of damaged or worn out red blood cells with the subsequent return of iron and globin to the liver.
81
The spleen is one of the major sites of lymphoid tissue within body. It has two parts; the white pulp and the red pulp. What is the function of the white pulp?
The white pulp contains the lymphoid tissue. As blood passes through the spleen it will encounter macrophages here which will destroy microorganisms by way of phagocytosis
82
83


