Epithelium Flashcards
(31 cards)
Eosin stain
PINK, Acidic dye, Na + radical
Stains cytoplasm, cytoplasmic fiaments, collagen fibers, basement membrane
Stained objects = “acidophilic” or “eosinophilic”
Hematoxylin Stain
PURPLE, Basic dye, Cl- radical
Stains heterochromatin, nucleolus, RER, sulfated GAGs
Objects stained = basophilic
Identify

Simple squamous
Location: lining of vessels, vacities, pericardium, pleura, peritoneum
Fx: Movement of viscera, active transport by pinocytosis, secretion of biologically active molecules
Identify
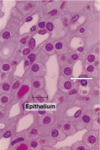
Simple Cuboidal
Location: Covering the ovary and thyroid
Fx: Covering and secretion
Identify
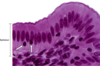
Simple columnar
Location: Lining of intestine and gallbladder
Fx: Protection, lubrication, absorption, secretion
Identify

Pseudostratified (columnar/cuboidal)
Location: lining of trachea, bronchi, nasal cavity
Fx: Protection, secretion, cilia-mediated transport of particles in mucus
(picture is columnar and ciliated)
Layers of Epidermis

Stratum basale
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum (with keratohyalin granules)
Stratum lucidum (clear, only in thick skin)
Stratum corneum
Melanocytes
Neural crest origin
Melanin granules passed to keratinocyte. Number and distribution of granules in keratinocytes determines skin color
Langerhans Cells
Antigen presenting cells from bone marrow
2-8% of epidermal cells
Unique organelle in TEM - Birbeck granule
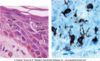
Merkel Cells
Found mainly in stratum basale of thick skin
Sensitive mechanoreceptor
Merkel cell carcinomas are rare but hard to treat
Basement membrane
Basement Membrane (LM) is the Basal Lamina (TEM) plus the Reticular Lamina (TEM) Examples of basement membranes: respiratory epithelium, glomerular basement membrane
Types of cells in simple columnar epithelium

- Goblet cells: mucus producing, pale/clear cytoplasm
- Enterocytes: pink, elongated, purple basal nucleus
Identify

Simple cuboidal epithelium surrounding follices from the thyroid.
Arrow points to blood vessels
Identify

Simple columnar epithelium lining the villi
From the ileum
Goblet cells (clear cytoplasm)
Enterocytes (boxed)
Identify
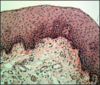
Stratified squamous epithelium (top)
Connective tissue (bottom)
Boundary: basal lamina/basement membrane
From esophagus
Identify

Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium (Thick Skin)
From Sole of Foot
Pink = keratinized layer
Purple = epidermis (see pegs)
Squames
Identify

Pseudostratified Columnar Ciliated Epithelium (aka respiratory epithelium)
From Human Trachea
Thick basement membrane (pink)
Connective tissue with glands and rings made of hyaline cartilage
Identify

Pseudostratified Columnar Ciliated Epithelium from Human Trachea
Goblet cells, ciliated cells, lymphocytes (black dots), basal bodies (dark pink line at base of cilia)
Thick basement membrane
Identify

Transitional Epithelium from Human Bladder (relaxed)
H & Chromotrope staining
Epithelium just the dark purple later at top
Identify

Transitional epithelium
Binucleated “dome” cells (cuticle above nuclei)
Pseduostratified epithlium
Thin basement membrane
Connective tissue
Identify

Transitional epithelium of distended bladder
Epithelial layer is thinner
Dome cells on lumen side, squamous in shape
Define stereocilia
Not normal cilia because they aren’t motile, more like microvilli but longer.
Found on apical surface of some cells
Define striated border
Microvilli and glycocalyx of small intestines


