Esophagus and Stomach Histology Flashcards
(45 cards)
1
Q
- What are the four layers of the cells of the GI tract (from lumen-superficial)
A
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis Externa
- Seroasa/Adventitia
2
Q
- Difference between serosa and adventitia
A
- Serosa=covered by peritoneum
- Adventitia=retropreitoneum (loose connective tissue with surrounding fat)
3
Q
- The _ layer differs considerably from region to region along the GI tract (helps with identifying certain areas)
A
- Mucosa
4
Q
- Label the four layers

A
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis externa
- Serosa
5
Q
- What are the components of the mucosal layer?
A
- Lining epithelium
- Lamina propria
- Muscularis mucosae (* smooth muscle layer controlling the mobility of GLANDS-NOT PERISTALSIS)
6
Q
- The _ of the mucosal layer contains lymphatic nodules, lymphatics, plasma cells, and macrophages
A
- Lamina propria
7
Q
- What types of epithelium are present in GI cells?
A
- Simple columnar epithelium
- Non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
8
Q
- What are the components of the submucosal layer?
A
- Dense irregular CT (w/ neurovascular and lymphatics)
- Glands (esophagus and duodenum)
9
Q
- What are the components of the muscularis externa?
- Function of each component
- __ plexus is located between the two layers_
A
-
Inner circular layer
- Constriction of lumen
-
Outer longitudinal layer
- Shortens tube
- Neurovascular
- Overall function is to break down food
10
Q
- _ has a mesothelium covering and is suspended by a mesentary/peritoneal fold
- _ does not have a mesothelium covering
- Can an organ have both?
A
- Serosa
- Adventitia
- Yes, depending on location
11
Q
- Identify the following

A
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis
- Serosa
- Inner circular layer
- Musculara mucosa
- Lamina propria
- Epithelium (Simple columnar)
- Outer longitudinal layer
- Serosa
12
Q
- Extrinsic component of GI innervation
- Intrinsic component of GI innervation
A
- Sympathetics and parasympathetics
- Enteric Nervous System
13
Q
- Parasympathetic innervation
- What nerves are involed?
- Ganglion and postsynaptic fibers are _
- Sympatheric innervation
- What nerves are involved?
*
- What nerves are involved?
A
- Vagus nerve
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves
- Fibers in these are presynaptic
- Gangion and postsynaptic fibers are intramural
- Greater, lesser and least splanchnic
- Synapse in paravertebral ganglion and post-synaptic fibers travel to organs on peri-arterial plexuses
14
Q
-
What two plexuses are part of the enteric nervous system?
- Where are they located
- What is their function
A
-
Submucosal plexus of Meissner
- Harder to see histologically
- Regulate secretion in glands of the submucosa
-
Myenteric plexus of Auerbach
- Between inner circular layer and puter longitudinal layer of the muscularis
-
Both function together to control:
- Peristaltic contractions of muscularis externa and movements of muscularis mucosae
- Secretory activities of mucosal and submucosal glands
15
Q
- What cells are the Pacemaker cells of the enteric nervous system?
A
- Interstitial Cells of Cahal
16
Q
Preganglionic axons of parasympathetics _ gastric motility
Postganglionic axons of the sympathetics _ gastric motility
A
- Increase
- Decrease
17
Q
- Identify the following

A
- Inner circular layer of the muscularis externa
- Myenteric plexus of Auerbach
- Outer longitudinal later of the muscularis externa
18
Q
- *The _ part of the esophagus has adventitia*
- *The _ part of the esophagus has serosa*
A
Thoracic esophagus
Abdominal esophagus (inferior to the diaphragm)
19
Q
- What are the two types of glands present in the esophagus?
- What are their functions?
A
-
Cardiac esophageal glands
- Lamina propria
- Produce mucus to lubricate the epithelium
-
Submucosal glands
- Small lobules with mucous and serous cell types
- In submucosal layer
*
20
Q
- Where has this tissue sample been taken from?
- Identify the numbered components

A
- Thoracic esophagus
- 1) Mucosa
- 2) Submucosa
- 3) Submucosal gland
- 4) Muscularis external
- 5) Adventitia
21
Q
- What type of epithelium is present in the mucosa of the esophagus?
- What are some other key features of the mucosa of the esophagus?
A
- Nonkeratinized stratified squamous
- Numerous folds
- Muscularis mucosae only present in lower segment and contains numerous cardiac esophageal glands
22
Q
- What is located in the submucosal layer of the esophagus
A
Submucosal venous plexuses
Collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels
23
Q
- Submucosal venous plexuses drain into both _ and _ venous system
- Increased pressure can lead to _
A
- Systemic and portal
- Esophageal varices (dilation of the submucosal venous sinuses)
24
Q
- Muscularis in:
- Upper third of esophagus
- Middle third of esophagus
- Lower third of esophagus
A
- Upper third-skeletal muscle (multi-nucleated, striated, nuclei on outer edges)
- Middle third-mixture of skeletal and smooth muscle
- Lower-smooth muscle (lighter, not as compact as the skeletal muscle)
25
* What is this tissue sample from?
* Identify the following
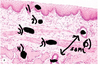
* Esophagus
1) Stratified squamous epithelium
2) Lamina propria
3) and 4) Muscularis
5) Gland
6) Duct
26
* Epithelium transitions from _ in the esophagus to _ in the stomach
* Epithelium in the stomach is \_
* Nonkeratinized stratified squamous
* Simple Columnar
* Glandular (with pits/glands)

27
* The upper esophageal sphincter is _ and involved in the _ reflex
* The lower esophageal sphincter is _ and prevents \_
* Anatomical, swallowing
* Functional, reflux of gastric contents
28
* **GERD v. Barrett's Esophagus**
* GERD
* Reflux of gastric contents thru LES
* Barrett's Esophagus
* Transitional zone of esophagus (should be nonkeratinized stratified squamous) becomes simple columnar and mucus secreting
29
* What are the four regions of the stomach?
* What are the two areas of the stomach?
* Cardia, fundus, body, pyloric antrum
* **Orad area**
* Fundus and upper part of body
* Relaxes during swallowing
* **Caudad area**
* Lower portion of body and the antrum
* Regulates gastric emptying
30
* Gastric mucosal folds (aka \_) are covered by _ and form a gastric mucosal barrier
* Gastric folds are located in the _ layers
* Rugae
* Gastric pits
* Mucosa and submucosal
31
* Where was this tissue sample from?
* Identify the components

* Stomach
1. Gastric pits
2. Mucosa
3. Muscularis Mucosae
4. Submucosa
5. Muscularis Externa
6. Oblique layer
7. Inner circular layer
8. Outer longitudinal layer
32
* Does the stomach have serosa or adventitia?
* Serosa-surrounded by peritoneum
33
* Mucosa of the stomach
* _ epithelium
* Contains _ glands
* _ fibers
* Muscularis mucosase facilitates release of \_
* Simple columnar
* Cardiac, Gastric, Pyloric
* Reticular and collagen fibers
* Gastric gland secretions
34
* Submucosa
* _ CT with _ and _ fibers
* Contains _ plexus
* Dense irregular, collagen and elastin fibers
* Meissner's
* Also contains arterioles, venous plexuses and lymphatics
35
* Muscularis/muscularis externa
* _ layers of smooth muscle (one of which is unique to the stomach)
* _ muscular layer thickens in pyloric region to help form the **pyloric sphincter**
* 3 (Oblique=unique)
* Circular
36
* Known as the hallmark of the stomach
* Contains three regions
* Present throughout gastric mucosa except for areas occupied by cardiac and pyloric glands
* Fundic/Gastric Glands
37
* ***_What are the three regions of the gastric glands?_***
* ***_Describe each/which cell types are present_***
* ***_Which part of the gastric gland DOES NOT produce secretions_***
* **Isthmus**
* ****Between gastric pit and gland below
* Contains **stem cells**
* **Neck**
* ****Narrow, long region
* **Mucous neck cells, Parietal Cells, Enteroendocrine Cells**
* **Fundic segment**
* ****Shorter and wider base
* **Chief Cells, Enteroendocrine cells, Some parietal cellsn**
* Isthmus

38
* **What is located superiorly to the isthmus of the gastric gland?**
* **What is its function?**
* **Gastric pit**
* **Contains surface mucosal cells**
39
* **Function of mucous cells (both surface and neck)**
* **Produce mucus layer 95% water, 5 % mucin**
* **Neutralizes microenvironment of the stomach to an alkaline pH**
40
* ***_Chief Cells_***
* ***_Location_***
* ***_Function_***
*
* **Located in fundus of gastric glands**
* **_Release zymogen granules that contain pepsinogen proenzyme_**
* **_Pepsinogen converted to pepsin in acidic environment of stomach_**
* **_Helps with protein digestion_**
* **_Exocytosis is stimulated by eating_**
41
* ***_Parietal Cells_***
* ***_Location_***
* ***_Function_***
* ***_3 Distinctive Features_***
* **Neck and upper segment**
* **_Produce HCl and intrinsic factor (binds Vitamin B12)_**
* **_3 FeaturesL_**
* **_Abundant mitochondria (for pumping H+)_**
* **_Intracellular canaliculus_**
* **_H+/K+ Dependent ATPase rich tubovesicular system_**
42
* ***_What are the two types of enteroendocrine cells?_***
* ***_Where are they located?_***
* ***_What is their function?_***
* Open
* Exposed to gland lumen
* Closed
* Unexposed to gland lumen
* **Located in fundus (prevalent in base)**
* **Secrete peptide hormones**:
* **Gastrin**
* Produced by G cells in pyloric antrum
* Stimulates Acid Secretion
* **Somatostatin**
* Produced by D cells
* Inhibits Gastrin Action
* **Ghrelin**
* Stimulates GH secretion
* Triggers hunger
43
* ***_Cardiac Glands of the Stomach_***
* ***_Describe them_***
* ***_HALLMARK?_***
* **_Located in cardia of the stomach_**
* **_Glands are tubular, coiled, and somewhat branched_**
* **_HALLMARK: APPEAR CIRCULAR AND OBLIQUE IN SECTIONS_**

44
* ***_Pyloric Glands of the Stomach_***
* ***_Location_***
* ***_Function_***
* Between fundus and pylorus
* **lined with mucus secreting cells**
* **Branches, tubular coiled glands**
* **Secrete large and pale secretory mucus**
* **Ocassionally will contain enteroendocrine cells and parietyal cells**
* **GALT**

45
* Identify the following cell types

1. Chief cells (more eosinophilic)
2. Parietal cells


