Organs of the GI Tract Flashcards
(60 cards)
1
Q
- What are the main organs of the GI Tract?
A
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- SI
- Duodenum
- Ileum
- Jejunum
- Large Intestine
- Cecum
- Ascending colon
- Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon
- Sigmoid Colon
- Rectum
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
Spleen
2
Q
What level are the following anatomical structures located:
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Pylorus
A
- Esophagus: T10-T11
- Stomach: T11
- Pylorus: L1
3
Q
- Esophagus
- Passes thru _ of the diaprhagm at what spinal level?
- Enters _ of the stomach at what spinal level?
- Attached to diaphragm via _ ligament
A
- Right crus of diaphragm at T10
- Enters cardiac orifice of stomach at T11
- Phrenicoesophageal ligament
4
Q
- What are the three esophageal constrictions?
A
- Cervical
- Pharyngo-esophageal junction controlled by cricopharyngeus muscle
- Thoracic (2 Part)
- Esophagus in contact with aorta and left main bronchus
- Diaphragmatic
- As it passes through the esophageal hiatus at T10
- Implicated in hiatal hernias

5
Q
- Para-esophageal hernias
A
- Usually asymptomatic
- Normal GEJ
- Fundus protrudes into thorax
- Less chance of GERD
- Left side more common (liver is in the way on the right side)

6
Q
- Sliding hiatal hernia
A
- Most common
- GEJ displaced superiorly
- *Cardia portrudes into thorax**
- Hourglass stomach

7
Q
- Identify the parts of the stomach

A
- Esophagus
- Cardia
- Angular incisure
- Pylorus
- Duodenum
- Pyloric antrum
- Lesser curvature
- Greater Curvature
- Body
- Fundus
- Cardial Notch
8
Q
- The stomach is a _ structure
A
- Dynamic/intraperitoneal structure
- Not fixed:
- Obese people have higher displaced stomach compared to very thin people
9
Q
- Anteriorly, the stomach relates with _
A
- Diaphragm
- Left lobe of liver
- Anterior abdominal wall
10
Q
- Inferolaterally, the stomach relates with _
A
- Transverse colon
11
Q
- Posteriorly, the stomach relates with _
A
- Diaphragm
- Spleen
- Left upper kidney and syprarenal gland
- Pancreas
- Omental bursa (lesser sac)-stomach forms most of its anterior wall
12
Q
- Important ligaments of the stomach
A
-
Gastrohepatic
- Connects lessure curvature of stomach to the liver
- *Contains gastric vessels*
-
Gastrocolic
- Connects greater curvature to transverse colon
- *Contains gastroepiploic vessels and part of the greater omentum*
13
Q
- Label the following

A
- Pylorus
- Transpyloric plane
- Transtubercular plane
- Cardial Orifice of Stomach
- Pyloric Antrum
14
Q
- Gastric ulcer
A
- Occurs in stomach
- 70% related to H. Pylori
- Left curvature ulcer can cause hemorrhage from left gastric artery
15
Q
- Duodenal/Peptic Ulcer
A
- Ulcer of the pylorus or duodenum
- 90% related to H.Pylori
- 65% occur on posterior wall of first part of duodenum
-
Complications
- Hemorrhage from gastroduodenal a. for posterior ulcers in first part of duodenum
- Ulcer in first part of duodenum can cause adhesions with liver and gallbladder
- Anterior ulcer can perforate into peritoneal space
- Pancreas may be affected
16
Q
- Vagotomy:
- Types
- What is it used to treat?
A
- GERD
- Truncal: Removes all nerves of the stomach and other portions of the GI tract
- Selective Gastric: Just stomach
- Selective Proximal: Proximal part of the stomach

17
Q
- Random histo question: Where are parietal cells located in the stomach? what do they do?
A
- Fundus and body of the stomach
- Secrete HCl
18
Q
- The duodenum is located on the _ plane (L3)
A
- Subcostal
19
Q
- The 1st part of the duodenum is _ and the rest is _ (in terms of peritoneum)
A
- Peritoneal
- Retroperitoneal
20
Q
- Which artery is an area of concern for stab/gunshot wound victims stabbed near the duodenum?
A
- Superior mesenteric artery
21
Q
- The Ligament of Treitz is a _ muscle
- What is its function?
A
- Suspensory
- Separates upper and lower GI tract
- Connects Diaphragm to Duodenum
22
Q
- Anterior relationship to superior duodenum
- Posterior
- Medial
- Superior
- Inferior
- Lateral
A
-
Anterior
- Peritoneum
- Gallbladder
- Quadrate lobe of liver
-
Posterior
- Bile duct
- Gastroduodenal Artery
- Hepatic Portal Vein
- IVC
-
Medial
- Pylorus
-
Superior
- Neck of Gallbladder
-
Inferior
- Neck of Pancreas
- Vertebral Level
- L1
23
Q
- Descending duodenum:
- Anterior relationship
- Posterior relationship
- Medial relationship
- Superior relationship
- Inferior relationship
- Vertebral Level
A
-
Anterior
- Transverse colon
- Transverse mesocolon
- Coils of small intestine
-
Posterior
- Hilum of right kidney
- Renal vessels
- Ureter
- Psoas Major
-
Medial
- Head of Pancreas
- Pancreatic duct
- Bile Duct
-
Superior
- Superior part of duodenum
-
Inferior
- Inferior part of duodenum
-
Vertebral Level
- Right of L2-L3 (Subcostal Plane)
24
Q
- Inferior Duodenum relationships:
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Medial
- Superior
- Inferior
- Vertebral Level
A
-
Anterior
- SMA
- SMV
- Coils of small intestine
-
Posterior
- Right psoas major
- IVC
- Aorta
- Right ureter
-
Superior
- Head and unicate process of pancreas
- Superior mesenteric vessels
-
Inferior
- Coils of small intestine (ilium)
-
Vertebral Level
- Anterior to L3
25
* **Ascending duodenum relationships:**
* Anterior
* Posterior
* Medial
* Superior
* Inferior
* Vertebral Leveln
* **Anterior**
* Beginning of root of mesentary
* Coils of jejunum
* **Posterior**
* ****Left psoas major
* Left margin of aorta
* **Medial**
* ****SMA
* SMV
* Unicate process of pancreas
* **Superior**
* ****Body of pancreas
* **Inferior**
* ****Coils of jejunum
* **Vertebral Level**
* ****Left of L3 Vertebra
26
* Most of the jejunum is in the _ quadrant
* Most of the ileum is in the _ quadrant
* The jejunum and ileum are attached to the posterior abdominal wall via _ which starts at which spinal level _ and ends at the _ junction at L5?
* LUQ
* RLQ
* Mesentary
* L2
* Ileocecal Junction (L5)
27
* **_Key anatomical features of the jejunum_**
* **High vascularity**
* **Long vasa recta**
* **Few large loops of arcades**
* **_Large, tall and closely packed circular folds_**
* **_Few lymphatic nodules (peyer's patches)_**

28
* **_Key anatomical features of the ileum_**
* **Less vascular**
* **Short Vasa Recta**
* **Many short loops of arcades**
* **_Low and sparse circular folds (absent in distal part)_**
* **_Many lymphatic nodules (Peyer's Patches)_**

29
* Identify the portion of the small intestine shown

* Ileum
30
* Identify the portion of the small intestine shown below
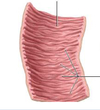
* Jejunum
31
* Identify the portion of the small intestine shown below

* Jejunum
32
* Identify the portion of the small intestine shown below

* Ileum
33
* ***_Meckel Diverticulum_***
* **Can be detected via technitium-99m scan (contain ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue)**
* **True diverticulum (contains mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis)**
* **Most common congenital anomoly of GI tract**
* **Most common pathological lead point for intussusception**
* **Symptomatic when ectopic tissue is present**
* **_Rule of 2s_**:
* 2 times more likely in males
* 2 inches long
* 2 ft from ileocecal valve
* 2% pop
* _Common in first 2 years of life if symptomatic_
* _2 types of epithelium may be present_
* _Sx:_
* _Blood per rectum_
* _Visible discomfort in RLQ_

34
* ***_Intussusception_***
* **Telescoping of proximal bowel segment into distal segment**
* **_Common at iliocecal jx_**
* **_Shown by Target sign on US_**
* **_Mostly Children_**
* **_Idopethic v. Meckel (kids) v. tumor v. adults_**

35
* Which two structures meet at the iliocecal junction?
* Which spinal level and plane is this located?
* Ileum and cecal colon (large colon)
* L5-Transtubercular
36
Diverticulitis can cause pain in the _ of adults
LLQ
Patients also typically present with diarrhea
37
* Identify the following features of the large intestine

1) Omental appendices
2) Mesocolic tenia coli
3) Cecum
4) Haustra (**not present in patients with ulcerative colitis)**
38
* ***_Where is McBurney's Point Located? Which anatomical feature does palpation of it assess?_***
* **1/3 of the way between right ASIS and umbilicus**
* **Appendix**
39
* ***_What does Murphy's sign test for?_***
* Gallbladder function
* **Palpate inferior to right costal margin on inspiration and assess for discomfort**
40
* Palpation below the **left** costal margin assesses which organ?
* Spleen
41
3 of _ converge on the appendix
* Omental tenia
42
* Features of the sigmoid colon
* **Located** **From iliac fossa to S3**
* **S shaped loop**
* **Teniae coli terminate at the recto-sigmoid junction**
* **Has long mesentary: sigmoid mesocolon**
* **Most common site of _volvulus in the elderly population_**
43
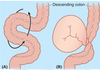
* ***_Volvulus_***
* **Rotation of loop of bowel**
* **Can cause constipation, ischemia, and necrosis**
* **Midgut volvulus more common in infants \*(2/3 terminal duodenum to transverse colon)**
* **Sigmoid volvulus more common in elderly**
* **Coffee bean sign on X ray**
44
* Key features of the liver
* Largest abdominal organ
* Occupies RUQ-can extend to left anterior axillary line if enlarged
* **top is located at xiphisternal plane (t9)**
* Will move inferiorly on inspiration which will aid palpation
* **Clinical note:**
* ****When doing biopsy, go superior to 10th rib, hold exhalation so collapsed lung will not occur
45
* What are the anatomical lobes of the liver?
* **What ligament separates them?**
* What are the accessory lobes of the right anatomic lobe?
* Right and left (NO FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE)
* **Falciform Ligament**
* **Quadrate lobe**
* **Left hemi-liver**
* **Caudate lobe**
* **Functionally separate**
46
* ***_What are the main ligaments of the liver?_***
* ***_What do these ligaments connect?_***
* **Falciform ligament**
* ****Connects right and left anatomic lobes
* Connects liver to anterior abdominal wall
* **Round ligament (Teres)******
* ****remnant of umbilical vein
* **Ligamentum venosum**
* ****Used to be the ductus venosus that shunted blood from the fetal liver
* **Hepatoduodenal Ligament**
* **_Contains the proper hepatic artery, bile duct, and portal vein_**
* **_Anterior boundary of epiploic foramen_**
47
* The _ maneuver can be used to identify if a hemorrhage is coming from the proper hepatic artery or some accessory artery to the liver
* Pringle
48
* ***_FUNCTIONAL LOBES OF THE LIVER_***
* ***_Separated into right and left based on primary division of portal triad_***
* ***_EXCEPTION: Caudate lobe-receives blood from both portal bundles_***
* ***_Important for hepatic segmentectomies_***
49
\_ line goes from fundus of gallbladder superiorly to the diaphragm
* **Cantlie**
50
* ***_FUNCTIONAL LOBES OF THE LIVER (KNOW THIS)_***

51
* Key features of the gallbladder
* Between **IV and V segments of the liver**
* Has fundus, body, and neck
* **_Attach to common bile duct via cystic duct_**
52
* **The common bile duct meets with the _ duct and empties into the ampulla of Vater (aka the hepatopancreatic ampulla) in the second part of the duodenum**
* **pancreatic**
53
* If a gallstone or blockage occurs, which segments are affected?
* Segments proximal to the blockage
54
**Cholelithiasis**
* Gallstones
* **Can lead to cholecystitis**
55
* Which population is at risk for **cholecystitis**
* **How do you test for it?**
* Female, fertile, forty, fat (4 fs)
* Murphy's sign
* Palpate RUQ and ask patient to inhale
* Sudden halt of inspiration d/t pain is (+) sign
56
**_*\_ is caused by an obstruction of the common bile duct*_**
* **_Choledocolithiasis_**

57
* ***_\_ is the obstruction of the ileocecal junction from a gallstone_***
* **Gallstone ileus**
* **Basically the gallstone travels down to the ileocecal valve**
58
* Key features of the spleen
* Largest lymphatic organ
* **LUQ**
* **Vulnerable to blunt trauma**

59
* Relationships of the spleen:
* Anterior
* Posterior
* Inferior
* Medial
* **Anterior**
* Stomach
* **Posterior**
* Diaphragm
* Ribs 9-11
* **Inferior**
* Left colic flexure
* **Medial**
* Left kidney
60
* ***_Ligaments of the spleen and their contents_***
* **Splenorenal ligament**
* Connects spleen to kidney
* **Contains splenic artery (main blood supply to the spleen)**
* **Gastrosplenic ligament**
* ****Connects fundus of stomach to superior pole of spleen
* **Contains short gastric arteries to supply above areas**


