Exam 1 Flashcards
Define anatomy.
The study of the parts of the body and how they relate to each other
Define physiology.
The study of the function of the body parts.
What is the directional term for above?
Superior.
What is the directional term for below?
Inferior.
What is the directional term for “toward or at the front of the body?”
Ventral; anterior
What is the directional term for “toward or at the back of the body?”
Dorsal; posterior
What is the directional term for “toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of?”
Medial.
What is the directional term for “away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of?”
Lateral
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
Intermediate
Name the floor criteria of anatomical position.
Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs pointing away from the body.
Which body plane is a vertical cut that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts?
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Which body plane is a vertical cut that divides the body into right and left parts?
Sagittal plane.
What is the difference between a midsagittal plane and a parasagittal plane?
Midsagittal: a sagittal cut exactly on midline, equal right and left parts
Parasagittal: sagittal cut not on the midline, unequal right and left parts.
Which body plane is a horizontal cut that divides the body into superior and inferior parts?
Transverse plane
Name the two body cavities.
Dorsal and ventral.
What cavities are in the dorsal body cavity?
Cranial cavity (brain) and vertebral cavity (spinal cord)
What cavities are in the ventral body cavity?
Thoracic (heart and lungs) and abdomino (digestive)– pelvic (urinary, reproductive)
Name the membrane that surrounds the organs in the dorsal body cavity.
Meninges
Name the membrane that surrounds the organs of the ventral body cavity.
serous membrane

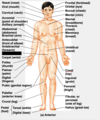
Nasal

Orbital (eye)

Cervical (neck)

Frontal (forehead)

Buccal (cheek)