Exam 1 Flashcards
(62 cards)
Non Vertebrates Immunity
All mammlas, fish, insects, and even bacteria have an innate immunity
Without circulatory sytem, adaptive surveillance is a problem
Vetrebrates
Innate immune system provides first line of protection, and informs the adaptive immune system to respond
recognition results in pro-inflammatory response to activate B/T cells type of recognition instructs the appropriate adaptive response
Opportunistic infections
occur when microbes gain cross epithelia
barriers
Cystic Fibrosis: defective chloride channel (CFTR) results in inefficient clearance of mucous to digestive tract (oral toilet), leading to chronic bacterial infection in lung and systemic infections
Example of opportunistic infection

PAMPS
Microbial structures that are recognized by
innate immune system receptors are called
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns
Innate Receptors that recognize PAMPs are
called
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
PRR recognition of PAMPs results in a
stereotyped response tailored to the type of
microbe that has that PAMP.
PRR/PAMP system maintains both self/nonself
discrimination and allows responses to be
tailored to the type of infecting microbe
LPS
anti-bacterial response
dsRNA
anti-viral response
Mutation of PAMPs
would incur significant cost
microbe (replication, altered structure/function)
For yeast, bacteria – unique lipid/carbohydratemoieties not found on host cells
For viruses – unique nucleic acids (non-host)

Scavenger receptors
recognize extracellular
anionic polysaccharides and lipoproteins of
gram positive bacteria
Lectins
recognize extracellular
polysaccharides of fungal cell walls
Toll Like Receptors (TLR)
recognize
extracellular and endosomal components
from many microbes
RIG-I Like Receptors (RLR)
recognize
intracellular nucleic acids from virus (and
some bacteria)
NOD Like Receptors (NLR)
recognize
intracellular imbalances due to infection
Different groups of PRR

Scavenger Receptors
recognize extracellular
anionic polysaccharides and lipoproteins
Involved in both host maintenance (scavenger function) and microbe recognition (innate immune function)
Host: recognize low density lipoproteins, high
density lipoproteins, and hemoglobin (from
RBC)
Microbe: recognize components of gram
negative bacterial cell wall
Scavenger receptors groups
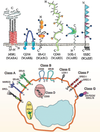
Lectins
recognize extracellular polysaccharides on free proteins (scavenger), host (cell signaling) or microbes (innate recognition)
Scavenger: glycoproteins are recognized,
broken down in endosomes, and reused
Host: cell to cell contact and adhesion,signaling
Microbe: polysaccharides on bacteria cause
cross linking and activation of innate pathways
Also Mannose binding lectin complement
pathway
Lectins in Innate Immune Activation

Discovery of Toll Like Receptors
Christiane Nusslein-Volhard showed that Toll proteins direct embryonic cell differentiation in fruit flies
Jules Hoffman showed different Toll genes conferred resistance to fungi vs. bacteria; some Toll mutants were susceptible to fungal infection but had normal resistance to bacteria
Toll Like Receptors Recognize Bacterial LPS
Bruce Beutler showed C3H mice have a mutation in LR4 that made them resistant to LPS, but unable to control live bacterial infection.

Recognizes triacyl lipoproteins, glycolipids, lipoteichoic acid (gram+ bacteria), zymosan (fungi), HSP70 (host), others…
TLR 1 and 2
TLR 2 and 6:
recognizes diacyl lipoproteins, along with other TLR1/2 ligands.
TLR 3:
recognizes double stranded RNA (viruses, some bacteria)