Exam 1 Spring Flashcards
(380 cards)
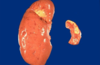
what is anatomic pathology?
- gross
- microscopic
- chem
- immuno
- molecular
what is clinical pathology
lab analysis of tissue and fluid
four aspects of disease
etiology (cause)
pathogenesis (mechanism)
morph changes (structural)
clinical-path (calinical manifestations)
disease etiology: genetic
mutations
disease associated gene varients
disease etiology acquired:
infectious
nutritional
chemical
physical
definition of disease
cluster of signs, symps, lab findings linked by common pathophysio seq
most of epidemiology is about…
disease
definition of illness
subjective state of individual
ill may or may not be suffering from disease
sickness
social role assumed by indiviual suffering from disease
what the patient brings to the doctor
a person’s subjective experience is called…
illness
natural hx of disease….
progression over tine in absense of tx –> recovery or death
nautral course of disease chart

An increase, decrease, or change in stress on an organ can result in ….
growth adaptations
if disturbed –> pathology
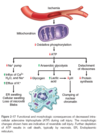
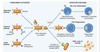
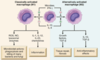
cellular adaptations to stress
reversible: number, size, phenotype, metab activity, fx
physio - normal stim
patho - modulate to escape injury
when there is increased demand or trophic stimutation on a cell, it resultsi n…
hypertrophy and/or hyperplasia
a decrease in nutrients and stimulation can result in…
hypoplasia
atrophy
chronic irritation can result in…
metaplasia
hypertrophy definition
increase cell size –> increased organ size
greater synth structural cmpts
in cells with limited cap to multiply
causes of hypertrophy
increased fx demand
GF/horm stim
physiological hypertrophic example
increased work load –> increase M fiber size
pathological hypertrophic example
chronic hemodynamic overload –> htn, valve deficiency –> injury/death (MI)
this is an example of…

physiological hypertrophy: increased work load –> increased M fiber size
this is an example of?

physio hypertrophy: estrogen stim –> uterus growth

chronic hemodynamic overload results in…
card enlargement (L vent hypertrophy as a result of htn - increase in afterload)