Exam 2 Flashcards
(568 cards)
True/False: Negative Ortolani Sign in Mature Dogs means the dog Does NOT have Hip Dysplasia
False
*Ortolani Sign is Typically Absent in Mature Dogs with Hip Dysplasia due to Remodeling
List common Tumors arising from the Penis
TVT
Papilloma
Squamous Cell
Mast Cell Tumor
Lateral Patellar Luxations are a _____ Image to Medial Patellar Luxations
Mirror
*Conformational Abnormalities of Lateral Patellar Luxations and Medial Patellar Luxations are Mirror Images of Each other
In a Partial Tear of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament, there will be a Positive Cranial Drawer or Tibial Thrust ONLY when the Joint is in Partial ______
Flexion
*When the Stifle is in Extension, it will Appear Stable

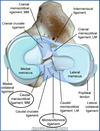
______ Collateral Ligaments have both a Short and Long Portion
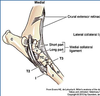
Tarsus

Procedure for Abdominocentesis where False Negatives are Common in Dehydrated Patients
Blind Tap

Two Components in the Etiology of Prostatitis
Ascending Infection from the Urethra- E.Coli Most Common
Pre-Existing Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Required
*What is the Most common Isolate in Prostatic Infections? E. Coli
True/False: Treatment for Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia is typically an Emergency
False

Complication of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus:
Tissue Blood Flow is Absent, Then Returned when GDV is Corrected
Accumulated Waste Products and Oxygen Radicals (Toxins) Release into General Circulation
Reperfusion Injury

Surgical Procedure Recommended for Recessed Vulva
Episioplasty (aka Vulvoplasty)

When Performing a Physical Exam on a Patient with Cancer, ______ Evaluates:

Size and Location of Masses
Mobility of Masses
Consistency of Masses
Body Mapping
*When you have Masses on the outside of the body, part of your physical exam should be measuring those masses and drawing them on a Body Map
*Body Map-Profile Picture of an Animal where you draw masses and Number them. Next to the Number you should Describe the Mass
*Helps when you evaluate the Patient in the Future- Make sure Masses haven’t Changed. Really helpful in tracking the Development of cancer in these Patients

Review Card: Pathophysiology of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Respiratory System: Increased CO2, Respiratory Acidosis
Cardiac System- Decreased Preload and Afterload, Arrhythmias
Gastric System- Mucosal Sloughing, Bacterial Translocation

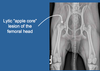
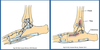
Corrective Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Fuses Pubic Symphysis with Cautery
“Tethers” Growth of Pelvis
Only useful in Dogs < 20 Weeks of Age
Low Complication Rate

Juvenile Pubic Symphiodesis (JPS)
*Once the Patient is Older than 5 Months this Procedure is NO longer Indicated

True/False: Prognosis for Dogs with Metastatic Mammary Tumors is Poor
True
*With Metastasis- Mean Survival Time is 5 Months
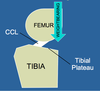
List the Factors playing a Role in Pathogenesis of Chronic Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
Degeneration of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Occurs with Age- This Degeneration tends to be worse in Larger Dogs (Over 15 kg/ 30lbs)
Factors that Contribute to Degeneration:
Obesity/Poor Fitness- More Stress/Strain on Ligaments
Conformation- Conformation of Femur, or even Stance/Gait would place Additional Stress on the Ligament
Excessive Plateau Angle- If the Slope is Steeper, the CCL would be under Greater Strain

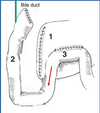
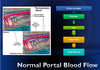
With Regards to Blood Supply to the Spleen:
Blood Supply Stems from ______ Artery
_____ Artery is a Major Contributor: It Supplies the Pancreas prior to Branching at the Level of the Spleen
Celiac Artery
Splenic Artery- Major Contributor
*Blood Supply comes from Celiac Artery. The Celiac Artery is going to Give off the Splenic Artery which will Supply the Pancreas prior to Branching and Feeding off a Branch to the Spleen

History Typical of _____ Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease:
Significant Hind Limb Lameness that is Aggravated by Activity or After Rest
Intermittent/Progressive Hind Limb Lameness- Slow Degeneration of Ligament leads to Degenerative Joint Disease
Difficulty Rising
“Bunny Hopping”- Bilateral
Chronic
*Highly Variable Presentation- Early in the Disease, signs may be Mild or Episodic with lameness seeming to Resolve between Bouts
*Envision the Diseased Ligament as a Weakened, Braided Fraying Rope- Individual Fibers give way Progressively

Corrective Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Improve Femoral head Coverage
Rotate Acetabulum Dorsally
Best in Animals 6-8 Months of Age

Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO)
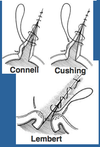
True/False: When Performing a Biopsy, you want to Obtain the Sample from the Junction of Normal and Abnormal Tissue
True

Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:
Incision through Right Abdominal Wall Caudal to Last Rib
Purse String Suture in Stomach
Place Foley or Mushroom Tip Catheter
Suture Stomach to Abdominal Wall
The Tube is Clamped and Bandaged
Tube Prevents Recurrent Dilatation

Tube Gastropexy
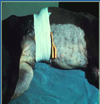
Uterine Rupture caused by Pyometra can lead to _____
Septic Peritonitis

True/False: In cases of Canines with Multiple Mammary Tumors, Each mass should be Removed and Tested Histopathically
True

Main Function of the Pancreas
Secretes Digestive Enzymes- Exocrine Function
*Secretes Digestive Enyzmes after the Patient has Eaten to Help break down food Products for metabolism
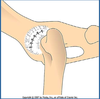
Grade of Patellar Luxation Described Below:

Grade II